|
Dr Chris Danbury - Consultant Intensivist
- Royal Berkshire Hospital
- Reading
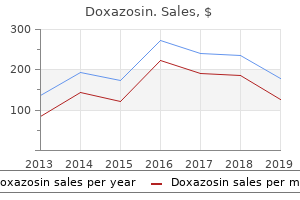
Doxazosin dosages: 4 mg, 2 mg, 1 mg
Doxazosin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase doxazosin pills in torontoA useful caveat to use in such situations is to examine the findings with the contralateral regular testis gastritis symptoms vomiting order doxazosin once a day. Techniques including energy Doppler imaging and the use of distinction brokers could improve detection of intratesticular move. The ultrasound look of the twisted testicular appendage has been described as an avascular hypoechoic or echogenic mass adjoining to a normally perfused testis and surrounded by an space of increased shade Doppler circulate. Traditionally, testicular scintigraphy has been used within the evaluation of testicular torsion, however this methodology suffers from the constraints of restricted entry out of hours, complicated gear needs, and prolonged examination instances. Possible causes include torsion, epididymo-orchitis, vasculitis, hypercoagulable states, sickle cell illness. Known complication of mumps, smallpox, scarlet fever, influenza, typhoid, and sinusitis. Comments Reactive hydrocele could also be associated with epididymo-orchitis or other inflammation. Sudden onset of a right-sided varicocele, or any irreducible varicocele, could additionally be due to retroperitoneal pathology. Often eliminated surgically as a outcome of it may be troublesome to differentiate from malignancy. Incidentally discovered; may be associated with prior infection, trauma, or scrotal surgical procedure Usually associated with elevated corticotropin level Arises from obstructed efferent ductules usually in patients with prior vasectomy. Condition Hydrocele Testicular cyst Varicocele Epidermoid cyst Tubular ectasia of rete testis Adrenal rests Spermatocele Painless mass or none None Often manifest as bilateral scrotal swelling Asymptomatic or could manifest as small focal scrotal lump Asymptomatic Asymptomatic or might manifest as nodular swelling Testicular microlithiasis Scrotal pearl Incidental diagnosis, could also be premalignant, follow-up imaging is usually advised. Epididymitis in older men normally outcomes from a decrease urinary tract an infection with the common causative organisms being Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, and Klebsiella. In younger males, organisms such as Chlamydia and Neisseria gonorrhoeae are extra common etiologic brokers. Mild repetitive trauma to the scrotum such as caused by driving a bicycle also might trigger mild noninfective "mechanical" epididymo-orchitis. A, Color Doppler ultrasound image in a 24-year-old man with acute onset of scrotal pain reveals a focal space of hypovascularity (arrowheads) surrounded by areas of normal vascularity. A, Color Doppler ultrasound image exhibits an avascular testis in a younger male with acute onset of scrotal pain over the past 6 hours. C, Gray-scale picture of the symptomatic facet revealed an enlarged and hypoechoic epididymis secondary to ischemia. Testicular ischemia and infarction may happen when the vascularity of the testis is compromised by venous occlusion. Changes of persistent epididymo-orchitis embrace persistent swelling of the epididymis as a heterogeneous mass and a striated appearance of the testis. However, the presence of elevated venous move suggests orchitis, because intratesticular venous move is normally troublesome to detect in regular testes. Blunt scrotal trauma is by far the commonest cause of testicular injury and normally results from athletic harm, motor vehicle accident, or assault. Testicular trauma might result in testicular hematoma, traumatic torsion, gangrenous or contaminated tumor, or primary pyogenic or end result of main orchitis. Hyperemic epididymis could also be misinterpreted as a halo, producing false-positive research. A, Sagittal gray-scale ultrasound picture demonstrates a markedly enlarged heterogeneous epididymal head. B, Color Doppler image shows elevated vascularity in the enlarged epididymal head. Ultrasonography is right for the assessment of scrotal trauma because it offers speedy and correct assessment of scrotal contents and their integrity. Rupture of the bulbar urethra might result in leakage of urine into the scrotum, mimicking a hydrocele. Heterogeneity of the testicular parenchyma with related hematocele suggests testicular rupture. A testicular fracture is a break within the continuity of the testicular parenchyma with an intact tunica albuginea. A testicular rupture involves discontinuity of the tunica albuginea with extrusion of testicular parenchymal contents into the scrotal sac. Testicular rupture necessitates emergent surgical procedure, whereas testicular fracture with preserved vascularity may be managed conservatively. Testicular fracture with out preserved vascularity also necessitates emergent surgical procedure, owing to the presence of testicular ischemia. Congenital hydrocele results from a patent processus vaginalis resulting in open communication between the scrotal sac and peritoneum. A, Sagittal gray-scale ultrasound picture of the testis in a young man struck in the scrotum with a baseball bat exhibits a testicular parenchymal hematoma (arrowheads) with edema and thickening of the scrotal skin (arrow). B, Transverse ultrasound image of the testis reveals the testicular hematoma (arrowheads) and a small hematocele (arrow). Transverse picture of a testis with adjacent multiseptated collection (arrowheads) with internal echoes. It can manifest as pain and/or swelling or may be detected by the way throughout a workup for infertility. Idiopathic varicoceles are thought to be because of incompetent valves within the testicular vein that permit retrograde passage of blood by way of the spermatic twine into the pampiniform plexus. Idiopathic varicoceles are more frequent on the left facet where the testicular vein enters the left renal vein at a perpendicular angle. The proper testicular vein enters obliquely into the inferior vena cava, and this seems to have some protecting impact on the right facet. It is caused by compression of the renal vein by tumor or can result from an aberrant or obstructed renal vein. Because varicoceles are much less common on the best side, the discovering of a right-sided varicocele in the absence of a left-sided varicocele should immediate further investigation to exclude an related stomach mass inflicting compressive signs. Secondary varicocele on the left could result from "nutcracker syndrome," by which the superior mesenteric artery compresses the left renal vein. A regular venogram is one by which a single testicular vein is seen up to the inguinal ligament and into the spermatic cord. If a varicocele is present, the internal spermatic vein shall be enlarged and there shall be reflux into the abdominal, inguinal, scrotal, or pelvic parts of the spermatic vein. There also will be venous collateralization and formation of anastomotic channels. Venography is now most commonly performed before definitive treatment with venous embolization. Hydroceles are characteristically anechoic collections with good sound transmission anterolateral to the testis due to the attachment of the testis to the epididymis and scrotal wall posteriorly. Although radionuclide studies have been historically used to diagnose hydrocele, that is not accomplished. A, A younger man offered with an enlarging scrotum after a severe motorcar accident. Sagittal gray-scale ultrasound image of the testis reveals rupture of the tunica albuginea (arrowheads) with seminiferous tubules spilling out into the scrotal sac (arrow).
Purchase 2mg doxazosin with visaEnhancement not solely reflects vascularity but in addition is influenced by the administration of a distinction agent (amount and rate) and imaging delay gastritis diet vegan doxazosin 4mg low cost. Measurements should embrace the nephrographic phase, which is superior for the detection of enhancement. On the opposite hand, a smaller region of interest is acceptable for heterogeneous lesions to detect small areas of enhancement. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan shows perceived enhancement (arrow) in the wall of the cyst. Follow-up was really helpful given the presence of thickened calcifications (not shown). However, Israel and Bosniak71 do describe "perceived" enhancement throughout the septa and partitions of these lesions. It must be considered when a cystic mass has greater than three or 4 septations. A and B, Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography photographs present a multiloculated cystic lesion within the interpolar area of the left kidney. The large solid areas and male gender favor a diagnosis of multiloculated renal cell carcinoma. Axial (A) and coronal (B) contrast-enhanced images show a well-encapsulated multiloculated cystic lesion with herniation into the renal pelvis. The herniation into the renal pelvis and feminine gender favored a prognosis of multilocular cystic nephroma, which was confirmed at laparoscopic nephrectomy. The lack of encapsulation, regular renal parenchyma in between some of the cysts, and several satellite cysts clearly separate from the main cluster all favor localized cystic disease of the kidney. Localized cystic disease is an uncommon renal cystic illness of unknown pathogenesis that may imitate a multiloculated renal mass. What the Referring Physician Needs to Know: Cystic Renal Diseases � A renal cyst that meets each of the standards for a given imaging modality could be confidently identified as a benign easy cyst and requires no further analysis. Oncocytoma � A well-defined, strong renal mass with central stellate scar is evident on imaging. Zamboni G, Pea M, Martignoni G, et al: Clear cell 'sugar' tumor of the pancreas: a novel member of the family of lesions characterised by the presence of perivascular epithelioid cells. Laperriere J, Lafortune M: Case of the day: basic: oncocytoma of the proper kidney. Hunter S, Samir A, Eisner B, et al: Diagnosis of renal lymphoma by percutaneous picture guided biopsy: expertise with eleven instances. Prerenal renal failure might come up from alterations in renal artery perfusion or venous drainage. Postrenal causes of abnormal renal function are typically those causing obstruction to the urine outflow from calculi, ureteropelvic dysfunction, or lots. Renal parenchymal abnormalities may be divided into people who involve the complete kidney, similar to rejection, glomerulonephritides, amyloidosis, and medicines, and people that are both primarily cortical or primarily medullary, corresponding to nephrocalcinosis. Corticomedullary differentiation is often higher visualized on the best than the left. The utility of ultrasonography is to evaluate for hydronephrosis and vascular abnormalities (inflow or outflow) as causes for renal failure. Doppler ultrasonography, although nonspecific, can help in the differential prognosis of acute renal failure. Thus, with out prior knowledge of the analysis, an elevation is useful only to recommend that renal parenchyma is indeed irregular. Pathologic and immunologic evaluation of biopsy samples continues to be the mainstay in analysis. Ultrasound evaluation of the kidneys is beneficial to exclude different causes of renal perform impairment. The kidneys could present poor contrast excretion, relying on the stage of renal failure. This is a nonspecific finding seen in sufferers with diffuse renal parenchymal disease. Renal measurement varies considerably inside populations and by gender from 10 to 14 cm in males and 9 to thirteen cm in females. Disease processes may initially cause a rise in renal size because of acutephase edema after which trigger a continual lower in renal size on account of fibrosis. Thus, prior or serial ultrasound evaluation may be of larger benefit than a single measurement. The extremely heterogeneous appearance is consistent with diffuse parenchymal infiltration by lymphoma. Ultrasound evaluation of renal size, echo texture, pelvicalyceal system Hydronephrosis Loss of renal tissue Normal renal size and contour Increase in renal bulk finding of small kidneys therefore implies that persistent diffuse renal disease is present. Contour irregularity is seen with renal infarction, reflux nephropathy, and advanced analgesic nephropathy. Smoothly marginated, small kidneys are seen in diseases that trigger tubular atrophy and fine interstitial fibrosis. Unilateral diffuse nephromegaly could also be secondary to renal edema from renal vein thrombosis or urinary obstruction. Diffuse unilateral nephromegaly also could additionally be seen when physiologic compensatory hypertrophy happens within the setting of contralateral renal failure. This group consists of illnesses inflicting nephrocalcinosis and those that present primarily with calyceal or papillary abnormalities. Yes No Unilateral small, smooth kidney Bilateral small, smooth kidneys Lobar infarction Dilated calyces at renal poles Widespread papillary 1. Vascular � Generalized arteriosclerosis � Benign/malignant nephrosclerosis � Atheroembolic renal disease � Arterial hypotension 2. It manifests as nephritic syndrome, with a positive antistreptolysin O titer as diagnostic, and recovery is the rule in 2 to 3 weeks. It is often idiopathic but may be related to cancers (lung, bowel), infection (hepatitis, malaria), medication (penicillamine), and systemic lupus erythematosus. Also observe that the renal contour is easy and the traditional pelvicalyceal relationships are preserved. Uncommonly, there may be alternative of the wasted renal tissue with fatty proliferation within the renal sinus (renal sinus lipomatosis). Diagrammatic illustration of the pyelocalyceal and corresponding renal contour abnormalities. A, Reflux nephropathy, which reveals papillary abnormality with overlying scar commonly seen at the renal poles. C, Papillary necrosis displaying random papillary abnormalities without cortical involvement. There could also be hypercellularity with thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, hyalinization with deposition of amorphous proteinaceous material, and sclerosis that results in obliteration of the glomerular tuft.
Syndromes - D3 (cholecalciferol)
- Insertion of a breathing tube
- Parathyroid
- Fatigue, lack of energy, or light-headedness when standing up or with exertion
- Stop talking in mid-sentence and start again a few seconds later
- Sodium bicarbonate - a medicine (partial antidote) to help neutralize and remove the chemicals (salicylates) from the body
- Keep blood pressure at or below 130/80 mmHg to delay kidney damage. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are the medicines most often used. ACE inhibitors may also help decrease the amount of protein lost in the urine.
- Narrowing of the spinal column (spinal stenosis)
- Eye exams
- Chlorthalidone (Thalitone, Hygroton)
Cheap generic doxazosin ukTherefore the lactate/pyruvate ratio is regulated by the oxidation-reduction potential of the cell gastritis hypertrophic cheap doxazosin 1mg amex. Important in considerations of acid-base pathophysiology are the redox pairs -hydroxybutyrate�acetoacetate and ethanol-acetaldehyde. However, ischemia accelerates lactate production and concurrently decreases lactate utilization. The production of lactic acid has been estimated to be roughly 15 to 20 mEq/kg/day in normal people. The rate of lactic acid production could be increased by ischemia, seizures, excessive train, leukemia, and alkalosis. Both the liver and the kidneys and maybe muscle have the capability for elevated lactate removal under the stress of elevated lactate masses. The quantitative aspects of normal lactate manufacturing and consumption within the Cori cycle show how the event of lactic acidosis could be the most rapid and devastating type of metabolic acidosis. Clinical Spectrum In the classical classification of the L-lactic acidoses (see Table 17. Severe arterial hypoxemia even within the absence of decreased perfusion can generate l-lactic acidosis. Inadequate cardiac output, of both the low-output or the high-output selection, is the same old pathogenetic factor. The prognosis is related directly to the increment in plasma l-lactate and the severity of the acidemia. Hepatic failure reduces hepatic lactate metabolism, and leukemia increases lactate production. Severe anemia, especially as a result of iron deficiency or methemoglobinemia, may cause lactic acidosis. Among the commonest causes of l-lactic acidosis is bowel ischemia and infarction in sufferers within the medical intensive care unit. Malignant cells produce more lactate than normal cells even under aerobic situations. This phenomenon is magnified if the tumor expands quickly and outstrips the blood provide. Therefore exceptionally large tumors may be related to severe l-lactic acidosis. Seizures, extreme exertion, heat stroke, and tumor lysis syndrome might all cause l-lactic acidosis. Of these, metformin and different biguanides (such as phenformin) are probably the most widely reported to have this effect. Although uncommon, metformin-induced lactic acidosis is the most frequent cause of lactic acidosis in sufferers with diabetes and is related to a mortality of up to 50%. Chronic low-grade hyperlactatemia is also associated with osteopenia and osteodystrophy, possibly due to the effect of chronic acidosis on bone calcium mobilization Associated Clinical Features Hyperventilation, stomach ache, and disturbances in consciousness are frequently present, as are indicators of insufficient cardiopulmonary function in kind A L-lactic acidosis. Leukocytosis, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and hyperaminoacidemia (especially extra of alanine) are frequent, and hypoglycemia may happen. The overall mortality of sufferers with L-lactic acidosis is approximately 60% but approaches one hundred pc in these with coexisting hypotension. The fundamental principle and solely efficient form of remedy for L-lactic acidosis is first to appropriate the underlying condition initiating the disruption in normal lactate metabolism. In type A L-lactic acidosis, cessation of acid production by enchancment of tissue oxygenation, restoration of the circulating fluid volume, enchancment or augmentation of cardiac operate, resection of ischemic tissue, and amelioration of sepsis are necessary in many cases. High L-lactate ranges portend a poor prognosis almost uniformly, and sodium bicarbonate administration is of little value on this setting. Use of vasoconstricting agents is problematic as a result of they might potentiate the hypoperfused state. Dopamine is preferred to epinephrine if pressure help is required, however the vasodilator nitroprusside has been instructed because it might improve cardiac output and hepatic and renal blood circulate to increase lactate removal. Paradoxically, bicarbonate therapy prompts phosphofructokinase, which is regulated by intracellular pH, thereby rising lactate production. Constant infusion of hypertonic bicarbonate has many disadvantages and is discouraged. The accumulation of lactic acid could also be relentless and will necessitate administration of diuretics, ultrafiltration, or dialysis. The use of continuous renal substitute remedy as a method of lactate removing and simultaneous alkali addition is a promising adjunctive remedy in critically unwell patients with L-lactic acidosis. Dichloroacetate, an activator of pyruvate dehydrogenase, was once advanced as a doubtlessly helpful therapeutic agent. In experimental L-lactic acidosis, dichloroacetate stimulated lactate consumption in muscle, decreased lactate production, and improved survival. In nonacidotic patients with diabetes, it successfully lowered lactate in addition to glucose, lipid, and amino acid levels. Features embody slurred speech, confusion, cognitive impairment, clumsiness, ataxia, hallucinations, and behavioral disturbances. D-Lactic acidosis has been described in patients with bowel obstruction, jejunal bypass, short bowel, or ischemic bowel illness. These issues have in common ileus or stasis associated with overgrowth of flora within the gastrointestinal tract, which is exacerbated by a high-carbohydrate diet. While results of particular testing are awaited, the patient ought to be under orders to obtain nothing by mouth. Treatment with a low-carbohydrate diet and antibiotics (neomycin, vancomycin, or metronidazole) is usually effective. In general, it seems prudent to initiate therapy with intravenous isotonic saline at a rate of a thousand mL/hr, particularly within the severely volume-depleted affected person. When the heartbeat and blood strain have stabilized and the corrected serum Na+ concentration is in the range of one hundred thirty to a hundred thirty five mEq/L, swap to zero. Total physique K+ depletion is usually current, though the + K degree on admission could additionally be elevated or regular. A normal or reduced K+ value on admission signifies severe K+ depletion and should be approached with warning. When urine output has been established, 20 mEq of potassium chloride must be administered in each liter of fluid as long as the K+ worth is less than 4. Hypokalemia and different complications of alkali therapy dramatically improve when quantities of sodium bicarbonate exceeding 400 mEq are administered. However, the effect of alkali remedy on arterial blood pH needs to be reassessed frequently and the total administered stored at a minimal, if alkali remedy is important. The acidosis is primarily as a result of elevated levels of ketones, which exist predominantly within the type of -hydroxybutyrate because of the altered redox state induced by the metabolism of alcohol.
Order generic doxazosin pillsRenal vesicle formation is distinctively compromised within the absence of Trps1 gastritis diet ������ order doxazosin online, with a concomitant depletion of the cap mesenchyme. The actual function of Cited1 in the condensing mesenchyme remains poorly understood because Cited1- and compound Cited1/Cited2-knockout kidneys have apparently intact mesenchyme-to-epithelial transitions. Overexpression of Six2, however, prevented epithelial differentiation of the cap mesenchyme. Six2, subsequently, is required to preserve the undifferentiated, self-renewing progenitor states of nephron precursors. Nevertheless, epithelialization in Six2-null mutants stays depending on Wnt9b induction. A finetuned activity of Six2 is subsequently required to stability the maintenance of a pool of self-renewing nephron progenitors and to prime these progenitors for dedication to an epithelial destiny through a canonical Wnt-dependent pathway. Significantly diminished cell proliferation and increased apoptosis have been noticed in the nephrogenic zone within the absence of Dlg1 and Cask. The Notch group of signaling molecules has been implicated in directing segmentation of the nephron. Notch family members are transmembrane proteins, the cytoplasmic domains of that are cleaved by the -secretase enzyme upon the interaction of the extracellular area with transmembrane ligand proteins of the Delta and Jagged families, discovered on adjacent cells. The cleaved portion of the Notch cytoplasmic domain translocates to the nucleus, where it has a task in directing gene expression. Mice homozygous for a hypomorphic allele of Notch2 have abnormal glomeruli, with a failure to form a mature capillary tuft. When the -secretase inhibitor was eliminated, there seemed to be a better restoration of expression of proximal tubule markers than of podocyte differentiation markers. Similar outcomes have been observed in mice carrying focused mutation of the Psen1 and Psen2 genes that encode a element of the -secretase complex. Taken collectively, these studies seem to indicate that native activation of Notch2 during tubule morphogenesis is important to determining the proximal cell destiny after the epithelialization of renal vesicle. Germline deletion of Pou3f3 leads to faulty patterning of the distal nephron segments. Without Pou3f3, elongation of prospective loop of Henle and total maturation of distal nephron segments are arrested. Although the event of glomeruli, proximal tubules, and accumulating ducts is seemingly not affected by the absence of Pou3f3, the severity of the distal nephron abnormalities causes renal insufficiency and perinatal death. The merchandise of Adamts1 and Adamts4 are secreted thrombospondin domain�containing metalloproteases recognized to cleave a category of proteoglycans referred to as lecticans. Null mutation of Adamts1 in mice leads to hydronephrosis and is characterized by the thinning of the renal medulla and a particular paucity in the loops of Henle. This finding means that Adamts1 and Adamts4 have overlapping significance in the growth of the distal nephron section by a mechanism but to be recognized. There is one instance thus far of a transcription factor involved within the differentiation of a specific cell kind within the kidney. Two cell types are normally found in the accumulating ducts-principal cells, which mediate water and salt reabsorption, and intercalated cells, which mediate acidbase transport. In the absence of the Foxi1 transcription issue, only one cell kind is present in amassing ducts, and many acid-base transport proteins usually expressed by intercalated cells are absent. In epithelia, cells are uniformly organized alongside an apicalbasal airplane of polarity. However, as properly as, cells in most tissues require positional info in the plane perpendicular to the apical-basal axis. This kind of polarization, referred to as planar cell polarity, is critical for morphogenesis of metazoans. These research additionally underscore the pivotal function played by the stroma in establishing the stereotypical radial patterning of the kidney. Bmp4 is a identified chemotactic agent for endothelial cells,267 so it is very likely that the ectopic Bmp4-positive cells account for the presence of endothelial cells within the broadened renal capsule of Foxd1 mutant kidneys. The accumulation of the cap mesenchyme can additionally be likely contributed partly by ectopic Bmp4 signaling within the absence of Foxd1, as a result of Bmp4 has been proven to antagonize epithelialization of the cap mesenchyme. In the absence of Foxd1, decorin turns into abundantly expressed in the presumptive cortical stromal area. Functional cell-culture�based assays and epithelialization assays of mesenchymal aggregates demonstrate that decorin inhibits Bmp7 signaling and mesenchymeto-epithelial transformation. These findings are corroborated by the partial rescue of the Foxd1-null phenotype through genetic inactivation of Dcn. Although many of the defects within the Tcf21 mutant kidneys phenocopy those seen in the Foxd1 mutant kidneys, there are essential variations. These differences would possibly result from the broader area of Tcf21 expression, which includes the condensing mesenchyme, podocytes, and medullary stromal cells in addition to the stromal cells that surround the condensates. In specific, it was proven that Fat4-dependent Hippo signaling initiated by the stroma integrates with canonical Wnt signaling derived from the ureteric lineage so as to steadiness nephron precursor propagation and differentiation. The absence of Fat4 within the stromal compartment phenocopies the growth of the nephrogenic precursor domain and failed epithelial differentiation of nephron progenitors seen in stroma-deficient kidneys. It was postulated that Fat4 performing through the Hippo pathway promotes the differentiation of the epithelial transition of nephrogenic precursors. This chance was further reiterated by the rescue of the depletion of nephrogenic precursors by Fat4 deficiency in Wnt9b-knockout mice. Interestingly, the ablation of Vangl2, a signaling companion of Fat4 identified to regulate renal tubular diameter,259 fails to rescue the lack of nephron progenitors in Wnt9b-knockout animals, suggesting that Fat4-mediated signaling throughout early differentiation of nephrogenic precursors is independent of the planar cell polarity pathway. Use of other knock-in strains permits identification of endothelial cells lining arteriolar or venous vessels. Similar to the dosage sensitivity noticed in the whole embryo, deletion of a single Vegfa allele from podocytes also led to glomerular endothelial defects generally known as endotheliosis that progressed to end-stage kidney failure at three months of age. A total knockout (loss of each alleles, -/-) ends in failure of glomerular filtration barrier formation and perinatal demise. Angiopoietin 1 (Angpt1) stabilizes newly formed blood vessels and is related to lack of vessel plasticity and concurrent recruitment of pericytes or vascular help cells to the vascular wall. The importance of Angpt1 in promoting the development of the renal microvasculature was first instructed on the idea of observations that exogenous Angpt1 enhanced the expansion of interstitial capillaries in mouse metanephric organ cultures. Angpt1, Angpt2, Tie2, and the orphan receptor Tie1 have all been shown to be expressed in the growing kidney. In one examine, Angpt2-null mice have been viable but exhibited defects in peritubular cortical capillary growth; the mice died prior to differentiation of vasa recta, precluding evaluation of the function of Angpt2 in these different capillary beds. Overexpression of EphB4 leads to defects in glomerular arteriolar formation, whereas conditional deletion of EphrinB2 from perivascular clean muscle cells and mesangial cells ends in glomerular vascular abnormalities. The T-box transcription issue Tbx18 is strongly expressed throughout early urogenital tract growth within the ureteral mesenchyme and in a subset of kidney stromal mesenchyme originating from Foxd1-positive precursor cells. Tbx18 is also specifically required within the regular improvement of the glomerular microvasculature. Loss of Tbx18 causes important oligonephronia and dilation of glomerular capillaries. These vascular phenotypes likely end result from the degeneration of the vascular mesenchyme and the failure to maintain the proliferation of mesangial precursors.
Order 1mg doxazosin with mastercardBecause of the comparatively high permeability of the proximal tubule gastritis red flags generic doxazosin 4mg otc, changes in interstitial Starling forces are prone to be transduced mainly through alterations in passive bidirectional paracellular flux through the tight junctions. In addition to peritubular capillary and interstitial Starling forces, luminal elements may also play a task in the regulation of proximal tubule transport. Moreover, research in isolated perfused rabbit proximal tubules have indicated that the presence of a transtubular anion gradient, usually present in the late portion of the proximal nephron, is critical for the move dependence to occur. The resulting transtubular anion gradient would then facilitate the "passive" reabsorption of the natural solutes and NaCl in this segment, but overall internet reabsorption can be lowered. Because the ultimate urinary excretion of Na+, in response to volume expansion or depletion, can be dissociated from the quantity delivered out of the superficial proximal nephron, more distal or deeper segments of the nephron contribute to the modulation of Na+ and water excretion. Several sites alongside the nephron, such as the loop of Henle, distal nephron, and cortical and papillary accumulating ducts, had been found (by micropuncture and microcatheterization techniques) to enhance or decrease the speed of Na+ reabsorption in response to enhanced delivery from early segments of the nephron. However, direct proof that these transport processes are mediated by modifications in Starling forces per se is lacking. In abstract, the intrarenal management of Na+ excretion could be generalized as follows. In addition, adjustments within the filtered load of small organic solutes, and perhaps other, as yet uncharacterized, glomerulus-borne substances in tubule fluid may influence Rateabs. Medullary Hemodynamics and Interstitial Pressure in the Control of Sodium Excretion: Pressure Natriuresis. The lower in water reabsorption within the thin descending limb lowers the Na+ concentration within the fluid coming into the ascending loop of Henle, thus decreasing the transepithelial driving force for salt transport on this nephron phase. At the same time, an identical mechanism was proposed to explain the natriuresis after elevations in systemic blood stress, a phenomenon termed pressure natriuresis. Measurement of medullary plasma flow with laser Doppler flowmetry and videomicroscopy in experimental animals has provided robust evidence for the redistribution of intrarenal blood circulate toward the medulla after quantity expansion and renal vasodilation. These studies were of specific curiosity with regard to the role of medullary hemodynamics in the management of Na+ excretion, especially in the context of pressure natriuresis. The coupling between arterial strain and Na+ excretion was discovered to happen within the setting of preserved cortical autoregulation. This has led to the suggestion that the strain natriuresis mechanism is triggered by modifications in medullary circulation. As talked about earlier, an increase in medullary plasma circulate would possibly result in medullary washout with a consequent discount within the driving drive for Na+ reabsorption within the ascending loop of Henle, particularly in the deep nephrons. In addition, the increase in medullary perfusion may be associated with a rise in Pi. The discovering that small changes in Pi are related to important alterations in tubular Na+ reabsorption has led to the speculation that the adjustments in Pi may be amplified by varied hemodynamic, hormonal, and paracrine components. The importance of endothelium-derived elements within the regulation of renal circulatory and excretory operate has been acknowledged. Studies have advised that endotheliumderived nitric oxide and P450 eicosanoids play a task within the mechanism of strain natriuresis. The response appears to be localized to the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle, in distinction to the nitric oxide effect, which happens in the vasa recta. Moreover, elevated arterial stress, induced by ligation of the distal aorta, led to diuresis and natriuresis in normal mice, however the response was attenuated in connexin 30 knockout mice. As noted in complete critiques, acute regulatory adjustments in renal salt excretion could happen without measurable elevation in arterial blood pressure. Initial research have determined that the greatest innervation is found in the renal vasculature, largely at the level of the afferent arterioles, followed by the efferent arterioles and outer medullary descending vasa recta. In accordance with these anatomic observations, stimulation of the renal nerve leads to vasoconstriction of afferent and efferent arterioles194,197 mediated by the activation of postjunctional 1-adrenoreceptors. The 1-adrenergic receptors and many of the 2-adrenergic receptors are localized in the basolateral membranes of the proximal tubule. In addition, although urine flow and Na+ excretion declined with renal nerve stimulation, there was no change in absolute proximal fluid reabsorption rate, which suggests that reabsorption is elevated within the more distal segments of the nephron. In rats receiving diets with different Na+ levels, DiBona and Kopp194 measured renal nerve activity in response to isotonic saline volume enlargement and furosemide-induced quantity contraction. A low-Na+ diet resulted in a reduction in right atrial pressure and a rise in renal nerve activity. The magnitude of the increase in renal nerve activity was roughly 20% for each 1-mm Hg fall in atrial stress. Conversely, the high-Na+ food plan resulted in increased proper atrial stress and a discount in renal nerve activity. Moreover, the contribution of efferent renal nerve exercise is of greater significance during situations of dietary Na+ restriction, when the necessity for renal Na+ conservation is maximal. Early studies confirmed that acute denervation of the kidneys is associated with increased urine circulate and Na+ excretion. However, absolute proximal reabsorption was considerably decreased within the absence of changes in peritubular capillary oncotic strain, hydraulic stress, and renal interstitial strain. This examine indicated that in conditions by which efferent neural tone is heightened above baseline level, renal nerve exercise could profoundly influence renal circulatory dynamics. Similarly, lowdose infusion of norepinephrine to normal salt-replete volunteers resulted in a physiologic plasma increment of this neurotransmitter in affiliation with antinatriuresis. Efferent sympathetic nerve exercise influences the speed of renin secretion in the kidneys by a big selection of mechanisms, both directly or by interacting with the macula densa and vascular baroreceptor mechanisms for renin secretion. In turn, the elevated filtration fraction may further modulate peritubular Starling forces, possibly by reducing hydraulic pressure and rising colloid osmotic strain within the interstitium. These peritubular changes eventually lead to enhanced reabsorption of proximal Na+ and fluid. These results imply that the circadian clock has a beforehand unknown position in the management of Na+ stability. Perhaps of more significance is that it provides molecular perception into how the circadian cycle instantly impacts Na+ homeostasis. The Na+-retaining effect of aldosterone within the collecting tubule induces a rise within the transepithelial potential difference, which is conducive to K+ excretion. The impact of a given circulating level of aldosterone on overall Na+ excretion is dependent upon the quantity of filtrate reaching the accumulating duct and the composition of luminal and intracellular fluids. In this regard, how renal Na+ reabsorption and K+ excretion are coordinately regulated by aldosterone has long been a puzzle. Conversely, hyperkalemia-induced aldosterone secretion stimulates most K+ excretion without major results on renal Na+ dealing with. Elegant research on the intracellular signaling pathways concerned in renal Na+ and K+ transport have make clear this puzzle. It exerts powerful effects on blood vessels,245 independently of actions that could be attributed to the blood strain rise by way of regulation of salt and water stability. It immediately will increase the expression and manufacturing of transforming progress factor- and thus is concerned in the growth of glomerulosclerosis, hypertension, and cardiac injury/hypertrophy. Two of those receptors, V1A and V2, are abundantly expressed in the cardiovascular system and the kidneys; V1B receptors are expressed on the surfaces of corticotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary gland, in the pancreas, and in the adrenal medulla.
Order doxazosin mastercardSince early pregnancy (6�8 weeks) gastritis diet 60 buy 2mg doxazosin, the latter two parameters had been fifty eight Anticoagulation Therapy on the increase (in comparison with pregravid interval for peak thrombin by fifty five. Box plots of reference intervals in pregravid period, at different phases of being pregnant, and in 2�3 days after spontaneous labor for (a) time to attain peak thrombin, (b) peak thrombin, and (c) endogenous thrombin potential. In figures, box plots symbolize the range of knowledge from the 25th to seventy fifth percentiles, while the bar in the midst of every box plot represents the median worth obtained excluding outliers. This approach was used for the initiation of heparin prophylaxis in girls who conceived after in vitro fertilization cycle, as an extension of the research published earlier [69]. Another perspective analysis methodology for the assessment of thrombotic state of readiness is the evaluation of spatial fibrin clot growth (thrombodynamics). This technique was widely used to examine hemophilia, mechanisms of action of antihemophilic medicine, and the development of latest ones [71, 72]. There are some information about the utilization of this method in pharmacology, such as the development of thrombin inhibitors [73], a research of their antidotes [74], or research of the procoagulant exercise of microparticles [75]. Clinical studies of the capability of thrombodynamics to identify the event of procoa gulant states are presented by the research of sufferers with sepsis [76]. Further improvement of this technique (with the tentative title thrombodynamics 4D) has been offered in a number of research [77, 78]. The approach, based on videomicroscopy of fluorescence, produced by thrombin-sensitive substrate, adopted by an answer of an inverse reaction-diffusion drawback, permits not solely statement of spatial clot growth but additionally the determination of thrombin as a operate of time and distance from the activator. The appearance of those built-in methods represents undeniable progress in the area of diagnostic enchancment of a variety of hemostatic disorders. Nowadays, highlighted thrombogenic danger factors in their prognostic value are sometimes equal to several types of thrombophilia; based mostly on this, their separation loses its sense. We consider that any cause selling thrombus formation may be referred to as thrombogenic threat elements, which may manifest itself or not, by thrombosis in sufferers throughout life. We recommend referring these pathological states or syndromes, which manifested themselves as thrombotic occasions. It allows for a reduction in hyperdiagnostics of thrombophilia and identifying sufferers with thrombophilia and patients in want of secon dary thromboprophylaxis, taking into account their identified thrombogenic danger components. From the point of view of personalized medication, controllable risk factors must be recognized 60 Anticoagulation Therapy in sufferers with the aim of elimination or modification, thereby lowering the chance of thrombosis. On the opposite hand, the presence of enhanced thrombin generation or extreme fibrin formation (in thrombodynamics test) among the many manifestations of thrombotic state of readiness can be referred to as goal causes for the prescription of anticoagulants. We hope that a consideration of the proposed approaches to the diagnostics of thrombophilia and thromboprophylaxis will promote further development of preventative direction on this field of medication. Acknowledgements the authors tremendously recognize the assistance of Gulnara Chueva and Anastasia Sidorenko in the preparation of this chapter for publication. Author details Andrey Momot1*, Irina Taranenko1, Lyudmila Tsyvkina1, Nadezhda Semenova2 and Irina Molchanova2 *Address all correspondence to: xyzan@yandex. Heart illness and stroke statistics � 2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Trends in the incidence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a 25-year popula tion-based research. Incidence of continual thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary embolism. All-cause and potentially disease-related health care prices related to venous thromboembolism in business, Medicare, and Medicaid beneficiaries. Diagnostic research for thrombophilia in girls on hormonal remedy and through pregnancy, and in kids. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized sufferers vs group residents. Guidelines on the investigation and administration of venous thrombosis at unusual sites. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and remedy in patients with most cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical follow guideline replace. Update of antithrombotic tips: medical professionalism and the funnel of data. Venous thromboembolism, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and being pregnant: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based scientific practice pointers (8th Edition). Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based casecontrol examine. Hypercoagulable states: elementary elements, acquired disorders, and congenital thrombophilia. Different dangers of thrombosis in 4 coagulation defects associated with inherited thrombophilia: a examine of 150 households. Hormonal replacement therapy, prothrombotic mutations and the danger of venous thrombosis. Oral contraceptives, hormone alternative therapy, thrombophilias and threat of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. Thrombotic risk throughout oral contraceptive use and pregnancy in women with factor V Leiden or prothrombin mutation: a rational method to contraception. A potential cohort research on absolutely the dangers of venous thromboembolism and predictive value of screening asymptomatic relations of patients with hereditary deficiencies of protein S, protein C or antithrombin. Perioperative management of antith rombotic therapy: antithrombotic remedy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis rating for overt disseminated intravascular coagulation predicts organ dysfunction and fatality in sepsis patients. Exclusion of deep venous thrombosis with D-dimer testing � comparison of 13 Ddimer methods in 99 outpatients suspected of deep venous thrombosis using venog raphy as reference commonplace. Comprehensive study on labora tory biomarkers for prediction and diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Familial transmission of venous thromboemb olism: a cohort research of eighty 214 Swedish adoptees linked to their biological and adoptive mother and father. Physiological perform of tissue factor pathway inhibitor and interplay with heparins. The Means of Progress in Improving the Results of in vitro Fertilization Based on the Identification and Correc tion of the Pathology of Hemostasis. Hemostasis and thrombosis past biochemistry: roles of geometry, move and diffusion. Investigation of the phenotype heterogeneity in severe hemophilia A utilizing thromboelastography, thrombin technology, and thrombo dynamics. Platelet microparticle membranes have 50- to 100-fold greater specific procoagulant exercise than activated platelets. Thrombin activity propagates in house throughout blood coagulation as an excitation wave.
Ilex vomitoria (Holly). Doxazosin. - Dosing considerations for Holly.
- What is Holly?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Coughs, digestive disorders, liver disorders, arthritis-like pain, heart disease, dizziness, blood pressure, and other conditions.
- How does Holly work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96515
Order doxazosin 1mg on lineUrine cytologic examination and imaging surveillance for transitional cell carcinoma are performed gastritis jelovnik order genuine doxazosin. Medullary Sponge Kidney (Benign Renal Tubular Ectasia) Medullary sponge kidney is a developmental anomaly with cystic dilation of the accumulating tubules in the renal pyramids. Medullary sponge kidney is believed to be secondary to hyperplasia of the renal amassing tubules. On plain radiographs, medullary sponge kidney could also be seen as nephrocalcinosis with clusters of calcifications within the renal medulla. Derangements in mesenchymal differentiation, development, and urine manufacturing are postulated to be the trigger of this anomaly. Bladder Duplication Bladder duplication is an especially rare condition with roughly 50 reported instances. Congenital Urachal Anomalies Congenital urachal anomalies include a extensive range of abnormalities, together with a patent urachus, urachal cyst, umbilicalurachal sinus, and vesicourachal diverticulum. If the entire allantois persists, there might be a communication between the bladder and the umbilicus leading to a patent urachus. If solely a localized space of the allantois stays, a urachal cyst forms because of secretory activity in the lining of the allantois. Patent Urachus A persistent communication exists between the bladder lumen and the umbilicus. Definitive confirmation could be made with injection into the umbilicus displaying communication with the bladder or cystography. Urachal Cyst A small cyst may develop when the urachus closes at each ends with a section of patent urachus between. Vesicourachal Diverticulum A vesicourachal diverticulum can arise from the dome of the bladder and represents persistent communication of the urachal remnant with the bladder. Patients are usually asymptomatic, and instances are usually discovered by the way. Bladder Diverticulum A bladder diverticulum is a small outpouching from the bladder. Congenital diverticula most frequently happen lateral and superior to the ureteral entrance. They are reported to outcome from a deficiency or weak spot within the Waldeyer fascial sheath. Prune Belly Syndrome Prune stomach syndrome, also identified as Eagle-Barrett syndrome or triad syndrome, is characterised by a wrinkled look of the distended and lax stomach wall; bilateral impalpable undescended testes; and abnormalities of the urinary tract, together with tortuous dilated ureters, dilated prostatic urethra, and renal dysmorphism. The syndrome is estimated to occur in 1 in 30,000 births and happens nearly completely in males, with only a few cases described in females. Prune stomach syndrome may be detected with screening ultrasonography during being pregnant. Findings embrace bilateral hydronephrosis, dilated and tortuous ureters, and ranging degrees of renal dysplasia. A vesicostomy may be carried out to allow the bladder to drain through a small gap in the abdomen. In severe instances, surgical reconstruction of the bladder and stomach wall could additionally be necessary. A thick valve-like membrane varieties from the wolffian ducts and extends from the verumontanum to the distal prostatic urethra. Abdominal ultrasonography can only suggest the diagnosis based mostly on the findings of bilateral hydronephrosis, a thickened bladder wall, and bladder diverticula. As their name implies, they characterize persistent anomalous valves alongside the anterior urethra. Typically, 40% are in the bulbar urethra, 30% are on the penoscrotal junction, and 30% are in the pendulous urethra. Proposed mechanisms include aborted try of urethral duplication, failure of alignment between the anterior and posterior urethra, extreme tissue growth in the growing urethra, and congenital cystic dilation of the periurethral glands. Symptoms can range from minimal obstruction to extreme hydronephrosis, endstage renal illness, and bladder rupture. Reflux into the ureters has been reported in a single third of cases, and atrophy of the higher urinary tract occurs in half of circumstances. What the Treating Physician Needs to Know � Screening ultrasound examination of the fetus is necessary in figuring out lots of the congenital anomalies of the urinary tract. Keller G, Zimmer G, Mall G, et al: Nephron number in sufferers with main hypertension. Winding L1, Loane M, Wellesley D, et al: Prenatal analysis and epidemiology of multicystic kidney dysplasia in Europe. Rathaus V, Konen O, Werner M, et al: Pyelocalyceal diverticulum: the imaging spectrum with emphasis on the ultrasound features. The form of the adrenals may be maintained, and mild enhancement could additionally be famous after intravenous administration of a distinction agent. It tends to be cystic and heterogeneous, which makes it difficult to differentiate from adrenal cortical carcinoma, pheochromocytomas, and metastasis. Typically, the enlargement is hypointense on a T1-weighted image and has variable or heterogeneous hyperintensity on T2-weighted images. In the subacute part, adrenal enlargement with peripheral enhancement and with cystic low-density or necrotic modifications could also be present. The limbs of the adrenal glands are longer than 5 cm and exceed 10 mm in thickness. The causes of diffuse enlargement include adrenal hyperplasia, lymphoma, metastatic disease, tuberculosis, and histoplasmosis. Local extension from renal most cancers or retroperitoneal sarcomas into the adrenal gland may be related to unilateral diffuse enlargement. In these circumstances, the gland shall be enlarged, with ill-defined margins and imaging options just like those of a focal mass or nodular metastasis. Focal Nodule or Mass Imaging manifestations of a focal adrenal nodule or mass are discussed in Chapter 71. On the other hand, bilateral a quantity of nodules could also be due to metastatic illness, a number of bilateral adenomas, or benign multinodular hyperplasia. Multiple nodular metastatic illness and nodular bilateral adenomas are comparatively uncommon. A to D, Note bilateral, giant a quantity of adrenal nodules on the upper stomach T2-weighted axial magnetic resonance images (arrows). There is minimal drop in signal depth on the out-of-phase image (D) compared with the spleen (curved arrow) and in-phase picture (C). The patient subsequently underwent bilateral adrenalectomy, and the histopathologic findings have been according to multinodular adrenal hyperplasia. The imaging features of nodular metastasis and adenoma are discussed in Chapter 71. In each situations, the adrenal glands are enlarged with multiple bilateral nodules.
Generic 1 mg doxazosin otcPatients with symptomatic hypophosphatemia and phosphate depletion do require alternative remedy chronic gastritis lead to cancer buy doxazosin 2 mg visa. Gaudio A, Pennisi P, Bratengeier C, et al: Increased sclerostin serum ranges associated with bone formation and resorption markers in sufferers with immobilization-induced bone loss. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, et al: Inactivating mutations within the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene in patients with pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets. In gentle or moderate hypophosphatemia, oral repletion with low-fat milk (containing zero. Alternatively, oral tablets containing 250 mg (8 mmol) of phosphorus from a mixture of sodiumphosphate and potassium-phosphate salts can be prescribed. A typical patient with moderate to severe hypophosphatemia would probably want one thousand to 2000 mg (32 to 64 mmol) of phosphorus/day to have physique stores repleted inside 7 to 10 days. Various regimens are utilized in medical apply, all based on uncontrolled observational research. Some are extra conservative within the quantity of phosphate delivered to keep away from unwanted effects, which can embody renal failure, hypocalcemic tetany, and hyperphosphatemia. Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, et al: Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: Molecular mechanisms. In Goldman L, Ausiello D, editors: Cecil textbook of medicine, ed 23, Philadelphia, 2008, Elsevier, pp 2983�2996. Jain A, Bhayana S, Vlasschaert M, et al: A method to predict corrected calcium in haemodialysis patients. Lind L, Skarfors E, Berglund L, et al: Serum calcium: a brand new, unbiased, prospective danger factor for myocardial infarction in middle-aged males followed for 18 years. Sociedade Brasileira de Endocrinologia e Metabologia, Bandeira F, Griz L, et al: Diagnosis and administration of main hyperparathyroidism-a scientific statement from the Department of Bone Metabolism, the Brazilian Society for Endocrinology and Metabolism. Rudberg C, Akerstrom G, Palmer M, et al: Late outcomes of operation for primary hyperparathyroidism in 441 sufferers. Khan A, Grey A, Shoback D: Medical administration of asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism: proceedings of the third worldwide workshop. Hoelting T, Weber T, Werner J, et al: Surgical treatment of parathyroid carcinoma [review]. Mune T, Katakami H, Kato Y, et al: Production and secretion of parathyroid hormone-related protein in pheochromocytoma: participation of an alpha-adrenergic mechanism. Ezzat S, Melmed S, Endres D, et al: Biochemical assessment of bone formation and resorption in acromegaly. Hinnie J, Bell E, McKillop E, et al: the prevalence of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. Bai M, Quinn S, Trivedi S, et al: Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca2+osensing receptor. Bai M, Janicic N, Trivedi S, et al: Markedly lowered exercise of mutant calcium-sensing receptor with an inserted Alu component from a kindred with familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism. Bendz H, Sjodin I, Toss G, et al: Hyperparathyroidism and longterm lithium therapy-a cross-sectional examine and the effect of lithium withdrawal. Marabelle A, Sapin V, Rousseau R, et al: Hypercalcemia and 13-cisretinoic acid in post-consolidation therapy of neuroblastoma. Christensson T, Hellstrom K, Wengle B: Hypercalcemia and primary hyperparathyroidism. Minaire P, Neunier P, Edouard C, et al: Quantitative histological data on disuse osteoporosis: comparability with biological data. Gaudio A, Pennisi P, Bratengeier C, et al: Increased sclerostin serum levels associated with bone formation and resorption 635. Sato Y, Asoh T, Kaji M, et al: Beneficial impact of intermittent cyclical etidronate therapy in hemiplegic patients following an acute stroke. Major P, Lortholary A, Hon J, et al: Zoledronic acid is superior to pamidronate in the treatment of hypercalcemia of malignancy: a pooled analysis of two randomized, controlled scientific trials. Camus C, Charasse C, Jouannic-Montier I, et al: Calcium-free hemodialysis: experience in the remedy of 33 patients with severe hypercalcemia. Kindgen-Milles D, Kram R, Kleinekofort W, et al: Treatment of severe hypercalcemia using steady renal substitute therapy with regional citrate anticoagulation. Demeester-Mirkine N, Hooghe L, Van Geertruyden J, et al: Hypocalcemia after thyroidectomy. Page C, Strunski V: Parathyroid danger in total thyroidectomy for bilateral, benign, multinodular goitre: report of 351 surgical circumstances. Laitinen K, Lamberg-Allardt C, Tunninen R, et al: Transient hypoparathyroidism during acute alcohol intoxication. Quitterer U, Hoffmann M, Freichel M, et al: Paradoxical block of parathormone secretion is mediated by elevated exercise of G alpha subunits. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements: Vitamin D reality sheet. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, et al: Inactivating mutations in the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene in a hundred and fifty. Maiya S, Sullivan I, Allgrove J, et al: Hypocalcaemia and vitamin D deficiency: an essential, however preventable, reason for lifethreatening toddler heart failure. Nakamura Y, Matsumoto T, Tamakoshi A, et al: Prevalence of idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism in Japan. The molecular basis of McCuneAlbright syndrome and Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. De Marchi S, Cecchin E, Basile A, et al: Renal tubular dysfunction in persistent alcohol abuse-effects of abstinence. Cundy T, Dissanayake A: Severe hypomagnesaemia in long-term customers of proton-pump inhibitors. Koulouridis I, Alfayez M, Tighiouart H, et al: Out-of-hospital use of proton pump inhibitors and hypomagnesemia at hospital admission: a nested case-control examine. Zehender M, Meinertz T, Faber T, et al: Antiarrhythmic effects of increasing the every day intake of magnesium and potassium in sufferers with frequent ventricular arrhythmias. Reffelmann T, Ittermann T, Dorr M, et al: Low serum magnesium concentrations predict cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Leone N, Courbon D, Ducimetiere P, et al: Zinc, copper, and magnesium and dangers for all-cause, cancer, and cardiovascular mortality. Tejpar S, Piessevaux H, Claes K, et al: Magnesium losing related to epidermal-growth-factor receptor-targeting antibodies in colorectal cancer: a prospective examine. Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A: Role of magnesium in the pathogenesis and treatment of migraine. Mohammed S, Goodacre S: Intravenous and nebulised magnesium sulphate for acute asthma: systematic review and metaanalysis. Quigley R, Baum M: Effects of development hormone and insulin-like development factor I on rabbit proximal convoluted tubule transport. Araya K, Fukumoto S, Backenroth R, et al: A novel mutation in fibroblast progress issue 23 gene as a cause of tumoral calcinosis. Yamaguchi T, Sugimoto T, Imai Y, et al: Successful treatment of hyperphosphatemic tumoral calcinosis with long-term acetazolamide. Sullivan W, Carpenter T, Glorieux F, et al: A potential trial of phosphate and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 remedy in symptomatic adults with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets.

Discount 1 mg doxazosin amexItami A gastritis symptoms burning buy discount doxazosin 1 mg, Kato M, Komoto I, et al: Human gastrinoma cells categorical calcium-sensing receptor. Condamine L, Menaa C, Vrtovsnik F, et al: Local motion of phosphate depletion and insulin-like development factor 1 on in vitro manufacturing of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D by cultured mammalian kidney cells. Diem K, Lentner C: Geigy scientific tables, ed 7, New York, 1970, Geigy Pharmacueticals. Nishida Y, Taketani Y, Yamanaka-Okumura H, et al: Acute effect of oral phosphate loading on serum fibroblast progress issue 23 levels in wholesome males. Biber J, Custer M, Werner A, et al: Localization of NaPi-1, a Na/ Pi cotransporter, in rabbit kidney proximal tubules. Custer M, Meier F, Schlatter E, et al: Localization of NaPi-1, a Na-Pi cotransporter, in rabbit kidney proximal tubules. Cellular mechanisms in proximal tubular Pi reabsorption: some answers and more questions. Murer H, Biber J: Membrane visitors and management of proximal tubular sodium phosphate (Na/Pi)-cotransport. Murer H, Forster I, Hilfiker H, et al: Cellular/molecular management of renal Na/Pi-cotransport. Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, et al: Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Murer H, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, et al: Molecular mechanisms in the regulation of renal proximal tubular Na/phosphate cotransport. Caverzasio J, Murer H, Fleisch H, et al: Phosphate transport in brush border membrane vesicles isolated from renal cortex of 203. Kawashima H, Kurokawa K: Localization of receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 alongside the rat nephron. Direct proof for presence of the receptors in each proximal and distal nephron. Kawashima H, Kurokawa K: Metabolism and sites of action of vitamin D in the kidney. Stoll R, Kinne R, Murer H, et al: Phosphate transport by rat renal brush border membrane vesicles: affect of dietary phosphate, thyroparathyroidectomy, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Renal adaptation to the dietary consumption in intact and thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Segawa H, Kaneko I, Yamanaka S, et al: Intestinal Na-P(i) cotransporter adaptation to dietary P(i) content material in vitamin D receptor null mice. Vainsel M: Tubular reabsorption of phosphate in regular kids and in kids with rickets. Barac-Nieto M, Alfred M, Spitzer A: Phosphate depletion in opossum kidney cells: apical but not basolateral or transepithelial adaptions of Pi transport. Biber J, Forgo J, Murer H: Modulation of Na+-Pi cotransport in opossum kidney cells by extracellular phosphate. Scanni R, vonRotz M, Jehle S, et al: the human response to acute enteral and parenteral phosphate masses. Kawashima H, Torikai S, Kurokawa K: Localization of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1 alpha-hydroxylase and 24-hydroxylase along the rat nephron. Lau K, Guntupalli J, Eby B: Effects of somatostatin on phosphate transport: evidence for the role of basal insulin. Corvilain J, Abramow M, Bergans A: Some results of human progress hormone on renal hemodynamics and on tubular phosphate transport in man. Hirschberg R, Ding H, Wanner C: Effects of insulin-like growth issue I on phosphate transport in cultured proximal tubule cells. Szalay L, Bencsath P, Takas L: Effect of splanchincotomy on the renal excretion of inorganic phosphate in the anaesthetized dog. Szenasi G, Bencsath P, Lehoczky E, et al: Tubular transport and urinary excretion of phosphate after renal denervation within the anesthetized rat. Debska-Slizien A, Ho P, Drangova R, et al: Endogenous renal dopamine manufacturing regulates phosphate excretion. Kaneda Y, Bello-Reuss E: Effect of dopamine on phosphate reabsorption in isolated perfused rabbit proximal tubules. Hafdi Z, Couette S, Comoy E, et al: Locally shaped 5-hydroxytryptamine stimulates phosphate transport in cultured 203. Carney S, Thompson L: Effect of differing concentrations of parathyroid hormone on rat renal electrolyte excretion. Poujeol P, Touvay C, Roinel N, et al: Stimulation of renal magnesium reabsorption by calcitonin within the rat. Bai X, Miao D, Li J, et al: Transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast development factor 23 (R176Q) delineate a putative function for parathyroid hormone in renal phosphate losing problems. Tsujikawa H, Kurotaki Y, Fujimori T, et al: Klotho, a gene related to a syndrome resembling human untimely getting older, capabilities in a negative regulatory circuit of vitamin D endocrine system. Kidneys in larger vertebrates transport solutes by mixed filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. The kidney adjusts the physique fluid content material as well as the focus of specific solutes. To obtain these regulatory capabilities, there are sensing mechanisms for the pool size and focus of the solute. Unlike inorganic solutes such as sodium or potassium, the whole pool for natural solutes is troublesome to define, because these solutes are continuously being absorbed, excreted, synthesized, and metabolized. For glucose, the upkeep of a discrete plasma focus is clearly important. Filtration-reabsorption commences by disposing every little thing and then selectively reclaiming and retaining substances that the organism needs to hold in the acceptable quantity. This mechanism economizes on gene products required to establish and excrete the myriad of undesirable substances. In the secretion mode, the burden is on the kidney to acknowledge the substrates to be secreted after which secrete them. In contrast to glucose reabsorption, which is extremely specific to certain hexose constructions, organic anion and cation secretion can engage tons of of structurally distinct substrates. The reabsorption and secretion of organic solutes are primarily carried out by the proximal tubule, with little or no contribution past the pars recta. This chapter summarizes the physiology, and cell and molecular biology of organic solute transport within the kidney. Although solely renal mechanisms will be coated on this chapter, you will want to observe that homeostasis of organic solutes includes the concerted action of a number of organs. Transport studies with brush border membrane vesicles and molecular cloning have established two transport systems with traits in keeping with earlier microperfusion findings.
Order doxazosin 4mg mastercardAkcay A chronic gastritis raw food buy generic doxazosin 4mg on-line, Yavuz T, Semiz S, et al: Pseudohypoaldosteronism kind 1 and respiratory distress syndrome. Bonny O, et al: Functional expression of a pseudohypoaldosteronism type I mutated epithelial Na+ channel missing the poreforming region of its alpha subunit. Oishi M, et al: A case of hyperkalemic distal renal tubular acidosis secondary to tacrolimus in residing donor liver transplantation. Higgins R, et al: Hyponatraemia and hyperkalaemia are more frequent in renal transplant recipients handled with tacrolimus than with cyclosporin. Further proof for variations between cyclosporin and tacrolimus nephrotoxicities. Pei Y, Richardson R, Greenwood C, et al: Extrarenal impact of cyclosporine A on potassium homeostasis in renal transplant recipients. Muto S, Tsuruoka S, Miyata Y, et al: Effect of trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole on Na and K+ transport properties within the rabbit cortical accumulating duct perfused in vitro. Alvestrand A, Wahren J, Smith D, et al: Insulin-mediated potassium uptake is normal in uremic and wholesome subjects. De Wolf A, Frenette L, Kang Y, et al: Insulin decreases the serum potassium focus during the anhepatic stage of liver transplantation. Mandelberg A, et al: Salbutamol metered-dose inhaler with spacer for hyperkalemia: how fast Blumberg A, Weidmann P, Ferrari P: Effect of extended bicarbonate administration on plasma potassium in terminal renal failure. Allon M, Shanklin N: Effect of bicarbonate administration on plasma potassium in dialysis sufferers: interactions with insulin and albuterol. Furuya R, Kumagai H, Sakao T, et al: Potassium-lowering impact of mineralocorticoid remedy in patients present process hemodialysis. Emmett M, et al: Effect of three laxatives and a cation trade resin on fecal sodium and potassium excretion. Gruy-Kapral C, et al: Effect of single dose resin-cathartic therapy on serum potassium focus in sufferers with end-stage renal disease. De Nicola L, et al: Effect of dialysate sodium concentration on interdialytic improve of potassium. Allon M: Medical and dialytic administration of hyperkalemia in hemodialysis sufferers. Wizemann V, Kramer W, Funke T, et al: Dialysis-induced cardiac arrhythmias: reality or fiction Importance of preexisting cardiac illness within the induction of arrhythmias during renal substitute remedy. Redaelli B, et al: Effect of a brand new mannequin of hemodialysis potassium removal on the management of ventricular arrhythmias. Santoro A, et al: Patients with advanced arrhythmias during and after haemodialysis endure from completely different regimens of potassium removal. Goutorbe P, et al: Intestinal necrosis related to orally administered calcium polystyrene sulfonate without sorbitol. Amaya F, Fukui M, Tsuruta H, et al: Simulation of potassium extraction by steady haemodiafiltration. Allon M, Shanklin N: Effect of albuterol therapy on subsequent dialytic potassium removing. This homeostatic system is modulated by dietary and environmental elements, including vitamins, hormones, medicines, and mobility. Disorders of extracellular calcium homeostasis could additionally be considered perturbations of this homeostatic system, either on the stage of the genes controlling this technique. Vitamin D and its metabolites improve intestinal absorption of calcium and cause bone resorption; therefore, extra vitamin D would induce hypercalcemia. Approximately one thousand mg of calcium is ingested per day, 200 mg absorbed by gut, primarily duodenum and 800 mg excreted through the intestine. Out of 10 g of calcium filtered by the kidney day by day, solely approximately 200 mg is excreted within the urine. The values for whole serum calcium focus in adults differ among scientific laboratories, depending on the methods of measurement, with the normal range being between eight. Plasma albumin is liable for 90% and globulins for 10% of protein-bound calcium. Free calcium is the physiologically energetic component of extracellular calcium with regard to cardiac myocyte contractility, neuromuscular activity, bone mineralization, and other calciumdependent processes. It is measured in most hospitals utilizing ion-selective electrodes; values in adults vary from four. The relationship between calcium ion and the concentration of protein within the serum is represented by a simple mass action expression: ([Ionized Ca 2+] � [protein]) [calcium proteinate] = K where [protein] equals the focus of serum proteins, primarily albumin. Because K is a constant, the numerator and denominator must change proportionately in any physiologic or pathologic state. A change in the concentration of whole serum calcium will happen after a change in the concentration of serum proteins or alterations of their binding properties and after a primary change within the concentration of calcium ion. A fall in the serum albumin stage reduces the protein and calcium proteinate levels proportionately, leading to a fall in the complete serum calcium level, with the free calcium ion concentration remaining regular. If plasma ranges of albumin are low, an adjustment of the measured serum levels of calcium ought to be made (commonly but erroneously referred to as a "correction"). For the routine medical interpretation of serum calcium needed for acceptable care of patients, a simple method for adjustment of total serum calcium concentration for changes in plasma albumin focus is utilized by clinicians. In conventional items: Adjusted total calcium (mg dL) = whole calcium (mg dL) + 0. This adjustment also can right for errors in measurement of complete calcium associated to hemoconcentration of a blood pattern due to the extended use of a tourniquet or due to hemodilution when blood is drawn in a supine place in hospitalized sufferers. However, in instances in which the globulin concentration in serum is extraordinarily excessive (>8. In addition, immunoglobulin G (IgG) myeloma proteins may have increased calcium-binding properties, and an elevation within the complete degree of serum calcium might occur, even with a reasonable increase in serum levels of globulins. Unfortunately, calcium status will be incorrectly predicted by this formulation in 20% to 30% of subjects,10 and the agreement between corrected and free calcium is only honest. Increase in bone resorption fee without enhance in bone formation price will trigger hypercalcemia. Increased intestinal calcium absorption might lead to the event of hypercalcemia, as in vitamin D overdose or milk-alkali syndrome. The clinical manifestations of hypercalcemia relate extra to the degree of hypercalcemia and rate of improve than the underlying cause. Hypercalcemia may be classified based mostly on the level of complete serum calcium15: Mild: [Ca] = 10. As many as 10% of sufferers with elevated ranges of serum calcium are detected by a routine screening test of blood chemistry and are thought of to have so-called asymptomatic hypercalcemia. However, even very delicate hypercalcemia may be of scientific significance inasmuch as some research have suggested an increased cardiovascular danger from mild but extended calcium level elevations. In sufferers with severe hypercalcemia, the most important symptoms usually have a tendency to be nausea, vomiting, constipation, polyuria, and psychological disturbances, ranging from headache and lethargy to coma. It is the underlying trigger of roughly 50% of hypercalcemic circumstances within the general population.
References - Nay PG, Elliott SM, Harrop-Griffiths AW: Postoperative pain. Expectation and experience after coronary artery bypass grafting, Anaesthesia 51:741, 1996.
- Lindros KO, Cai YA, Penttila KE. Role of ethanol-inducible cytochrome P-450 IIE1 in carbon tetrachloride-induced damage to centrilobular hepatocytes from ethanol-treated rats. Hepatology. 1990;12:1092-1097.
- Craggs JG, Price DD, Perlstein WM, et al. The dynamic mechanisms of placebo induced analgesia: evidence of sustained and transient regional involvement. Pain. 2008;139(3):660-669.
- Edinger JD. Controversial and Unresolved Issues in the Treatment of Insomnia. Panel discussion at the meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies, Chicago, Wilson GT, Vitousek KM, Loeb KL. Stepped care treatment for eating disorders. J Consult Clin Psychol 2000;68(4):564-72.
- Nguyen, J.N., Burchette, R. Outcome after anterior vaginal prolapse repair: A randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:801-808.
|

