|
Frank Craparo, MD - Division Director
- Maternal Fetal Medicine
- Abington Memorial Hospital
- Abington, Pennsylvania
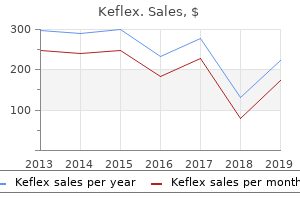
Keflex dosages: 750 mg, 500 mg, 250 mg
Keflex packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills,

Purchase 500 mg keflex free shippingHuman native kappa opioid receptor functions not predicted by recombinant receptors: implications for drug design antibiotics walking pneumonia generic keflex 500mg mastercard. The functional-organic dichotomy: postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease-irritable bowel syndrome. Established and rising strategies for evaluation of small and enormous intestinal motility. Study of intestinal circulate by mixed videofluoroscopy, manometry, and multiple intraluminal impedance. The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist exenatide inhibits small intestinal motility, flow, transit, and absorption of glucose in wholesome subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes:a randomized controlled trial. Expert consensus doc: advances within the analysis and classification of gastric and intestinal motility disorders. Jejunal brake: inhibition of intestinal transit by fats in the proximal small gut. Effect of intravenous amino acids on interdigestive antroduodenal motility and small bowel transit time. Gastric emptying of a strong meal is accelerated by the removing of dietary fibre naturally current in food. Small bowel homing T cells are related to symptoms and delayed gastric emptying in functional dyspepsia. Phenotypic modifications of morphologically identified Guinea-pig myenteric neurons following intestinal inflammation. Changes in colonic motility and the electrophysiological properties of myenteric neurons persist following restoration from trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis within the Guinea pig. Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content material and decreased serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. Loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and inhibitory innervation in insulin-dependent diabetes. Immune derived opioidergic inhibition of viscerosensory afferents is decreased in Irritable Bowel Syndrome patients. Increased kappa-opioid receptor expression and function during chronic visceral hypersensitivity. Opioid-receptor-mediated excitation of rat mesenteric afferent fibres supplying the rat jejunum. Sensory neuro-immune interactions differ between irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Activated Schwann cells in pancreatic cancer are linked to analgesia by way of suppression of spinal astroglia and microglia. Effects of enteral suggestions inhibition on motility, luminal circulate, and absorption of vitamins in proximal gut of minipigs. Quantitative evaluation of peristalsis in the Guinea-pig small gut using spatio-temporal maps. Downregulation of Gq-11 protein expression in Guinea pig antral and colonic circular muscle throughout pregnancy. Gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes: prevalence, evaluation, pathogenesis, and management. The London classification of gastrointestinal neuromuscular pathology: report on behalf of the Gastro 2009 International Working group. Brookes water deprivation or severe diarrhea, the flexibility of the colon to reabsorb fluids is of main physiologic significance; applicable motility patterns are important in achieving this operate. The colon has the capability to increase its fluid absorption 5-fold when required, however this capacity is tremendously impaired when transit is accelerated. Under normal circumstances, viscous contents are often propelled aborally at a speedy rate, and if circumstances are acceptable, stool is evacuated under voluntary management. Thus, the colon is capable of exhibiting a diverse range of motor patterns fitted to specific physiologic features. The generic term motility describes the range of motor patterns and the mechanisms that management them. Clearly these signs and dysmotility have to be linked, though our present understanding of such linkages is restricted, largely because of technical difficulties involved in studying the human colon. Because of differences between species, care is required in extrapolating knowledge from animal research to people. The contents of the colon turn into more and more viscous distally, and this alteration complicates the connection between propulsion and the contractile activity of the sleek muscle. The highly propulsive stereotypical motor patterns related to stool expulsion typically occur only once or twice daily. Prolonged recording techniques have to be used to seize such rare motor patterns. Recent advances in high-resolution manometry have made it attainable to document detailed strain profiles throughout most of the colon. Measurement of colonic wall tone using a barostat offers data on nonocclusive colonic wall actions, but imparts no details about the spatiotemporal patterning of motility. Smooth muscle electromyography provides perception into the patterning of muscle exercise however typically requires access to the muscular wall of the colon, which is problematic in humans for moral causes. The colon mixes its contents to facilitate transmural change of water, electrolytes, and short-chain fatty acids and, in doing so, shops stool for prolonged intervals. The mixing course of includes rhythmic to-and-fro motions, together with brief stepwise movements of contents, resulting in an overall internet aboral circulate rate that averages 1 cm/hr. The former can provide total colonic transit occasions, whereas the latter could be tracked in actual time and thus present detailed actions of the capsule within specific regions of the colon. In-vitro study of the mobile basis of motility utilizing isolated specimens of colon faces fewer technical and ethical limitations, however data obtained at the cellular degree, often beneath quite nonphysiologic situations, could be troublesome to extrapolate to the extra complicated integrated responses of the entire organ in vivo. Three types of rhythmic myogenic exercise have been recognized in isolated preparations of human colon. These embrace rhythmic motor patterns at three to 6 cycles per minute (cpm), 10 to 12 cpm, and a slower pattern at 0. This region produces larger-amplitude, slower myogenic oscillations in membrane potential (slow waves), which spread decrementally via the thickness of the circular smooth muscle by the use of hole junctions. When slow waves attain a threshold for contractions, phasic pressure waves are sometimes recorded by manometry. Slow waves happen all through the human colon at a frequency of 2 to 4/min and propagate over brief distances up or down the colon. Complex interactions occur as waves coming from different initiation websites collide, resulting in mixing of contents with slow overall propulsion. These small oscillations unfold through gap junctions into each the longitudinal and circular clean muscle layers, the place they summate with slow waves and often attain the threshold potential to generate smooth muscle motion potentials. The currents produced by pacemaker cells at the submucosal and myenteric borders decay as they unfold by way of the thickness of the round muscle layer. Enteric neuronal output can simply augment the phasic myogenic contractions, bringing them to threshold stage to drive easy rhythmic exercise, or, alternatively, enteric neural circuits can generate highly effective patterned contractions of for a lot longer period than these produced by gradual waves. These contractions can propagate for lengthy distances along the colon and include patterns similar to high amplitude propagating contractions (see later, "Propagating Motor Patterns"), the manometric equivalent of the mass actions described in radiologic observations.
Cheap keflex american expressGastroschisis in the United States 1988-2003: analysis and danger categorization of 4344 sufferers antibiotics xerostomia order keflex australia. Left-sided gastroschisis: larger incidence of extraintestinal congenital anomalies. Development of gastroschisis: review of hypotheses, a novel speculation, and implications for analysis. Sonographic markers related to antagonistic neonatal outcomes amongst fetuses with gastroschisis: an 11-year, single-center evaluate. Congenital stomach wall defects and reconstruction in pediatric surgery: gastroschisis and omphalocele. Contemporary outcomes of infants with gastroschisis in North America: a multicenter cohort examine. Adult case of an omphalomesenteric cyst resected by laparoscopic-assisted surgical procedure. Adenocarcinoma of the small intestine: a multi-institutional examine of 197 surgically resected cases. Insights from a population-based epidemiological examine and implications in surgical administration. The feasibility of wireless capsule endoscopy in detecting small intestinal pathology in children beneath the age of 8 years: a multicentre European research. Intestinal malrotation with midgut volvulus presenting as acute abdomen in children: worth of diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy. The danger of midgut volvulus in sufferers with belly wall defects: a multi-institutional study. The surgical administration of malrotation: a Canadian Association of Pediatric Surgeons survey. Associated congenital anomalies in sufferers with anorectal malformations-a need for developing a uniform practical approach. Clinical features of neurointestinal illness: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapy. Transanal pullthrough for Hirschsprung illness: matched case-control comparison of Soave and Swenson methods. A population-based, full follow-up of 146 consecutive patients after transanal mucosectomy for Hirschsprung illness. Follow up of youngsters present process antegrade continent enema: experience of over two hundred cases. A crucial appraisal of the morphological standards for diagnosing intestinal neuronal dysplasia sort B. Application of Pyridostigmine in pediatric gastrointestinal motility problems: a case series. Asymptomatic malrotation: analysis and surgical management: an American Pediatric Surgical Association outcomes and evidence based mostly follow committee systematic review. Colonic duplication in adults: report of two cases presenting with rectal bleeding. Adenocarcinoma arising from a gastric duplication cyst with invasion to the stomach: a case report and with literature evaluate. Enteric duplication cysts in children: a single-institution series with forty sufferers in twenty-six years. High-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma arising in a gastric duplication cyst: a case report with literature evaluation. The fibroblast development factor pathway serves a regulatory function in proliferation and apoptosis within the pathogenesis of intestinal atresia. A proposed classification system for familial intestinal atresia and its relevance to the understanding of the etiology of jejunoileal atresia. Operative administration of intestinal atresia and stenosis based mostly on pathologic findings. The etiologic position of intrauterine volvulus and intussusception in jejunoileal atresia. Congenital jejunal and ileal atresia: pure prenatal sonographic historical past and affiliation with neonatal outcome. One hundred three consecutive sufferers with anorectal malformations and their related anomalies. Mice missing Zfhx1b, the gene that codes for the Smad-interacting protein-1, reveal a role for multiple neural crest cell defects in the etiology of Hirschsprung disease�mental retardation syndrome. The contribution of the sonic hedgehog cascade in the improvement of the enteric nervous system in fetal rats with anorectal malformations. Are congenital anorectal malformations more frequent in newborns conceived with assisted reproductive techniques Bladder outlet obstruction causes fetal enterolithiasis in anorectal malformation with rectourinary fistula. Features of gastric and colonic mucosa in congenital enteropathies: a examine in histology and immunohistochemistry. Microvillous inclusion disease: tips on how to enhance the prognosis of a extreme congenital enterocyte disorder. New perspectives for children with microvillous inclusion disease: early small bowel transplantation. Evaluation of intestinal biopsies for pediatric enteropathy: a proposed immunohistochemical panel strategy. Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency: identification of a standard Inuit founder mutation. Functional variants in the sucrase-isomaltase gene associate with increased risk of irritable bowel syndrome. Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency: diagnostic challenges and response to enzyme alternative remedy. Congenital lactose intolerance is triggered by severe mutations on each alleles of the lactase gene. Association of lymphocytic colitis and lactase deficiency in pediatric population. Genotype-dependency of butyrate efficacy in children with congenital chloride diarrhea. Congenital sodium diarrhea: a type of intractable diarrhea, with a Link to inflammatory Bowel Disease. These contractions ship luminal contents again to the stomach for ejection into the esophagus throughout emesis. This coordinated motor pattern underscores the versatile modulation of small intestinal motility based on precise physiological needs. The motor perform of the small intestine depends directly on easy muscle in the intestinal wall, which accommodates the essential management mechanisms that initiate contractions and regulate their frequency. In addition, numerous hormones modulate the frequency and patterning of small intestinal contractions.
Discount 750mg keflex with visaThis chapter evaluations a heterogeneous group of disorders of the hepatic vasculature as properly as liver involvement in heart problems antimicrobial herbs buy keflex visa. Restoration of hepatic venous drainage through giant collaterals may alleviate all symptoms and signs and carries a good prognosis. Asynchronous involvement of the varied venous and portal structures explains the appreciable variation of one space of the liver from one other. In patients with a myeloproliferative dysfunction, blood cell counts are usually normal or decreased because of marked hypersplenism. Collateral veins draining peripheral segments of a venous territory into one other vein, either hepatic or extrahepatic, are traditional. The liver is dysmorphic (better seen in A) and enhances in an inhomogeneous trend. The hepatic veins are visible as slender, unenhanced buildings converging towards an enhanced patent inferior vena cava (most prominent in B) (arrow). Numerous regenerative macronodules lower than 2 cm in diameter are hyperintense in the T1-weighted sequence and hypointense in the T2-weighted sequence. Marked enhancement of the nodules is seen within the arterial part, with isointensity within the portal venous part. Direct (transhepatic) or retrograde (transjugular) hepatic venography is nearly by no means wanted for making the diagnosis, however when combined with venous strain measurements, venography permits percutaneous remedy (see later). Early studies advised that 90% of the sufferers would die from liver disease within three years of analysis. Subsequent data have indicated that sufferers with asymptomatic illness have an excellent medium- and long-term outcome. Anticoagulation therapy, given to 85% of sufferers, was associated with a bleeding price of 17%. Portal hypertension was the principle explanation for bleeding, adopted by intracranial hemorrhage. The fee of bleeding-related deaths was 2%, just like that in patients anticoagulated for venous thromboembolism in general. Portal cavernoma is characterised by the disappearance of the conventional portal vein and its substitute by a network of portoportal collaterals. When a portal cavernoma is present in a child, a congenital malformation must also be considered. Chronic liver disease and belly malignancy are each present in about one third of patients. The implementation of routine anticoagulation has been accompanied by a marked improvement in end result. In symptomatic sufferers, venous lesions amenable to percutaneous angioplasty must be investigated and handled accordingly. Furthermore, one third of the patients with a local factor also had a systemic threat factor for thrombosis. Hepatic blood flow is maintained due to elevated arterial blood circulate and speedy opening of portoportal collaterals that let blood move across the obstructed section of the portal vein. The thrombotic occlusion is extremely variable in diploma (partial or complete) and extent (involving only the portal vein or one of its 2 branches or the splenic or superior mesenteric vein [or both]). By distinction, an infected thrombus ab initio is characteristic of septic pylephlebitis. Liver biochemical test results usually show no alterations or minor transient modifications. Diagnosis and Natural History Abdominal imaging often exhibits the thrombus as strong material filling the lumen of the portal vein and extending variably into portal vein branches or to the splenic and superior mesenteric veins. Evidence for malignant obstruction contains demonstration of a tumor in the vicinity of the portal vein, enhancement of endoluminal material within the arterial phase, or neoplastic cells on biopsy specimens of the endoluminal material. Dilated veins are seen in the porta hepatis, significantly within the gallbladder wall (arrow). When the thrombus is lower than 30 days old, unenhanced pictures seem as hyperattenuated materials. A small quantity of ascitic fluid may be detected on imaging in the absence of intestinal ischemia. Signs of multiorgan dysfunction, acidosis, or lactic acidemia are major indicators of extreme intestinal involvement requiring surgical exploration. The extension of the thrombus, and the type of underlying prothrombotic condition, should be taken into account when a choice is made to extend anticoagulation. Early initiation of anticoagulation remedy is likely important to stopping this dreaded complication. Structures that improve in the wall of the bile duct correspond to biliary veins (arrowhead). Portoportal collaterals come up from preexisting veins within the porta hepatis and pancreas. Collaterals that emanate from the bile duct veins can produce deformity of the bile ducts, a condition termed portal hypertensive biliopathy or portal cholangiopathy. In the absence of preexisting liver disease, liver construction and function stay normal because the cavernoma restores, a minimal of partially, the abolished portal venous influx to the liver, while hepatic arterial influx increases. Plasma levels of coagulation factors and inhibitors are decreased,sixty two and these alterations are increased by portosystemic shunting however ameliorated by portal reperfusion. Liver biochemical check ranges are normally normal or near normal, though plasma ranges of coagulation components and inhibitors could be moderately decreased. Conversely, patients with cholangiopathy often have regular liver biochemical test outcomes. In rare patients, the appearance is that of a solid mass that causes biliary obstruction. The differential feature is the enhancement of the "pseudotumor" within the portal phase of the study. In different sufferers, the choice concerning long-term anticoagulation should be made on an individual foundation, bearing in mind the prothrombotic potential of the underlying situation and the chance of adherence to remedy. Mortality in sufferers with a portal cavernoma is expounded largely to the underlying situation, to not the complications of portal hypertension. On the opposite hand, extension to the superior mesenteric vein could induce intestinal ischemia. With respect to anticoagulation, full recanalization can be expected in about 50% of patients, extension is sort of completely prevented, and the danger of bleeding is decreased. Slender bridging septa are common and are outstanding within the associated entity of incomplete septal fibrosis. Scattered, less well-defined areas of regenerative adjustments of hepatocytes are widespread. Sclerotic portal tracts devoid of patent venules, irregularly distributed in a noncirrhotic parenchyma, are seen. Small regenerative nodules throughout the acini are surrounded by atrophic hepatocytes in a nonfibrous parenchyma. On the opposite hand, obliterative portal venopathy could be found in sufferers in whom options of portal hypertension are inconspicuous or lacking. Abnormalities of the serum bilirubin, albumin, and coagulation issue ranges are common, however pronounced modifications are unusual.
Buy keflex cheap onlineThe epithelium of the small gut consists of various cell varieties: absorptive cells (columnar cells) virus 65 discount keflex 250 mg, secretory cells (goblet cells), undifferentiated cells, tuft cells, M cells, cup-like cells, and enteroendocrine cells. Crypts include an identical cell population as the villi, with the addition of Paneth cells and stem cells. The lamina propria is a layer of reticular connective tissue that provides the structural support for the mucosa, nevertheless it also incorporates many cellular parts necessary for absorption and immunity. The lamina propria is wealthy in arterioles, venules lacteals, nerve fibrils, and fibroblasts, lymphocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, and mast cells. The muscularis mucosae consists of a thin layer of easy muscle only 3 to 10 cells thick on the boundary of the mucosa and submucosa. Stem cells are pluripotential cells positioned on the bases of the intestinal crypts. With intense mitotic activity, stem cells give rise to all forms of mature intestinal epithelial cells and on the similar time replenish themselves by way of self-renewal. Intestinal epithelial cells are mature by the time they reach the higher third of the villus. Undifferentiated cells have fewer intracellular organelles and microvilli than absorptive cells. A, Clear, empty-looking cytoplasm (arrow) and basal nuclei are seen with use of H&E, �250. B, Metachromatic staining of the cytoplasm outcomes with use of the alcian blue stain, �50. C, the cells show pink staining with use of periodic acid�Schiff stain, �150. Enterocyte microvilli are estimated to improve the luminal floor space of the cell 14to 40-fold. Goblet cells are mucin-producing cells which are scattered amongst intestinal villi but are extra frequent within the distal ileum and large intestine. Mucin is secreted by 2 pathways: in a neutrally mediated continuous manner, and by the energetic exocytosis of granules in response to extracellular stimuli. Tuft cells are marked by a tuft of lengthy microvilli projecting from the apical floor of the cell. The mucosa additionally contains specialised cells called enteroendocrine or neuroendocrine cells. Intestinal endocrine cells are sparsely distributed and consist of 11 different cell sorts (Table ninety eight. These are tall columnar cells present in each the crypts and villi and include lc. The amine precursor, uptake, and decarboxylation concept characterizes the cells as having a common embryonic origin from the neural crest and displaying related cytochemical and electron microscopic features. The differential expression of certain proteins additionally makes it potential to subdivide neuroendocrine cell populations. C, Granules in neuroendocrine cells are stained black with the Grimelius stain (arrow), �150. Serotonin-producing enterochromaffin cells, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide cells, and somatostatin D cells are distributed throughout the small and large intestine. M cells are an essential site of luminal antigen sampling for immune processing by the mucosal lymphoid system. This process of sampling plays an necessary role in the development and maintenance of immune tolerance, host defense in opposition to pathogens, and intestinal homeostasis. They affect the frequency of smooth muscle contraction, amplify neuronal alerts, mediate neurotransmission from enteric motor neurons to clean muscle cells, and set the graceful muscle membrane potential gradient. It contains lymphocytes, fibroblasts, mast cells, blood and lymphatic vessels, and a nerve fiber plexus-Meissner plexus- composed of non-myelinated postganglionic sympathetic fibers and parasympathetic ganglion cells. The submucosa supports the mucosa in specialised capabilities of nutrient, fluid, and electrolyte absorption by conveying a rich network of blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves that ensure environment friendly handling of absorbates. The secretions that drain into the bottom of the duodenal crypts contribute to increased luminal pH by selling pancreatic secretion and gallbladder contraction. The myenteric plexus (mp) is seen as a pale area with ganglion cells between the inner and outer layers (il, ol) of the muscularis propria (arrow). It consists of two layers of easy muscle: an inside round coat and an outer longitudinal coat arranged in a helicoidal sample. A distinguished nerve fiber plexus called the myenteric or Auerbach plexus is situated in the airplane between these 2 muscle layers. The ganglia within the myenteric plexus are extra outstanding than their submucosal counterpart. Parasympathetic and postganglionic sympathetic fibers terminate in parasympathetic ganglion cells, and postganglionic parasympathetic fibers terminate in easy muscle. Serosa the serosa is the outermost layer of the intestinal wall and consists of a thin layer of mesothelial cells, representing an extension of the visceral peritoneum and mesentery as it envelops the gut. Villi are mucosal folds that decrease in measurement from the proximal to distal small gut and are of different shapes in the various segments of the small intestine. They may be broad, short, or leaf-like within the duodenum, tongue-like within the jejunum, and finger-like extra distally. The villous pattern might differ in several ethnic teams; biopsy specimens from Africans, Indians, South Vietnamese, and Haitians have shorter and thicker villi, an increased number of leaf-shaped villi, and extra mononuclear cells compared with specimens from North Americans. Enterocytes are tall columnar cells, each with a basally positioned, clear, oval-shaped nucleus and a number of other nucleoli. The cells are tightly cemented to the basal lamina and adjoined to adjoining enterocytes at the apical pole by intracellular tight junctions. The luminal floor has microvilli that contain needed enzymes for nutrient absorption; a central core cytoskeleton is made of actin, villin, fimbrin, brush border myosin, and spectrin. The apical surface of the epithelium carries brush border transporters, Na+/ H+ exchangers, and anion exchangers (see Chapter 101). The junction complexes are made up of 3 elements: the proximal tight junction (zonula occludens), the intermediate junction (zonula adherens), and the deep junction, which includes the spot desmosome and the macular adherens zone (see Chapter 101). Movement through junctions is by paracellular transport and is the dominant pathway for passive ion and fluid flow. Tight junctions encompass claudins, occludens, and junctional adhesion molecules that bind and prevent passage of molecules between them in a regulated method. They are leakier and have a lower resistance in the proximal small gut, and tighter in the distal intestine. Spot desmosomes are thought to increase transmembrane linkages spanning the intercellular gap and are concerned in cell wall communications. The basolateral membrane is responsible for carriers to facilitate diffusion of natural solutes not coupled to ion actions. Gap junctions permit for communication and intercellular passage of ions and low molecular weight vitamins and intracellular messengers such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate. The crypts of Lieberk�hn are tubular glands that stretch to the muscularis mucosae During this migration, these cells mature and differentiate right into a secretory lineage (goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells) and enterocytes.
Buy genuine keflex on linePreoperative measure-For higher visu alization of the tract antibiotic resistance conference buy discount keflex on-line, methylene blue could additionally be injected into the fistulas opening on the sight before operation and the opening. Head and Neck Swellings BrancHial cySt It is a cystic swelling arising in connection with the persistent cervical sinus which is shaped because of the fusion of overgrowing 2nd branchial arch, with the sixth branchial arch. Normally the cervical sinus disappears, but when it persists, accumulation of fluid happens inside the sinus and offers rise to the branchial cyst. It is delicate, If the epithelial lining remains, recurrence cystic, fluctuant and transillumination will observe. Mobility-Not very mobile because of its Precautions throughout Operation adherence to the sternomastoid muscle. The cyst wall is skinny and delicate, so to not Fluctuation is often tough to elicit as the be held by any tissue forceps. Congenital variety-The external opening partly underneath cover of the higher 1/3rd of is on the anterior border of sternomastoid anterior border of sternomastoid. This muscle at the junction of lower and mid may be defined due to the develop dle 1/3rd. Nature of discharge: MucoidorMucopurulent with or without excoriation of the encompass ing skin. Preoperative measure � Fistulogram, which may be of some help throughout excision of the tract. Precaution throughout Operation � As the tract passes through the bifurca tion of frequent carotid artery, the vessel must be protected. Solitary lymph cyst-Usually it appears in the grownup life and is often discovered within the supraclavicular area. Sudden enhance in measurement of the cyst could cause respiratory misery, when the treat ment is aspiration of the cyst with or with out tracheostomy. It might extend upto the jaw above and down over the anterior chest wall and axilla. Contents: Clear watery or strawcolored fluid consisting of cholesterol crystals and lymphocytes. Age: It seems very early and may be discovered at birth or throughout the first few years of life. Aspiration alone, especially when the cyst is big enough to trigger pressure signs. Due to injection of sclerosing brokers, fibrosis happens which provides rise to the following i) the scale diminishes. Stage of lymphadenitis Lymph nodes are enlarged, nontender or barely tender, generally higher deep cer vical nodes are involved. Stage of Periadenitis or Matting � Duetoinvolvementofcapsule,thenodes move collectively, turn out to be agency and non tender. Cystic hygroma in the mediastinum could present as a growth with mediastinal syn drome characterised by dyspnea, dysphagia, and so on. There are fingerlike projections from the cyst wall invading the encircling struc tures. Ultimately the fascia is eroded at one point and the pus radiotherapy Cystic hygroma is comparatively radioresistant. In untreated circumstances, the pores and skin at the heart undergoes necrosis and offers rise to the continual discharging sinus. Diffrential Diagnosis of continual cervical lymphadenopathy the frequent conditions are: 2. Lymph node biopsy reveals central casea tion surrounded by epithelioid cells with Langhan kind of big cells. Nonspecific-Chronic pyogenic lymph pores and skin of leg (melanoma) buttock, exter adenitis. Examination of different lymph node areas - Almost all the time malignant For example axilla, groin, abdomen, and so forth. Secondary � Metastatic lymph node a reticulosis, sarcoid or glandular from a primary development. Any mass-For instance retroperito node in the neck are carcinoma scalp (via neal nodes in seminoma testis. Chemodectoma,PotatoTumor) It is a sluggish rising tumor which arises within the carotid physique at the carotid bifurcation. It is a laterally positioned swelling of the neck Microscopic positioned behind the sternomastoid muscle beneath the thyroid cartilage. It happens as a result It shows the identical histologic pattern of a nor StErnomaStoiD tumor of protrusion or herniation of the mucosa of mal carotid body. The later is a weak area of pharyngeal wall between the oblique fibers of thyropha this can be a firm, homogeneous and compact a tumor. During childbirth, injury to the sterno ryngeus and the sphincter like transverse fib tumor, almost looks like a potato. Excision of the pouch is finished via the treatment therapy cervical strategy followed by repair of the � It is commonly potential to dissect the tumor Division of the decrease finish of the sternomas pharynx in two layers, cricopharyngeal myo 145 tomy and closure with drain. Each lateral lobe extends vertically from the infrahyoid muscles (sternothyroid and center of the thyroid cartilage to the 6th ring sternohyoid), the sternocleidomastoid overof the trachea. A third lobe of conical form, called the tubes-esophagus and trachea, two nerves � pyramidal lobe, incessantly arises from the recurrent laryngeal and external laryngeal upper part of isthmus or from the adjoining por- and two muscles-cricothyroid and inferior constrictor. The posterior floor overlaps the carotid A fibrous or muscular band is sometimes found connected above to the body of sheath containing the widespread carotid artery, internal jugular vein and the vagus nerve. Coverings the thyroid gland is covered by two capsules � the true capsule and the false capsule. True capsule is a fibrous capsule which covers the gland and sends numerous fibrous septae within it. False capsule is a fascial sheath derived from the pretracheal layer of the deep cervical fascia. On the posteromedial side of each lobe this sheath is thickened to kind the ligaments of Berry extending from the posteromedial border of thyroid lobes to the decrease border of the cricoid cartilage. From the superior aspect the lymph drains medially to the prelaryngeal nodes and laterally to the higher deep cervical nodes. From the inferior side, the lymph drains medially to the pretracheal and paratracheal lymph nodes and laterally to the decrease deep cervical lymph nodes. Superior thyroid artery, a branch of exterior carotid artery, goes to the higher pole of every lobe accompanied by external laryngeal nerve. Inferior thyroid artery � A department of thyrocervical trunk which arises from the 1st a half of the subclavian artery, lies posterior to the gland on the degree of the cricoid cartilage. The recurrent laryngeal nerve crosses both in entrance or behind the artery or might pass between the branches. The thyroidea ima, if current, arises from the brachiocephalic artery or the arch of aorta. The thyroid gland strikes with deglutition due After partial thyroidectomy they preserve to its attachments with the larynx and trachea the blood supply of the remaining glanduas follows: lar tissue. The posterior lamina of the pretracheal the veins type a plexus on the surface fascia which is carefully adherent to the rings of the trachea on the again and the of the gland and on the front of the trachea. Sometimes the presence of levator glan- middle thyroid veins drain into the internal jugular vein whereas the inferior thyroid dulae thyroidae.
Keflex 750mg mastercardPhosphorescence of the vomitus and stools and a typical garliclike odor on the breath are characteristic anti bacteria purchase keflex with amex, when present. The predominant hepatic lesion is steatosis and necrosis, most distinguished in the periportal area. Ingestion of poisonous quantities (1 to 10 mg) is normally seen with suicidal intent, especially on the Indian subcontinent. Jaundice outcomes from each hepatic damage and acute hemolysis brought on by excessive blood copper levels. Although liver failure from hepatic necrosis is mentioned in some case reviews, the mechanism is poorly understood and medical details to affirm causality are often scant. This subacute dosing routine produced severe toxicity in 75% of mice after 3-4 days. The long latency is assumed to be due partially to the uneven distribution of radionuclides and the limited range of the emitted alpha particles. The authors instructed that glutathione depletion and oxidative stress from both drugs was heightened in this setting. Mushrooms There are roughly one hundred toxic sorts of mushrooms among the many more than 5000 species, but solely about one third have been related to fatalities. The amatoxin-containing species belong to three genera: Amanita, Galerina, and Lepiota. A latent interval of 6 to 20 hours after ingestion of a mushroom precedes the primary signs of intense abdominal ache, vomiting, and diarrhea. Hepatocellular jaundice and renal failure happen over the next 24 to 48 hours and are adopted by confusion, delirium, convulsions, and eventually coma by 72 hours. No function for glucocorticoids has been found, but plasmapheresis or hemoperfusion has been useful in some instances. A small epidemic of acute hepatic injury attributable to the ingestion of cycad nuts was reported from Japan. The purported toxin is methylazoxymethanol, which is generally eradicated or rendered inactive in making ready the nuts before ingestion. They contaminate peanuts, cashews, soybeans, and grains saved underneath heat, moist circumstances and are well-known hepatotoxins and hepatocarcinogens. When consumed in giant portions, aflatoxin B1 is liable for a medical syndrome characterized by fever, malaise, anorexia, and vomiting, followed by jaundice. Portal hypertension with splenomegaly and ascites may develop over the subsequent few weeks. Other histologic findings embrace cholestasis, microvesicular steatosis, and bile duct proliferation. Although many patients produce other danger elements for continual liver illness (including hepatitis B and C, alcohol, and schistosomiasis), case-control research have strongly implicated khat as a rising health hazard. Vitamin A (retinol) is a dose- and duration-dependent hepatotoxin capable of causing injury starting from asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase ranges with minor hepatic histologic modifications to perisinusoidal fibrosis leading to noncirrhotic portal hypertension and, in some instances, cirrhosis. Hypervitaminosis A normally is the results of self-ingestion, somewhat than intentional overdose, and all age teams have been affected. Resulting hyperplasia and hypertrophy produce sinusoidal obstruction and elevated collagen synthesis, main in flip to portal hypertension. Ethanol interferes with the conversion of beta carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, to retinol, and the mix of ethanol and beta carotene has resulted in hepatotoxicity in various experimental models. The enlarged clear stellate cells compress the hepatic sinusoids, giving rise to a "Swiss cheese" or honeycombed appearance. Hepatic fibrosis in a perisinusoidal distribution can arise from activated stellate cells that rework into myofibroblasts. In a broadly cited sequence,168 cirrhosis was present in 59%, chronic hepatitis in 34%, microvesicular steatosis in 21%, perisinusoidal fibrosis in 14%, and peliosis in 3% of instances. In affected persons, hepatomegaly is frequent, and in severe instances, splenomegaly, ascites, and esophageal variceal bleeding may be features. The analysis of vitamin A toxicity rests on a dietary and drugs history and scientific suspicion. Plasma vitamin A levels may be regular, and the diagnosis is supported by the demonstration of elevated hepatic stores of vitamin A and characteristic histologic findings. Vitamin A dietary supplements generally should be averted in other kinds of liver illness due to possible accentuation of hepatic harm and fibrosis. Liver toxicity related to herbs and dietary supplements: online table of case stories. Liver injury has been reported to happen after a extensively variable latent period ranging from 1 week to so long as 2 years. The authors concluded that natural medicines rarely irritate current liver damage and that de novo harm is unusual. Aegeline Pennyroyal Abortifacient (squawmint oil) Hedeoma pulegoides, Mentha pulegium Multiple Sassafras albidum Cassia angustifolia Scutellaria Pulegone, monoterpenes Prostata Sassafras Senna Skullcap Prostatism Herbal tea Laxative Anxiolytic Uncertain Safrole Sennoside alkaloids; anthrone Diterpenoids vs. Anthraquinone Traditional Chinese Medicines Jin bu huan Ma huang Shou-wu-pian Sleep help, analgesic Weight loss Lycopodium serratum Ephedra spp. More disturbing was the discovering of undisclosed anabolic steroids in half of the body-building supplements and undisclosed potential hepatotoxins (diclofenac and tamoxifen) in other merchandise. Jaundice was current in 78% and was probably the most frequent symptom that brought a patient to medical consideration. The disease was characterised histologically by centrilobular hepatic congestion with occlusion of the hepatic venules, resulting in congestive cirrhosis. The acute form is characterized by zone three necrosis and sinusoidal dilatation, leading to a Budd-Chiari�like syndrome with belly pain and the speedy onset of ascites inside three to 6 weeks of ingestion. Approximately one half of the patients with the acute kind recovered spontaneously; transition to a more continual form of harm occurred within the remainder. At one time, this form of damage accounted for one third of the instances of cirrhosis seen in Jamaica, with dying typically ensuing from problems of portal hypertension in as few as 1 to 3 years. Associated signs and indicators included fever, fatigue, nausea, pruritus, abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, and jaundice. Liver biopsy specimens from a small variety of patients showed a range of histopathologic modifications, together with lobular hepatitis with distinguished eosinophils, delicate hepatitis with microvesicular steatosis, and fibrotic expansion of the portal tracts. The harm resolved inside a mean of eight weeks (range, 2 to 30 weeks) but might recur on rechallenge. The explanation for germander hepatotoxicity is an interplay between poisonous metabolites and immunoallergic mechanisms. Multiple reports of hepatitis have appeared; most cases have occurred inside 1 to 12 months of use and resolved inside a couple of weeks to months of discontinuation. The suspected hepatotoxic ingredient was N-nitroso-fenfluramine, a derivative of the appetite suppressant fenfluramine, which was withdrawn from the U. Usnic acid is also a part of Kombucha tea, which has been associated with hepatic injury. Contamination of the raw materials by molds has been cited in its place explanation for hepatotoxicity,216 although no onerous evidence for aflatoxicosis was found. A majority of the sufferers have been girls who have been taking the agent for various dyspeptic complaints. Several reviews of hepatocellular (and much less often cholestatic) harm have been published, with a latent period starting from 1 to several weeks, and a clinical presentation that often consists of nausea, vomiting, fatigue and jaundice, and situations of severe injury and acute liver failure have appeared.
Generic keflex 250mg free shippingDiet � High protein and low residue food plan have some relation antimicrobial resistance definition keflex 250mg with amex, in all probability because of formation of onerous fecal concretions or fecolith. Obstruction-Anyfactorcausingobstruction of the lumen can produce obstructive appendicitis. Acute nonobstructive or catarrhal appendicitis-Where the entire length of the lumen can drain into the cecum. Acute obstructive appendicitis-In this kind of appendicitis, symptoms are abrupt and extra severe. The appendix turns into a closed loop and persevering with secretion by appendicular mucosa leads to distension and pain first within the periumbilical region in accordance with nerve supply of the appendix. Once the serosa is concerned ache is migrated from the periumbilical region 212 to the evening iliac fossa. Macroscopic: � In early acute appendicitis the organ is Signs swollen and serosa exhibits hyperemia. Cough tenderness-It signifies inflam� In well-developed acute inflammation mation of parietal peritoneum. This is an known as acute suppurative appendicitis the essential physical sign which differentiserosa incorporates engorged vessels on the ates acute appendicitis from right-sided surface with fibrinopurulent exudates. Guarding and rigidity - Muscle guarding � An impacted overseas body, fecolith or correspond to the severity of the inflamconcretion may be seen in the lumen. As peritoneal irritation progresses, voluntary muscle guarding will increase and is ultimately changed by Clinical Features involuntary rigidity. This might that is often adopted by diffuse abdombe seen in retrocecal appendicitis. This is as a result of of � Nausea and vomiting are as a end result of reflex the fact that the inflamed appendix is action induced by rise in intraluminal in contact with the obturator internus pressure in appendix. Generalized peritonitis -Featuresofgeneralized peritonitis are seen only when is determined by bacterial status. Rectal examination - There is tenderness in the best rectal wall � differential B. Total 10 A rating of 7 or more is strongly predictive of acute appendicitis and instant operation is required. When the rating is 5 or 6, these are borderline instances and further checks like abdominal ultrasonography, and so forth. Abdominal ultrasound is done to rule out different causes together with gynecological causes, of acute stomach. Ctscan-Itisnotrequiredtodiagnosea case of straightforward appendicitis but to detect an appendicular mass, appendicular abscess or pelvic abscess. The mass is marked to establish the pro- ture of appendix and spreading peritonitis. Broad spectrum antibiotics began ini- appendicitis - the remedy of alternative is early tially parenterally, then orally. There is little doubt that in experienced palms, the endoscopic operation is protected even in the presence of perforation as a lot as the traditional process. Of course profit from the laparoscopic strategy remains to be confirmed by more trials. Majority of the tumors occur within the distal third of the appendix and solely less than 10 % occur at the base. It is recommended that metaplasi of the peritoneal cells could produce local spread and additional manufacturing. Surgical elimination of the pseudomucin and the underlying tumor adopted by peritoneal toilet provides one of the best prospects of treatment. Treatment Appendicectomy is the therapy of choice unless the lymph nodes are involved. Mechanical or dynamic obstruction � There is physical occlusion of the lumen stopping the intestinal contents from passing alongside the gut. Mechanical Obstruction Mechanical obstruction is further categorised in accordance with: 1. The velocity of onset determines whether or not the obstruction is acute, chronic or acute on persistent. When a narrowed lumen will get completely occluded by inspissated bowel contents this is termed acute on continual obstruction. Simple or non strangulated when the bowel is occluded with none vascular compromise and ii. Strangulated � When the blood provide of the concerned section of gut is reduce off. In case of volvulus closed loop obstruction occurs when both ends of the involved intestinal segment are obstructed. According to etiology Whenever we contemplate obstruction of a tube wherever within the body, this must be categorized into: 1. Outside the wall � Strangulatedhernia(externalorinternal) � Bands and adhesions-These are the commonest causes in previously operated patients and account for 40% of all causes. Section 8 Gastrointestinal Surger y 216 of the fuel distending the small bowel is It is also helpful to think of the common derived from i) swallowed air, ii) gasoline due causes of intestinal obstruction in varied age to bacterial exercise releasing H2S and teams. Volvulus neonatorum (Syn: Midgut bile, pancreatic juice and succus entericus malrotation). When with an inflammatory response which play the ileocecal valve is competent (present a key function. For simmotor processes by launch of cytokines, ple (nonclosed loop) obstruction this scereactive proteolytic enzymes and different nario hardly ever occurs. Symptoms � During the primary 12 hours of an obstruction of small bowel water and electrolytes the cardinal symptoms of intestinal obstrucaccumulate throughout the lumen second- tion are four viz. Abdominaldistension-Thereiscentral abdominal distension in ileal obstruction and peripheral distension in large bowel obstruction. Failure of passing feces in addition to flatus is called absolute constipation or obstipation. Vomiting - It is because of reverse peristalsis first abdomen contents, then bile followed by feculent vomiting happens in ileal obstruction. If the final condition of the affected person is nice and blood is out there, resection and anastomosis is finished for small bowel obstruction. Hernial orifices should be seemed for any � Acute obstruction of sudden onset is invariably an pressing downside requiring strangulated hernia, particularly a small emergency surgical intervention. Internal intestinal strangulation (constant ache for 2 hours in spite of gastroduodenal cates peritonitis. Erect film demonstrates multiple Operation is begun when the patient has air�fluid levels in a ladder pattern of been rehydrated and very important organs are funcdilated loops suggesting small bowel tioning properly. At operation, the affected bowel is examined carefully to determine its viability. Management Hot mops are applied and anesthesioloAlthough the remedy of particular causes of gist, is requested to administer pure O2 for at intestinal obstruction is taken into account beneath the least three to 5 minutes. The signs of viability are: applicable headings, sure common princi- � Colorimproves(greenishorblackbowel ples could be enunciated here.
Buy keflex 500mg lineAtorvastatin and antioxidants for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver illness: the St antibiotic for uti pseudomonas purchase keflex visa. Long-term mixture remedy of ezetimibe and acarbose for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Efficacy of long-term ezetimibe remedy in sufferers with nonalcoholic fatty liver illness. The use of statins alone, or in combination with pioglitazone and other drugs, for the therapy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and related cardiovascular threat. Rosiglitazone versus rosiglitazone and metformin versus rosiglitazone and losartan within the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitisin human: a 12-month, randomized, prospective open-label trial. Review article: emerging anti-fibrotic therapies within the remedy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- and �, induces decision of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with out fibrosis worsening. The results of discontinuing pioglitazone in sufferers with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Long-term pioglitazone therapy for sufferers with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exenatide within the therapy of diabetic patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a case-series. High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ursodeoxycholic acid for remedy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: outcomes of a randomized trial. Pentoxyfylline inhibits progress and collagen synthesis of cultures human hepatic myo-fibroblastlike cells. Pentoxyfylline improves nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pentoxyfylline for the therapy of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized managed trial. Effect of pentoxyifylline on histological activity and fibrosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients: a one yr randomized management trial. The liver is well outfitted to deal with these agents by an adaptable (inducible) sequence of metabolic pathways. These pathways embrace people who alter the parent molecule (phase 1); synthesize conjugates of the drug or its metabolite with a extra watersoluble moiety, corresponding to a sugar, amino acid, or sulfate molecule (phase 2); and excrete in an energy-dependent method the parent molecule, its metabolites, or conjugates into bile (phase 3). For any given compound, 1, 2, or all 3 steps could additionally be essential for drug elimination. Expression and subcellular location of the proteins (enzymes, membrane transporters) that mediate these steps are managed by a set of nuclear receptors that perform as transcriptional regulators and co-regulators, thereby accounting for coordinated regulation of the 3 phases of hepatic drug elimination. Pathways of Drug Metabolism Phase 1 and Cytochrome P450 Phase 1 pathways of drug metabolism embrace oxidation, reduction, and hydrolytic reactions. The ensuing "activated oxygen" is included into the drug or another lipophilic compound. Reduction of oxygen and insertion into a drug substrate ("mixed function oxidation") generates chemically reactive intermediates, including free radicals, electrophilic "oxy-intermediates" Other examples of reactive quinone compounds embody metabolites of troglitazone, quinine, and methyldopa. Likewise, hepatic metabolism of some plant toxins can generate potentially hepatotoxic epoxide metabolites of diterpenoids (see Chapter 89). This explains in part the zonality of hepatic lesions produced by medication and toxins, similar to acetaminophen and carbon tetrachloride, which are transformed to reactive metabolites. This finding largely explains the 4-fold or larger variations in rates of drug metabolism amongst healthy subjects. Exposure to lipophilic substances generates an adaptive response that normally includes transient liver cell harm (discussed later) as properly as synthesis of recent enzyme protein, a course of termed enzyme induction. Second, the influence of 1 drug on expression and activity of drug metabolizing enzymes and drug elimination (phase 3) pathways can alter the metabolism or disposition of other brokers. Such drug-drug interactions could additionally be related to mechanisms of drug-induced liver harm. This might explain partly why agents similar to zidovudine and phenytoin lower the dose threshold for acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Examples include nitroradicals from nitrofuran derivatives (nitrofurantoin, cocaine). Phase 2 (Conjugation) Phase 2 reactions contain formation of ester links to the mother or father compound or to a drug metabolite to type hydrophilic conjugates that could be excreted readily in bile or urine. The responsible enzymes include glucuronyl transferases, sulfotransferases, glutathione S-transferases, and acetyl and amino acid N-transferases. In common, drug conjugates are unhazardous, and phase 2 reactions are considered to be detoxification reactions, with exceptions. In basic, conjugation reactions are minimally affected by liver disease, with the potential exception of some discount of enzyme exercise and ensuing drug clearance in decompensated cirrhosis; that is relevant to selection of major analgesics (morphine quite than pethidine) and hypnotics (oxazepam somewhat than diazepam). Phase 3 this part includes secretion of drugs, drug metabolites, or their conjugates into bile. Polymorphisms involving these genes are related to human cholestatic liver diseases. Altered expression or impaired activity (by competitors between brokers, modifications in membrane lipid composition, or damage from reactive metabolites or covalent binding) might result in drug accumulation, impairment of bile move, or cholestatic liver injury. This has been demonstrated for estrogens,12,thirteen troglitazone,14 terbinafine,15 and flucloxacillin16 and has wider mechanistic implications for druginduced cholestasis and different forms of liver damage. Instead of doses used for cardiovascular indications (such as 160 to 320 mg daily), the standard starting dose in a patient with cirrhosis should be 10 to 20 mg day by day. Other high-clearance compounds affected by extreme liver illness include pethidine, tricyclic antidepressants, and salbutamol. Drugs that rely on hepatic elimination through biliary excretion are minimally affected by liver illness, aside from most cancers chemotherapeutic brokers. By contrast, liver illness has a lot much less effect on conjugation pathways (phase 2 drug metabolism), a property that might be exploited within the selection of sedatives or main analgesics (see later). Patients with cirrhosis have impaired creatinine clearance and are susceptible to developing gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Another challenge is the appropriate alternative of a sedative to manage alcohol withdrawal in a patient with alcohol-associated cirrhosis. Acetaminophen seems to be the most secure analgesic agent to use in cirrhosis (see later). Indeed, proof signifies that some types of hepatic adaptation to medication follow an earlier transient strategy of self-limiting liver injury, followed in turn by operation of innate immunity. The latent period is longer (typically from 1 week to three to 6 months) than that for direct hepatotoxins (from hours to a few days), and extrahepatic features of drug hypersensitivity could also be present.
References - Mant TGK. Clinical studies with dimercaptopropane sulphonate in mercury poisoning. Hum Toxicol. 1985;4:346.
- Xu AJ, Taksler GB, Llukani E, et al: Long-term natural history of lower urinary tract symptoms following radical retropubic prostatectomy: a prospective 15 year longitudinal study, Urology 120:167n172, 2018.
- Tabet JY, Meurin P, Driss AB, et al: Determination of exercise training heart rate in patients on-blockers after myocardial infarction. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 2006;13:538-543.
- Desar IME, Ottevanger PB, Benson C, et al. Systemic treatment in adult uterine sarcomas. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2018;122:10-20.
- Wallentin L, et al, for the PLATO Investigators: Tricagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2009;361:1045-1057.
- Mustard WT. Successful two-stage correction of transposition of great vessels. Surgery. 1964;55:469.
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 425 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology. 1998;28:751.
- The Impella Recover 2.
|

