|
Thomas S. Roukis, DPM, FACFAS - Chief of Limb Preservation Service, Vascular, and Endovascular
- Surgery Service
- Department of Surgery
- Madigan Army Medical Center
- Tacoma, Washington
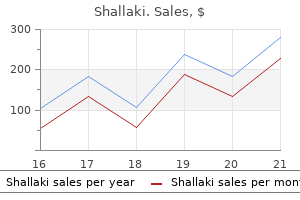
Shallaki dosages: 60 caps
Shallaki packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles

Buy shallaki 60caps low priceThe edge of one of these aggregates could characterize a spotlight of preexisting endosalpingiosis (arrowt muscle relaxant vs painkiller order shallaki 60 caps free shipping. In addition to the cribriforming glandular aggregates of serous borderline tumor, a portion of a cystically dilated focus of endosalpingiosis is present at the bottom. These eosinophilic cells resemble these seen in foci of microinvasion, from which they could be derived in some instances. When pure, this pattern could require immunohistochemistry to distinguish it from intranodat hyperplastic mesothelial cells; in this scenario, caf. This sample options nested aggregates of tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm. Most such tumors involve both ovaries, and the vast majority of patients have cnraovarian illness at the time of presentation. There is robust proof for a dualistic pathway of ovarian serous carcinogenesis, which helps a division of serous car� cinomas into two rather than three grades. As mentioned below, high� grade serous carcinomas are thought to arise via an indcpen� dent pathway and exhibit a different mutational sample. Low-grade serous carcinoma has a median size of eight em and generally has a grossly recognizable noninvasive papillary component. Low-grade serous carcinoma infiltrates the ovarian stroma at right, and is seen arising adjoining to the micropapillary variant of serous border1ine tumor. It should be noted that the distinguished nested and miaopapillary architectural patterns that are typical oflaw-grade serous carcinoma may also be seen in the high-grade �0nu,66 which is distinguished primarily by its nuclear features. A: Nests and micropapillary groups of neoplastic epithelial cells that are typically surrounded by clear spaces infiltrate the ovarian stoma. The sectioned surface demonstrates an admixture of stable tumor, geographic areas of necrosis. The precise origin of many ovarian high-grade serous carcinomas is probably intraepithe� lial carcinoma of the distal fallopian tube, though de novo improvement by way of transformation of ovarian epithelial inclusion cysts (which may also in the end be of tubal origin) is one other possibility. Grossly, high-grade serous carcinomas average about 8 em in diameter and are predominandy solid tumors with. Histologically, high-grade serous carcinoma often exhibits no less than focal areas of destructive stromal invasion and archi� tectwally frequendy consists ofsheets of tumor cells with some differentiation into slit-like glandular areas admixed with vari� ably distinguished papillae, stable nests, and tubules. In this context, huge substitute of the ovarian stroma by a neoplastic epithelial proliferation of this sort is considered enough evidence of suomal invasion. In an intraoperative setting, both areas ought to be sampled for frozen part evaluation. Mitotic activity is brisk, and atypical division 6gun:s are usu� ally readily identified. As indicated above, some serous carcinomas lack traditional damaging stromal invasion, but may be confidently diagnosed as absolutely malignant by advantage of confluent carcinomatous elements. This low-magnification view of the tumor in the preceding figure exhibits the nodule of grade 3 serous carcinoma (left adjacent to the serous adenofibroma right). Nate the presence of slit-like areas, which is attribute of tumors with serous differentiation. The problem of the way to deal with a serous tumor with borderline-like architecture and high-grade nuclear features is addressed within the above discussion. The presence of patches ofsquamous c:lifferentiation, tubular rather than slitlike glands, and related endometriosis additionally favor finish. In addition, highgrade serous carcinoma additionally virtually always exhibits a much greater mitotic fee than pricey cell carcinoma. The distinction between higb�stage ovarian serous carcinoma and primary peritoneal serous carcinoma with ovarian involvement is mentioned in Chapter 8. High-grade serous carcinoma without identifiable stromal invasion (serous borderline tumor with intraepithelial carcinoma). B: this high-magnification view demonstrates the presence of numerous high-grade nuclei with macronucleoli. This function, coupled with the ability of the ovaries involved by metastatic mucinous tumors to simulate primary ovarian neoplasia, makes sufficient sam� pling especially necessary in this group of tumors and creates distinctive challenges in the setting of an intraoperative consultation. As is true for ovarian carcinoma normally, intraabdominal unfold is typically manifested as nodules studding the peri� toncal floor, replac:emcnt of parts of the omentum, and involvement of regional lymph nodes. When visceral organs are concerned, it nearly at all times represents development of metastatic carcinoma that started on the serosal floor. That mentioned, paren� cbymal metastases to the liver and spleen do happen on rare events. Mucinous Tumors Mucinous ovarian tumors form cysts, glands, or papillae whose epithelial lining incorporates a major variety of cells with plentiful intracytoplasmic mucin exhibiting endocervical� like or gastrointestinal options. Tumors of gastrointestinal kind far outnumber those resembling endocervical cells. Revised Criteria for Benign, Borderline, and Malignant Categories the genesis for standards formulated within the Seventies to separate mucinous carcinomas from borderline tumors was the obser� vation that some mucinous ovarian tumors have the flexibility to metastasize without exhibiting a harmful sample ofstromal invasion within the ovary. High-grade serous carcinoma of ovarian origin with parenchymal metastasis to the spleen (sectioned surface. It was not spccified bow widespread the stratification and nuclear atypia needed to be so as to qualify for the latter sort of mucinous carcinoma. In addition, many pathologists ignored the requirement for severe nuclear atypia, which was underemphasized in the authentic report. Although the Hart and Norris methodology of categorizing muci� nous ovarian tumors captured the few legitimate mucinous car� cinomas with an expansile sort ofstromal invasion (see section on mucinous carcinoma), lots of the carcinomas diagnosed solely on the premise of stratification and atypia have since been proven to have a superb prognosis and are at present classi� fiod as mucinous borderline tumors with intrat:pithelial carci� noma. S Just as there has been justification for taking the decrease end of mucinous carcinomas and placing them within specialiu:d classes of borderline tumor, there are compelling causes for reinterpreting the lower end of mucinous borderline tumors as mucinous cystadenomas. Vutually the entire malignant habits that bas been beforehand attributed to occasional circumstances of ovar� ian mucinous borderline tumors of gastrointestinal sort is due to considered one of four situations: (a) misdiagnosis of a secondary tumor derived from a ruptured appendiceal mucinous cystadenoma (major source), (b) misdiagnosis of a deceptively benign�appear� ing metastatic tumor from an occult primary tumor originating in sites such as the pancreas, biliary tract, and endocervix (minor source), (c) an undersampled main ovarian tumor with occult foci of invasion (minor source), and (d) misdiagnosis of an endoccrvical�like mucinous borderline tumor that subsequently recurs in an aggressive &shion (rare source). In those stage I old�style borderline tumors that have been suboptimally sampled, lack tip matura� cion in a minimal of 10% of their epithelial area, or exhibit more than focal moderate nuclear atypia, I retain the "borderline" or "low malignant potential" terminology as a hedge towards the potential for something worse lurking inside unsampled areas of the tumor. Hendrickson and Kempson have championed the concept of "maturation of the ideas" as an indication of the benisn nature ofan ovarian mucinous proliferation when pres� ent throughout the tumor. The villous construction coursing horizontally through the center of the picture has an lively base with some nuclear stratification. The Imprecision of Histologic Subtyping Ovarian mucinous tumors have historically been categorized as exhibiting intestinal (more accwatcly gastrointestinal), endocervical, or combined endocervical�intestinal differcn� tiation. However, the excellence between endocervical�lih (miillcrian) and gastrointestinal differentiation in ovarian mucinous neoplasms is more subjective and less apparent than many standard tc:nbooks of gynecologic pathology would point out. When such tumors are subjected to histochemical, immunologic, and ultrastruc� tural anal)l3is, the vast majority arc found to exhibit gastric differentiation. The superliciallfoveolar muci� nous cells that line the gastric mucosa are commonly distended with mucin and goblet-shaped, but these arc not true goblet cells. One can respect 1he issue in definitively classifying the sort of epithelial differentiation based mostly solely upon routine histology. A: In this sample from the gastric pylorus, many of the superficial/foveolar lining cells are distended with mucin and simulate goblet cells. B: In 1his pattern from the duodenum, ttue goblet cells are present which stand out as scattered barrel-shaped cells wi1h clear cytoplasm. However, nearly all such tumors could be discovered to exhibit some degree of gastrointestinal differentiation if completely investigated.
Syndromes - Drooling
- Amount swallowed
- Whether it is cancer or not
- Stool test
- Provide supportive care to maximize independence
- Enlarging tonsils or tumors of the neck and throat
Buy shallaki 60 caps without a prescriptionAs mentioned elsewhere on this chapter muscle relaxant wiki order 60caps shallaki mastercard, endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial adenocarcinoma could involve foci of adenomyosis, and distinguishing this phenomenon from true myometrial invasion is clinically relevant. Differential Diagnosis the differential diagnosis of endometrial polyps consists of polypoid items of normal endometrium, fragments of basalis or decrease uterine phase, adenofibroma, and delicate fOrms of adenosarcoma. To avoid the mistake ofconfusing the presence of the nonnal finding of thick-walled vessels within the basalis. Distinction of endometrial polyps &om adenofibromas and adenosarcomas is discussed later in this chapter. B: Islands of endometrial glands and stroma of weakly proliferative type are surrounded and partially compressed by hypertrophic smooth muscle. A: An intravascular mixture of endometrial stroma lies beneath a spotlight of adenomyosis. A: Cross part via the wall of a formalin-fixed uterus, revealing adenomyosis inside the inner half of the myometrium. The inset highlights the tendency for the central zone of this type of adenomyosis to be more pale than the hypercellular peripheral zone. This process could possibly be confused with a nicely differentiated endometrioid adenocarcinoma with mvoinvasion. When confronted with this problem, features that favor ade� nomyosis embrace the atrophic appearance of the glands, the absence of a low�magnification infiltrative pattern, recogniz� able w. Submucosal polypoid adenomyoma consisting of islands of endometrial glands and stroma embedded within a prominent clean muscle stroma. Note the resemblance to adenosarcoma imparted by the elongated, compressed, and/or clefted glands surrounded by endometrial stroma. The inset highlights the abrupt transition between endometrial stroma and easy muscle. Although some investigators cite a distinction between the my<>metrial muscle of adenomyosis and the leiomyomatous muscle of adenomyomas, the hypertrophic, intersecting fascicles of myometrial clean muscle that encompass foci of adenomyosis are often indistinguishable from those seen in leiomyomas. This cross part via a formalinfixed uterus reveals a 9 em pretty nicely circumscribed adenomyoma with distinguished trabeculations and scattered cysts. Note that a superficial biopsy of this lesion would doubtless yield only proliferative or disordered proliferative endometrium. Compression of endometrial stroma and elongated endometrial glands by myomatous tissue within a polypoid adenomyoma could outcome within the forp marion of leafplike, defted glands sunounded by cuffs of endometrial stroma, resulting in simulation ofan adenofibroma or adenosarcoma. Moreover, the low�grade sarcomatous stroma of adenosarcoma usually exhib� its hyperceUular periglandular cuffs that blend with much less eel� lular sarcomatous stroma away from the glands, whereas the periglandular endometrial stroma of polypoid adenomyomas is sharply demarcated from its smooth muscle part. A: High-magnification view of a formalin-fixed specimen with outstanding endometriosis of the uterine serosa. B: the corresponding histologic part shows extensive involvement of the uterine serosa in a pattern that simulates disordered proliferative endometrium with stromal hemorrhage. The primary differential diagnostic consideration ofendometriosis on this location is endosalpingio� sis, which is normally an incidental microscopic finding that fea. Numerous hemorrhagic adhesions related to endometriosis are current on the posterior uterine serosa and ovaries of this Iightly fixed specimen. Hysterectomy spetimen from a patient with uterine prolapse with putting cervical elongation. In failed endometrial ablations, endomyometrial tissue sam� ples or hysterectomy specimens may be submitted for histologic evaluation. The endometrium may be entirdy absent patches of basalis might survive beneath coagulated tissue, relatively nor� mal endometrium could also be present or a skinny layer of glandless endometrium lined by surface epitbdium may be found. B: Postablation tissue reaction in chronic reparative phase following thermal ablation of the endometrium. After these stains have been confinned as unfavorable, the pathology report ought to mention the un. In some instances, ydlow tissue fragments according to fat may be grossly identified inside the specimen, which assist to exclude the potential of tissue contamination from another case. In addition to adipose tissue, different items of tissue originating from the bowel, bladder, or different abdominopelvic websites may be inadvertently sampled by way of a perfOrated uterus and found admixed with endometrial fragments. Upon microscopic confirmation of the presence of any of the aforementioned extr:lutcrine tissue, the clinician should be notified that the histologic findings are greatest explained by the presence of a uterine perforation. The pathology n:port ought to docwnent the details of this notification together with the kind and amount ofextrauterine tissue. Foreign physique large cell response to pigmented materials, 2 months following hysteroscopic resection of a submucosal leiomyoma. Idiopathic Granulomatous Inflammation of the Uterine Stroma On rare events, the myometriwn or cervical stroma contains nonnecrot:izing granulomas that appear to be wue. As seen in additional typical sites such as the urinary bladder, malakoplakia options sbeeu of histi. Malakoplakia is mentioned in additional element in Chapter 2, since the vagina is the most typical web site ofinvolvement within the fimlale genital tract. A: Golden yellow, refractile, crystalline deposits of hematoidin in a case of xan1hogranulomatous endometritis from a patient with a historical past of hematometra. A: the curettings contain a full-thickness fragment of small bowel (cireledl lurking amongst fragments of benign endometrial tissue. Less typically, true osseous metaplasia of endometrial stromal cells may happen as a response to inflammation or trauma. In some instances, endometrial glands are stripped from their associated stroma and aggregated in a compacted method that may simulate endometrial hyperplasia. The key function that enables for recognition of those dissociation arti~ facts is the truth that a minimal of a few of the traumatized glands arc lacking or de6cient in stromal assist, and sometimes appear to be free floating. Postoperative spindle cell nodule in a patient 2 months after endometrial curettage. The lesion resembles infiamed granulation tissue and nodular fasciitis, and sometimes has a mitotically lively spindle cell element of probable fibroblastic origin. A: Sheets of histiocytes with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm are present some of which contain MichaelisGutmann bodies. B: this high-magnification view highlights the presence of a Michaelis-Gutmann physique with a �bull~-eye� look a~rowl. Fragments of devitalized bone are admixed with items of proliferative endometrium. A: Cross section via the uterine wall, revealing numerous abnormal vessels positioned predominantly throughout the outer half of the myometrium. In these instances, an apparent stable architec� twa1 pattern is created by collapse and epithelial sloughing of the architecturally complicated glandular buildings which are supponed by minim. In addition to the presence of epithelial sloughing, recognition of this artifact is Endometrial Surface Epithelial Coiling Artifact Scant suips of benign floor endomeaial epithelium may be all chat are obtained in some endomeaial samples. When such strips fOrm coiled aggregates, the resulting histologic sections can mimic endometrial hyperplasia. If the coiled epithelial strips originate from contaminating superficial endocervical components, a mucinous lesion could additionally be simulated (see section on mucinous metaplastic hyperplasia).
Buy cheap shallaki 60caps on-lineThe glands of endometrial polyps have an altered architecture characterized by variation in size muscle relaxant with alcohol shallaki 60 caps line, shape, extent of crowding, and diploma ofcystic dilatation, and are lined by cells that vary from atrophic: to pseudostrati6cd and mitotic:ally lively. The stroma is often a minimum of partially hypocellular and fibrotic:, which is typical of polyps from postmenopausal women. A: Cross section 1hrough a formalin-fixad, 7-cm sessile polypoid mass (myometrium is at left). B: Histologic examination of this well-sampled lesion reveals an endometrial polyp composed of dilated glands set within a fibrous stroma. Polyps originating near the intcmal os may exhibit hybrid features of endocervical and endometrial polyps. This polyp has predominantly endometrial-type stroma and exhibits the characteristic of elongated endometrial glands oriented parallel to the floor epithelium. Endometrioid adenocarcinoma replacing the superficial portion of an endometrial polyp inset and much proper of image). Possible explanations of this phenomenon are a) sampling of polypoid murosa quite than a real endometrial polyp, b) extreme fragmentation of the polyp, rendering it unrecognizable, and (c) super6cial sampling of nondiagnostic portions of a polyp. In this circumstance, the pathologist ought to point out that histologic options of a polyp arc not evident, and that dinical com:lation is recommended to determine if any of the aforcmentioned o:planarions apply. B: the endometrial stroma of the lower uterine phase is less cellular and extra fibrotic than that of proliferative endometrium from the uterine body or fundus. In premenopausal patients, bona fide adenomyosis is often accompanied by clean muscle hypertrophy, which is typically grossly recognizable as thickened, trabeculated areas of the myometrium. Not uncommonly, these trabeculated areas are punctuated by small cysts that include fluid associated to recent (rcd) or distant (brown) accumularion of blood products. Although super6cial adenomyosis detected solely on the premise of histologic examination is often a fuca1 and incidental finding, grossly detectable adenomyotic foci are more likely to be related to the nonspecific signs of menorrhagia or dysmenorrhea. A potential pitfall associan:d with extensive adenomyosis is the ocasional discovering of intravascular endometrial tissue, which may include an admixture of glands and stroma or be composed solely of stromal cells. B: Corresponding consultant histologic part reveals amorphous calcified material in a starlike configuration. Artifactually crowded aggregates of proliferative endometrial glands have been dissociated from their stroma, making a free-floating appearance. In 1his less traumatized instance, clusters of collapsed proliferative endometrial glands simulate islands of endometrial hyperplasia. An architectural pattern similar to this may be most unusual for true hyperplasia, which is often ei1her unifocal or diffuse. The collapse of 1he neoplastic glands, coupled wi1h the sloughing of 1heir epithelial lining, leads to a solid-appearing lesion that can be misinterpreted as a grade 3 endometrioid carcinoma. Note 1he partial preservation of the gland architecture and the lowgrade nuclear options. Wwed by the partially preserved outlines of the glands, the similar old low-grade nuclear features of the neoplastic cd1s (which would he uncommon for ~ with nonsquamous solid c:iiftm. This artifact is rather more likdy to be fOund in hysterectomy specimens than in endometrial samples. Although this phenomenon bas bei:n acknowledged for many years,38 it has only recently been systematically studied and reported within the literature. The section of 1his winding aggregate of endometrial floor epi1helium ends in a crowded appearance that simulates endometrial hyperplasia. Sectioning of this late proliferative gland with papillary infoldings has resulted in an artifactual epithelial bridge (arrowt. When this phenomenon occurs repeatedly inside a hyperplastic endometrial proliferation, it can be misinterpreted as a cribriform sample. Telescoping Artifact this widespread artifact, which ends from cross-sectioning of intussuscepted glands recoiling ttom the trauma of the sampling process, creates the impression of glands throughout the lumens of different glands. It tends tD happen in straight glands, which can be of both proliferative or secretory sort. This artifact ought to be expected every time prominent papilp lary infoldings are current that approach the scale of the luminal diameter of the glands. Tangential Sectioning Tangential sectioning of randomly oriented fragments ofendometrium can create the looks of elevated architectural complexity or lead to buildings that simulate cysts or polyps. Superficial sections parallel Bridging Artifact Sectioning of coiled glands with papillary infoldings can create the looks of epithelial bridges. Tangential sectioning has resulted within the misunderstanding of mark:ed nuclear stratification within the gland at proper. Caution should be exercised when diagnosing angiolymphatic invasion in low-risk endometrial carcinomas that have been eliminated with this system, since intravascular tumor in most of these cases represents a. This apparently cystic house truly represents a dip within the endometrial lining that has been sectioned parallel to and simply benea1h 1he floor. Although not readily obvious at this magnification, many of the cells lining the floor epithelium (the pseudocyst have apical blebs or cilia, whereas the neighboring glands are of the traditional proliferative type. As discussed in the part on the differential analysis of endometrial hyperplasia. These lesions might happen in polyps or be seen in affiliation with odd, hyper~ plastic, or malignant endometrial proliferations. In other situ~ ations, n:energetic nuclear atypia can lead to a resemblance to a premalignant process. Yet one other subset of these lesions fea~ t:un:s metaplastic glandular proliferations with various dcgn:c:s of an:hitcc:tural complexity, some of which could be troublesome to distinguish &om carcinoma. This polypoid fragment of normal endometrium, whose stroma is dominated by biopsy-related hemorrhage, is 1he product of sectioning parallel to 1he endometrial floor close to the tip of an elevated portion of endometrium. Morular/Squamous Metaplasia the most typical form of endometrial squamous metapla� sia is morular metaplasia. B: Less frequent sample with morular metaplastic cells blending with hyperplastic glands and occupying the imerglandular spaces. Other than the potential for these findings to be misinterpreted as proof of carcinoma. More mature forms of squamous metaplasia with kerati� nization, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, and intercellular bridges also happen within the endometrium. Note the formation of a peripheral rim of punched-out spaces where glandular and morular epithelium converge. Four of the nearly back-to-back morules exhibit central necrosis, certainly one of which is shown at greater magnification within the inset. Note the intermingled neutrophils, some hobnailing, and the associated rounded aggregates of endometrial stroma with features of breakdown. Granulomas an: generally confused with squamous morules, however the former are distinguished by their association with at least occasional multinucleated large cells and a surp rounding lymphocytic in6ltrate of variable prominence. Moreover, morules are sometimes found in the setting of endometrial hyperplasia or wellpdifferentiated adenocarcinoma, whereas granulomatous irritation is rm:ly associated with a hyperp plastic/malignant endometrial glandular lesion apart from kerp atin�induced granulomas in adenocarcinomas with squamous diffi:rentiation.
Discount shallaki 60caps overnight deliveryRecommendations concerning optimum submission of tissue sections when evaluating uteri with myoinvasive endometrial carcinoma are given within the section on myometrial invasion spasms that cause shortness of breath order shallaki 60 caps overnight delivery. Submit one full-thickness part of abnormal endometrium with related myometrium, and then submit the remainder of the endometrium with inside myometrium as 2 to 3 sections per cassette (label the anterior and posterior halves separately). The pathologist must also be aware that uterine weight impacts the gynecologist when it comes to procedure coding and reimbursement for vaginal hysterectomies and myomectomies; reimbursement is significantly higher for these procedures when the specimen weighs >250 g. Properly sectioned and fixed uteri which have been obtained by early afternoon could be processed within the late afternoon without compromising section high quality. Tbe American Fertility Society c:lassilic:ations of adnaal adhesions, distal tubal ocdusion, tubal ocdusion secondary to 2. A aitical evaluation of the accuracy, reproducibility, and scientific utility of hi11tologic endometrial relationship in fertile ladies. A morphologic corrda� tion of ova, endometrium, and corpora lutca during early being pregnant. Nontrophoblastic pathology of the female genital tract and peritoneum related to being pregnant. Normal and irregular mito� ses within the atypical endometrial chan~ astociatcd with chorionic tissue dfcct. Subinvolution of the placental website u an anawmi~ cause of postpartum uterine bleeding: a evaluation. Hi11tologi~ dating of the endometrium: aa:uracy, reproducibility, and sensible wluc. Taman� fen remedy fur breast most cancers and risk of endometrial cancer: a case-control examine. Mullerian adenosarcoma of the uterine ~orpus asiOciated with tamoxifcn remedy: a n:port of six circumstances and a review of wnoxifi:n-u! The morphology, biology, and pathology of int~:rmcdiate tropho� blast: a glance back to the pretcnt. Histological study of decidual spital arteries and the presence of maternal erythrocytes in the intervil-lous space through the first trimester of regular human pn:gnancy. A diagnostically useful histopathologic characteristic of endometrial polyp: the lengthy of endometrial glan<h arranged parallel to floor epithelium. Endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma in endometrial polyps: clinicopathologic and follow-up findings. Vascular involvement in adenomyosis: report of a giant sequence of a standard phenomenon with observations on the pathogenesis of adenomyosis. Endometrial stromal sarcomas of the uterus with in depth endometrioid glandular differentiation: a report of three circumstances that caused problems in differential prognosis. Endometrial stromal sarcomas with extensive endometrioid glandular differentiation: report of a series with emphasis on the potential for misdiagnosis and dialogue of the differential diagnoais. Uterine adenomyomas c:xcluding atypical polypoid adenomyomas and adenomyomas of endocervical type: a clinicopathologic study of 30 circumstances of an underemphasized lesion that will cause diagnostic problems with briefconsideration of adenomyomas of other feminine genital tract sites. Uterine adenomyoma: a clinicopathologic evaluation of 26 cases and a review of the literature. Postoperative granulomas of the endometrium: histological features afier endometrial ablation. Post-hyneroscopic ablation reaction: a histopathologic research of the effects of dcctrosurgical ablation. Necrotizing granulomas of peritoneum following diathermy ablation of endometriosis. Idiopathic uterine granulomas: report of a sequence with morphological similarities to idiopathic ovarian cortical granulomas. Pscudolipomatosis in hyneroscopically resected tissues from the gynecologic tract: pathologic description and frequency. Vascular "pseudo invasion" in laparoscopic hysterectomy specimens: a diagnostic pitfall. Vascular pscudoinvasion in laparoscopic hysterectomy specimens for endometrial carcinoma: a grossing artifact Endometrial epithelial metaplasias: proliferations frcquendy misdiagnosed as adenocarcinoma. Endometrial eosinophilic syncytial change associated to breakdown: immunohistochemical proof suggests a regressive process. Surface epithclial changes in endometrial adenocarcinoma: diagnoatic pitfalls in curettage specimens. Proliferative mucinous lesions of the endometrium: evaluation of present standards for diagnosing carcinoma in biopsies and curettings. Histologic alterations in endometrial hyperplasia and wdl-differentiatcd carcinoma treated with progestins. Prediction of endometrial carcinoma by subjective endometrial intracpithelial neoplasia diagnosis. Risk of subsequent endometrial carcinoma associated with endometrial intracpithclial neoplasia classification of endometrial biopsies. Low-grade endometrial adenocarcinoma: a diagnostic algorithm for distinguishing atypical endometrial hyperplasia and other benign (and malignant) mimics. Reproducibility of the diagnoais of endometrial hyperplasia, atypical hyperplasia, and wdl-diffcrcntiated carcinoma. RcproducibUity of the analysis of atypical endometrial hyperplasia: a Gynecologic Oncology Group research. Problems with the present diagnostic approach to com pia atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Diagnosing endometrial hyperpwia: why is it so troublesome tn agrec1 Am j Surg Pt#ho� 2008;32:691-698. The molecular genctia and morphometry-hued endometrial intraepithclial neoplasia classification Item predicts disease progression in endometrial hyperplasia extra accurately than the 1994 World Health Organization das. Morphologic and immunophcnotypic characterization of foam cells in endometrial lesions. Absolute threat of endometrial carcinoma throughout 20-ycar follow-up among girls with endometrial byperpwia. Simple and complicated hyperplastic papillary proliferations of the endometrium: a clinicopathologic examine of nine circumstances of apparently localized papillary lesions with fibrowscular stromal cores and epithdial mctapluia. Adenocarcinoma of the endomeuium: evaluation of 256 cues with carcinoma limited tn the uterine corpus. Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma: a pathologic evaluation of 827 consecutive instances. Evaluation of criteria for dininguishing atypical endomeuial hyperpluia from wdl-differentiatcd carcinoma. Toward the dcvdopment of morphologic standards for wdl-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the endomeuium.
Buy generic shallaki 60capsIf the patient is sufficiently forty four relaxed muscle relaxant carisoprodol purchase 60caps shallaki, this downward stress on the perineum causes the introitus to open, permitting for simpler insertion of the speculum. The speculum is initially inserted in a horizontal plane with the width of the blades indirect to the vertical axis of the introitus. The speculum is then directed posteriorly at an roughly 45� angle from horizontal; the angle is adjusted because the speculum is inserted, in order that the speculum slides into the vagina with minimal resistance. As the speculum is inserted, a slight steady downward stress is exerted so that distension of the perineum is used to create space into which the speculum could advance. Taking advantage of the distensibility of the perineum and vagina posterior to the introitus is a vital concept for the environment friendly and comfortable manipulation of the speculum examination (and later for the bimanual and rectovaginal examination). Pressure superiorly causes ache in the delicate area of the urethra and clitoris and ought to be deliberately prevented. With slight tilting of the speculum, the cervix slides into view between the blades of the speculum. Failure to discover the cervix most commonly results from not having the speculum inserted far sufficient, often as a end result of concern of causing affected person discomfort. When the speculum is locked into position, it usually stays in place with out being held. For most patients, the speculum is opened sufficiently by use of the higher thumbscrew. This could also be obtained by gently increasing the vertical distance between the speculum blades by means of the screw on the handle of the speculum. With the speculum in place, the cervix and the deep lateral vaginal vault could also be inspected and specimens obtained of any discharge or lesion. Before obtaining samples for the Pap check, the patient should be advised that she may feel a slight "scraping" sensation but no pain. Specimens are collected to fully consider the transformation zone, where cervical forty five intraepithelial neoplasia is more likely to be encountered. Specimens are obtained from the exocervix and endocervix and either plated on slides, which are immediately mounted with a preservative spray, or placed in a liquid assortment medium. After telling the affected person that the speculum is to be removed, the blades of the speculum are opened barely by putting stress on the thumb hinge, and the thumbscrew is totally loosened. Opening the speculum blades slightly earlier than beginning to withdraw the speculum avoids pinching the cervix between the blades. The blades of the speculum are naturally introduced together by vaginal wall stress. As the tip of the speculum blades approaches the introitus, there must be no stress on the thumb hinge, as otherwise the anterior blade can flip up, hitting the sensitive vaginal, urethral, and clitoral tissues. Bimanual Examination the bimanual examination uses both a "vaginal" hand and an "abdominal" hand to entrap and palpate the pelvic organs. The bimanual examination begins by exerting gentle strain on the abdomen roughly halfway between the umbilicus and the pubic hair line with the belly hand, while inserting the index and center fingers of the forty six vaginal hand into the vagina to roughly 2 in. The affected person is requested to feel the muscles being pushed on and to chill out them as a lot as potential. Then each the index and middle fingers are advanced into the vagina until they rest on the restrict of the vaginal vault in the posterior fornix behind and beneath the cervix. Occasionally, only the index finger of the vaginal hand can be comfortably inserted. During the bimanual examination, the pelvic structures are "caught" and palpated between the stomach and vaginal palms. Whether to use the dominant hand as the stomach or vaginal hand is a query of private choice. A frequent error on this a part of the pelvic examination is failure to make effective use of the stomach hand. Pressure should be utilized with the flat a half of the fingers, not the fingertips, starting halfway between the umbilicus and the hairline, transferring downward in conjunction with upward movements of the vaginal hand. The bimanual examination continues with the circumferential examination of the cervix for its dimension, form, position, mobility, and the presence or absence of tenderness or mass lesions. Bimanual examination of the uterus is accomplished by lifting the uterus up toward the abdominal fingers so that it may be palpated between the vaginal and abdominal palms. The uterus is evaluated for its measurement, shape, consistency, configuration, and mobility; for lots or tenderness; and for position. The uterus could tilt on its lengthy axis (from cervix to fundus, version) yielding three positions (anteverted, midposition, and retroverted). It may tilt on a shorter axis (from just above or at the space of the lower uterine section, flexion) yielding two positions (anteflexed and retroflexed). A posterior cervix is often associated with an anteverted or midposition uterus, whereas an anterior cervix is commonly associated with a retroverted uterus. The bimanual examination technique varies considerably with the place of the uterus. Examination of the anterior and midposition uterus is facilitated with the vaginal fingers lateral and deep to the cervix within the posterior fornix. The uterus is gently lifted upward to the abdominal fingers and a delicate side-to-side "looking" movement of the vaginal fingers is mixed with regular pressure and palpation by the belly hand to determine the characteristics of the uterus. In some circumstances, the vaginal fingers may be slowly pushed beneath or on the degree of the uterine fundus, after which gentle stress exerted inward and upward causes the uterus to antevert, or a minimum of to transfer "upward," somewhat facilitating palpation. Bimanual examination of the adnexa to assess the ovaries, fallopian forty eight tubes, and help structures begins by inserting the vaginal fingers to the aspect of the cervix, deep in the lateral fornix. The abdominal hand is moved to the same aspect, just inside the flare of the sacral arch and above the pubic hairline. Pressure is then utilized downward and toward the symphysis with the stomach hand, on the same time lifting upward with the vaginal fingers. The identical movements of the fingers of each arms used to assess the uterus are used to assess the adnexal constructions, which are introduced between the fingers by these maneuvers to evaluate their measurement, form, consistency, configuration, mobility, and tenderness as well as to palpate for lots. Special care have to be taken when analyzing the ovaries, which are delicate even in the absence of pathology. The ovaries are palpable in normal menstrual women roughly half of the time, whereas palpation of ovaries in postmenopausal women is much less common. Rectovaginal Examination When indicated, a rectovaginal examination varieties part of the entire pelvic examination on preliminary and annual examination in addition to at interval examinations whenever clinically indicated. The rectovaginal examination is begun by changing the glove on the vaginal hand and utilizing a liberal provide of lubricant. The examination could also be comfortably performed if the pure inclination of the rectal canal is followed: upward at a 45� angle for approximately 1 to 2 cm, then downward. This is completed by positioning the fingers of the vaginal hand as for the bimanual examination, besides that the index finger is also flexed. The center finger is then gently inserted via the rectal opening and inserted to the "bend" the place the angle turns downward. The index (vaginal) finger is inserted into the vagina, and both fingers are inserted until the vaginal finger rests in the posterior fornix beneath the cervix, and the rectal finger rests so far as it could go into the rectal canal. Palpation of the pelvic constructions is then accomplished, as in their vaginal palpation.
Myrica heterophylla (Bayberry). Shallaki. - Colds, diarrhea, fevers, and nausea.
- How does Bayberry work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Bayberry?
- Dosing considerations for Bayberry.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96199
Purchase cheap shallaki on-lineThis ought to be considered when any treatment is prescribed by a doctor or when any over-the-counter drugs are contemplated by the patient muscle relaxant otc cheap shallaki american express. Specific medications that may contraindicate breastfeeding include lithium carbonate, tetracycline, bromocriptine, methotrexate, and any radioactive substance. All substances of misuse are included as well, such as amphetamine, cocaine, heroin, marijuana, and phencyclidine. Prolactin Release At the time of delivery, the lower in estrogen ranges and other placental hormones is a important component in eradicating the inhibition of the motion of prolactin. Also, suckling by the toddler stimulates launch of oxytocin from the neurohypophysis. The elevated levels of oxytocin in the blood result in contraction of the myoepithelial cells and emptying of the alveolar lumen of the breast. The oxytocin additionally will increase uterine contractions, thereby accelerating involution of the postpartum uterus. Prolactin release is also stimulated by suckling, with resultant secretion of fatty acids, lactose, and casein. Colostrum is produced in the first 5 days postpartum and is slowly replaced by maternal milk. Colostrum accommodates more minerals and protein but less fat and sugar than maternal milk, though it does comprise giant fats globules, the so-called colostrum corpuscles, which are in all probability epithelial cells which have undergone fatty degeneration. Colostrum also contains immunoglobulin A, which may offer the new child some safety from enteric pathogens. Subsequently, on approximately the third to sixth day postpartum, milk is produced. Thus, colostrum is steadily changed by milk around the fifth postpartum day, providing some vitamin as well as helping the new child with immunologic response to enteric pathogens. The minimal caloric requirement for sufficient milk manufacturing in a girl of average dimension is 1,800 kcal/day. In basic, 312 an additional 500 kcal of energy day by day is really helpful all through lactation. Vitamin K could additionally be administered to the toddler to stop hemorrhagic disease of the new child (see Chapter 10). Lactational Amenorrhea the natural contraceptive impact of exclusive breastfeeding (elevated prolactin levels and associated anovulation) could additionally be used to benefit in what is called the lactational amenorrhea technique. The nipples should be washed with water and exposed to air for 15 to 20 minutes after each feeding. A water-based cream similar to lanolin or A and D ointment could additionally be applied if the nipples are tender. Temporary cessation of breastfeeding, manual expression of milk, and use of a nipple defend will assist in recovery. Clinicians ought to display ladies for despair and anxiety signs using a standardized, validated software a minimal of one through the perinatal period. Women with present anxiousness or melancholy, a history of mood issues or threat factors for perinatal temper disorders as outlined in Box eleven. Anxiety and insomnia are very common symptom of perinatal temper issues and it could be useful to inquire about intrusive, frightening ideas and about inability to sleep even when the infant is resting. The 10 query Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale takes lower than 5 minutes to full. In addition, it contains anxiousness signs, however excludes constitutional symptoms which are frequent in being pregnant which will in any other case scale back its specificity. The clinician should include follow-up and remedy where indicated along with applicable referrals. The affected person should be provided directions for pelvic muscle exercise/kegel, milk expression, weight retention, start spacing, train, vitamin as indicated. Efforts ought to be made to facilitate the location of lengthy performing reversible contraception in patients who expressed an interest whereas in hospital. Patients should be reminded about being pregnant problems that may affect their future health or complicate subsequent pregnancies. Follow-up glucose screening and cardiometabolic dangers must be mentioned with sufferers with gestational diabetes or hypertension. You clarify that this will likely persist so long as a few weeks and is just an extended expression of the top of a standard delivery process. She is 315 moderately reassured but more so when the lochia alba ceases in the following week. Soon after her supply, and before the placental expulsion happens, sudden, profuse hemorrhage is famous. Sequelae embrace grownup respiratory misery syndrome, coagulopathy, shock, loss of fertility, and pituitary necrosis (Sheehan syndrome). The estimation of blood loss is subjective, introducing wide variance and inaccuracy. Additionally, the identical absolute volume loss for a affected person weighing 50 317 kg could have vastly totally different results than it might for someone weighing seventy five kg or for a affected person with triplets versus a singleton. Criteria in use embrace a 10% drop in hematocrit, need for transfusion, and signs and signs along the spectrum of physiologic results of blood loss, described under. Maternal hemodynamic responses to blood loss also needs to be monitored, insofar as these responses are indicators of well-being, volume deficit, and prognosis. The loss of 10% (500 mL for a mean patient with a singleton pregnancy) of blood volume may be tolerated with no indicators or signs. As blood loss approaches 15% to 20%, the first indicators of intravascular depletion manifest, together with tachycardia, tachypnea, and delayed capillary refill, followed by orthostatic changes and narrowed pulse pressure (due to elevated diastolic strain secondary to vasoconstriction with maintenance of systolic pressure). Beyond roughly 30% volume loss, breathing and heart price further increase, and overt hypotension develops. Finally, with profound blood loss above 40% to 50%, oliguria, shock, coma, and demise might occur. Retained placenta, genital tract trauma, lacerations, and coagulation disorders are different causes. If this discovering is confirmed, oxytocin infusion must be elevated and both methylergonovine maleate or prostaglandins administered if extreme bleeding continues. Such measures embody large-bore intravenous access; rapid crystalloid infusions; kind, 321 cross-match, and administration of blood or blood elements as wanted; periodic assessment of hematocrit and coagulation profile; and monitoring of urinary output. There has been a shift in philosophy concerning transfusion of blood products in the setting of lively hemorrhage, with larger willingness to intervene earlier and prevent coagulopathy somewhat than to delay therapy till coagulopathy is recognized. Depending on the clinical scenario, the use of laboratory measurements to information transfusion of plasma, cryoprecipitate, and platelets could also be reasonable. This muscular contraction, somewhat than coagulation, prevents extreme bleeding from the placental implantation site. The clinical analysis of atony is based largely on the tone of the uterine muscle on palpation.
Buy 60caps shallaki with mastercardDuring being pregnant muscle relaxant drug test purchase generic shallaki pills, the uterus undergoes an unlimited increase in weight from the 70-g nonpregnant size to roughly 1,100 g at term, primarily via hypertrophy of present myometrial cells. Similarly, the uterine cavity enlarges to a quantity of as a lot as as much as 5 L, compared with less than 10 mL within the nongravid state. Breasts the breasts increase in size during being pregnant, rapidly in the first 8 weeks 133 and steadily thereafter. The nipples become bigger and extra cell and the areola larger and more deeply pigmented, with enlargement of the montgomery glands. Some patients could complain of breast or nipple tenderness and a tingling sensation. Estrogen stimulation also results in ductal growth, with alveolar hypertrophy being a result of progesterone stimulation. During the latter portion of being pregnant, a thick, yellow fluid can be expressed from the nipples. This visual change is primarily attributable to elevated thickness of the cornea related to fluid retention and decreased intraocular strain. These modifications manifest within the first trimester and regress inside the first 6 to 8 weeks postpartum. Women may be reassured that changes in vision during normal pregnancy are often transient, not requiring glasses after delivery. It is estimated that as a lot as 70% of the glucose transferred from the mother is utilized by the placenta. Other solutes which may be transferred from the mom to the fetus rely upon the concentration gradient as well as on their degree of ionization, measurement, and lipid solubility. There is energetic transport of amino acids, leading to ranges which are higher in the fetus than within the mother. Free fatty acids have very restricted placental switch, leading to levels that are lower within the fetus than in the mom. These hormones are essential for the upkeep of pregnancy, for labor and supply, and for lactation. Fetal Circulation Oxygenation of fetal blood happens in the placenta somewhat than within the fetal lungs. This oxygenated blood (80% saturated) is carried from the placenta to the fetus through the umbilical vein, which enters the portal system of the fetus and branches off to the left lobe of the liver. Another branch joins the blood move from the portal vein to the right lobe of the liver. The blood circulate from the left hepatic vein is blended with the blood within the inferior vena cava and is directedtoward the foramen ovale. Less-oxygenated blood in the right hepatic vein enters the inferior vena cava and then flows by way of the tricuspid valve into the proper ventricle. Blood from the superior vena cava additionally preferentially flows by way of the tricuspid valve to the proper ventricle. Blood from the pulmonary artery primarily flows by way of the ductus arteriosus into the aorta. Note the adjustments in operate of the ductus venosus, foramen ovale, and ductus arteriosus within the transition from intrauterine to extrauterine existence. Red, oxygenated blood; pink/purple, partially oxygenated blood; blue, deoxygenated blood. The fetal ventricles work in a parallel circuit, with blood circulate from the best and left unequally distributed to the pulmonary and systemic vascular beds. Within a fetal heart fee range of a hundred and twenty to one hundred eighty bpm, the fetal cardiac output remains relatively constant. Overall, less than 10% of proper 137 ventricular cardiac output goes to the fetal lungs. The the rest of the right ventricular cardiac output is shunted via the ductus arteriosus to the descending aorta. Output from the left ventricle into the proximal aorta provides highly saturated blood (65% saturated) to the mind and upper body. Once joined by the ductus arteriosus, the descending aorta then supplies blood to the lower portion of the fetal body, with a significant portion of this blood being delivered to the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. The umbilical blood move represents about 40% of the combined output of each fetal ventricles. In the last half of being pregnant, this circulate is proportional to fetal growth (approximately 300 mL/mg/minute), in order that umbilical blood flow is comparatively constant, normalized to fetal weight. This relationship allows measurement of fetal blood move to be used as an oblique measure of fetal progress and fetal well-being. Hemoglobin and Oxygenation Fetal Hgb, like grownup Hgb, is a tetramer composed of two copies of two different peptide chains. But not like adult hemoglobin A (HgbA), which is composed of - and -chains, fetal Hgb consists of a sequence of different pairings of peptide chains that change as embryonic and fetal improvement progresses. In late fetal life, hemoglobin F (HgbF), composed of two -chains and two -chains, predominates. The key physiologic distinction between adult HgbA and fetal HgbF is that, at any given oxygen tension, HgbF has larger oxygen affinity and oxygen saturation than HgbA. Hence, a good gradient is created, facilitating diffusion of O2 from the maternal to the fetal circulation. Therefore, although the partial strain of oxygen in fetal arterial blood is simply 20 to 25 mm Hg, the fetus is adequately oxygenated. The oxygen saturation curve for fetal hemoglobin (blue) seems left-shifted compared with adult hemoglobin (red), as a end result of fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen. Kidney the fetal kidney becomes functional in the second trimester, producing dilute, hypotonic urine. The price of fetal urine production varies with fetal measurement and ranges from 400 to 1,200 mL/day. Fetal urine turns into the primary supply of the amniotic fluid by the middle of the second trimester. The fetal liver capability for glycogen synthesis and bilirubin conjugation increases with gestational age. As a consequence, during fetal life, bilirubin is primarily eliminated through the 139 placenta. Hepatic production of coagulation factors is poor and may be attenuated in new child life because of vitamin K deficiency. Routine neonatal administration of vitamin K prevents new child hemorrhagic disorders. The mother is the first supply of the thyroid hormone for the fetus previous to 24 to 28 weeks of gestation. Gonads the primordial germ cells migrate in the course of the eighth week of gestation from the endoderm of the yolk sac to the genital ridge. This testicular differentiation appears to rely upon the presence of the H�Y antigen and the Y chromosome. If the Y chromosome is absent, however, an ovary develops from the undifferentiated gonad. The development of different genital organs is decided by the presence or absence of specific hormones and is impartial of gonadal differentiation.
Cheap shallaki 60 caps overnight deliveryIn the region of the vulva spasms jaw muscles buy shallaki 60caps, the most typical websites of invol~ent are the mons pubis and labia majora, and these lesions appear as thick, leathery, scaly skin with exaggeration of the traditional skin markings (licbenification). In addition, the papillary dermis is thickened, vertical streaks of dense collagen may be discovered between rete ridges, and scat� tered lymphocytes may he present throughout the dermis. Lichen sclerosus the prognosis of lichen sclerosus is secured by the characteristic dermal homogenization and the bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate As this case illustrates. Differential Diagnosis the differential prognosis of lichen simplex chronicus consists of fungal an infection (the presence of neutrophils within the epi� dermis ought to prompt fungal stains; see. Treatment Management of lichen sclerosus contains topical software of potent corticosteroids, with sufferers monitored over the lengthy term because of their elevated danger for the development of squamous cell carcinoma. A: the hyperkeratosis, acanthosis with elongated rete ridges, and collagenization of the papillary dermis are indicative of a element of lichen simplex chronicus that has been superimposed on this subacute (active chronic! B: the presence of intercellular edema within the epidermis partially separates the keratinocytes from each other and accentuates their intercellular bridges. Condyp loma acwninata are regularly multiple and vary from barely perceptible micropapillary lesions to lesions with grossly n::cog� nizable papillations to large, caulifl. C: Small collections of intracomeal neutrophils with pyknotic nuclei are current throughout the parakeratotic layer (Munro microabscessesl. In addition to verruca vulgaris, the differential prognosis ofcondyloma acw:ninata consists of fi. A: Prominent koilocvtosis is evident within the higher epidermis on this portion of the lesion. B: A mound lvenical tier) of parakeratosis is perched atop one of the spikes of papillomatous epithelium in this image from a different cutaneous wart. The small squamous papillomas are lined by glycogen-rich, nonkeratinized squamous epithelium. A: Diagnostic herpetic inclusions are most probably to be discovered at the margins of the ulcer (anows). B: Multinucleated cells with �ground glass� intranuclear inclusions attribute of herpes virus an infection. The plasma cell in61trate ought to immediate ordering of a WarthinStarry or equal stain in an attempt to identify spirochetes, and serologic tests for syphilis also needs to he obtained. The nature of the herpes-induced intranuclear inclusions is discussed and illustrated in additional element within the part on chosen microorganisms of the lower feminine genital tract in Chapter three. In the setting of vulvar involvement in an grownup girl, the mode of uansmission is usually by way of sexual contact. Immunodeficient sufferers usually have a tendency to develop lesions associated to molluscum contagiosum, which characteristically take the fOrm ofasymptomatic, small (usually 3-6 mm), multiple, Besh-colored, easy, firm papules with umbilicated centers. Although the analysis of molluscum contagiosum is usually made clinically, biopsies are sometimes obtained. In optimally oriented histologic sections, the cup-shaped nature of the lesion is quickly apparent. Hyperplasia and downward growth of the infected squamous epithelium (thought to be derived from a hair follicle in most instances) produce a lobulated, squamous-lined nodule within the dermis that accommodates diagnostic molluscum our bodies. These bodies are large, homogeneous, eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions that turn into extra quite a few and extra deeply stained as they method the surface. Given that syphilis, granuloma inguinale, lymphogranuloma venereum, chancroid, parasitic infestations, infections with cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus, and tuberculosis produce vulvar lesions that are rare and/or only rarely seen by swgical pathologists, the reader is referred to more in-depth textbooks ofgyne� cologie pathology for a dialogue of these entities. Herpes Genital is Infection of the vulva by herpes virus produces vesicles which are quickly converted into painful ulcers. Portion of a cup-shaped lesion displaying outstanding epidermal hyperplasia with lobulated margins. The molluscum our bodies are most numerous within the aggregates of dead keratinocvtes that are enmeshed within keratinous debris close to the surface. The key to making the correct diagnosis is noting the presence of neutrophils throughout the cornified layer and/or epilhelium (top center). If biopsied, these lesions are often fowtd to be keratotic and acanthotic, and can be misinter� preted as lichen simplex: chronicus (Ftg. The presence of neuttophils within the cornified layer ("neuu in the hom") and/or epithdiw:n is an indication to order a fungal stain, as are patches of parakeratosis or epidermal spongiosis. If present, the fungal organisms will often be found throughout the cornified layer and/or superficial epitheliwn. Candida organisms are essentially the most frequent causative agent and are usually recognized by the mixture of yeast types, pseudohypha. The cyst may be lined by nonkeratinizing stratified squamous, transitional, or mucinous epitheliwn (F~. A: Note how the molluscum bodies turn into extra numerous and more deeply stained as they method the surface at top. B: Large, dartly stained keratohyalin granules are outstanding in the area of the granular layer in close association with molluscum our bodies. B: Fungal elements are highlighted with a periodic acid-Schiff stain with diastase pretreatment to remove "noise" from inttaepithelial glycogen). A: this portion of the epithelial lining consists of an admixture of squamotransitional and mucinous epithelial cells. A: In this instance, lhe cyst lining at right consists largely of nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium. B: High-magnification view of the cyst lining reveals asimple layer of columnar mucinous epithelium similar 1D that discovered lini! A: the cyst is located throughout the stroma, 2 mm beneath the squamous-lined skin surface. B: the cyst is Iined by a flattened layer of inconspicuous cells that are according to atrophic mesothelial cells. In addition to these mucinous vestibular cysts, some vestibular cysts are lined by an admixture of mucinous and ciliated epithelium, and ciliated epithelium dominates the lining of occasional cysts. The ciliated cells in these cysts are thought to be of metaplastic origin, as are occasional foci ofsquamous epithelium. Ciliated cysts with a tuboendometrioid�type lining are distinguished from endome� triotic cysts by their absence of related endometrial stroma and lack of hemosiderin-laden mac:rophages. These cysts are usually found in the superior portion of the labia majora or the inguinal canal and are lined by a single layer of flattened mesothelium. These lesions are lined by squamous epithelium that normally reveals hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis, although 6broepithelial polyps also can have an attenuated epithelial lining. When the papillomatosis is pronounced and repetitive, some pathologists prefer the prognosis of squamous papilloma. Polyps of this sort are extra com~ monly seen in the vagina, and are discussed in larger detail in Chapter 2. The inset highlights the ciliated epithelial cells that are the dominant cell kind lining this cyst. Fibroepilhelial polyp with atypical stromal cells (fibroepithelial stromal polyp). This phenomenon typically happens on a background of chronically irritated pores and skin in young grownup girls, is normally focal, and is believed to characterize a reactive course of. The multinucleated cells are composed ofaggregates of uniform nuclei that ahibit distinct nucleoli and no significant hyperchromasia or contour abnormalities.
Buy shallaki amexEvents and outcomes within the perioperative interval include exacerbated myocardial dysfunction spasms hand discount shallaki express, cardiac arrest, and extreme neurologic and metabolic decompensation. Many of these children are maintained with one or more nutritional dietary supplements and different brokers such as carnitine analogues, different substrate precursors and cofactors. Few, if any (except perhaps for coenzyme Q), have been proven to have meaningful benefit. Aspiration risk (and the presence of underlying lung illness and airway reactivity) could also be higher in some of these kids, a minimum of partly when they develop muscle weak spot that impairs swallowing and/ or coughing. In addition to normal non-invasive anesthetic monitoring, one should have the ability to measure blood glucose concentration frequently. Laboratory analysis ought to include hemoglobin, hematocrit, and serum electrolyte measurements if the patient is taking diuretics. Levels above 60 p.c may predispose to capillary sludging and secondary endorgan damage, including stroke. Echocardiography with Doppler shade move imaging (echo-Doppler) is invaluable, providing a non-invasive means of assessing intracardiac anatomy, blood circulate patterns, and estimates of physiologic status. For many cardiac defects, extra invasive studies are generally not required if a great echocardiographic evaluation is made. Although the complexity and number of medical defects are larger in youngsters, the anesthesiologist must be concerned in the interpretation, medical management, and additional operative interventions based on intraoperative echocardiogram. A careful evaluation of the cardiac catheterization knowledge and an understanding of how this data affects the operative and anesthetic plans are important. Not all of the medical problems could be evaluated and corrected preoperatively; the surgeon and anesthesiologist must discuss potential administration problems and any need for further evaluation or intervention earlier than operative intervention is taken into account. Appropriate communication and cooperation between the pediatric cardiologist and the surgeon maximize patient care and facilitate perioperative clinical management. The current curiosity lies with the survivors who can have host of issues related to the underdeveloped organ methods and may current for a selection of surgical procedures. Premature Surgical Baby the term prematurity has conventionally been utilized to infants weighing less than 2,500 g at start. Or a live toddler delivered before 37 weeks from the primary day of last menstrual interval is defined as untimely or preemies. Premature infants are additionally categorised as-low delivery weight infants (31�34 weeks, 1�1. However, the designation preterm toddler is more applicable and is defined as one born before 37 accomplished weeks of gestation. Preterm start (latin: partus praetemp oraneus or pretus prematurus) refers to the delivery of baby before developing organs are mature sufficient to enable normal postnatal survival. Specific risks for preterm neonates: They usually present bodily signs of prematurity in reverse proportion to the gestational age. Thus, after they need a variety of surgical procedures, they current enormous challenges throughout anesthesia, surgery, and postoperative care. Oral or intranasal administration of premedication is effective and is the most widely accepted premedication for youngsters with coronary heart disease. Operating Room Preparation Advanced, cautious preparation of the working room is crucial. The anesthesia machine should have the capacity to provide air as properly as oxygen and nitrous oxide to help steadiness pulmonary and systemic blood circulate. Resuscitative medication, labelled and prepared for administration, ought to embody injection calcium gluconate or calcium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, atropine, phenylephrine, lidocaine, and epinephrine. Injection atropine and succinylcholine are usually loaded due to the potential for airway reactivity, hypotension, and bradycardia throughout anesthetic induction. In pediatric cardiac anesthesia, lots of the patients have high endogenous catecholamines as an adaptive response to their underlying cardiac illness and have limited cardiovascular reserve. For congenital heart surgical procedure, the flexibility to rapidly alter body temperature for cooling and rewarming is essential. Surface cooling with a heating/cooling water mattress, warm air convection system, and an efficient room cooling/ heating system are important within the operative management of these sufferers. The use of ice packs to the top is usually utilized if circulatory arrest is a part of the operative plan. Premedication the goal of premedication is to achieve adequate sedation in a nontraumatic style and to preserve respiratory and hemodynamic stability. This improves oxygen saturation, diminishes myocardial oxygen consumption and promotes a more satisfactory induction. Many premedication combos have been used, but reviews of apnea, bradycardia, and respiratory despair in 1 to 2 p.c of Physiologic Monitoring the monitoring used for any explicit patient ought to be dependent on the condition of the patient and the kind and extent of the surgical procedure. In the crying pediatric patient, monitoring units could be utilized instantly after the induction of anesthesia, apart from precordial stethoscope and pulse oximetry. Foley catheters are used in neonates and infants present process hypothermic circulatory arrest or reoperations and may be electively withheld in older kids for much less advanced procedures except dictated by renal insufficiency, extended procedures, significant fluid intake, or surgeon preference. Continuous monitoring of arterial strain is feasible solely via using an indwelling intraarterial catheter. In younger youngsters, cannulation of the radial artery with a 22-gauge catheter is most popular. Other websites out there for cannulation include the ulnar, femoral, or axillary artery. Myocardial and cerebral preservation is principally maintained through hypothermia, so the accurate and steady monitoring of body temperature is essential. Rectal or urinary and nasopharyngeal temperatures are monitored as a outcome of they mirror core and mind temperatures respectively. Monitoring of esophageal temperature is an efficient reflection of cardiac and thoracic temperatures. Alternative sites such because the ear lobe or the tongue sensor have been used efficiently in the new child to present a more central measure of oxygen saturation, with much less temperature-related variability. Failure to maintain this gradient results in no forward circulate, low cardiac output, and death. Monitoring of intracardiac common atrial pressure is beneficial within the intraoperative and postoperative administration of these patients. The increased viewing angles out there with these multi plane imaging probes have considerably improved the power to evaluate the complete coronary heart each earlier than and after the restore. In small neonates or when the surgeon attempts to present smaller, more cosmetically appealing incisions, the uncovered floor space of the heart is quite limited. Although monoplane probes are able to being placed in infants weighing less than 2 kg, the obtainable views remain limited, notably within the extra complex repairs carried out in neonates. Occasionally, the preoperative analysis might lead to a revision of the initial analysis or determine an additional defect not beforehand recognized. It might help in the analysis of hemodynamic effects of sternal closure, termination of ventricular help units or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Post-bypass echo-Doppler analysis is in a position to instantly assess the standard of the surgical restore and to assess cardiac perform by inspecting ventricular wall motion and systolic thickening. This method can present residual structural defects after bypass, which can be immediately repaired in the same operative setting and forestall the patient from leaving the operating room with vital residual structural defects that later require reoperation. Importantly, post-bypass ventricular dysfunction and residual structural defects are identified by echo-Doppler assessment; left uncorrected, these are related to an increased incidence of reoperation and higher morbidity and mortality.
Discount shallaki master cardPortion of an opened early gestational sac composed of amnion that has been turned inside out and folded back muscle relaxant remedies shallaki 60caps cheap. The formation of a transparent pseudocavity, coupled with regular undulations within the amnion, creates the false impression of a cavitated villus with scalloped outlines. All cases of"diploid partial mole" ought to be evaluated for this possibil� ity, especially if �0Uow�up discloses the development of c:ho� riocarcinoma, which is 25 occasions extra widespread in complete moles than partial moles. Placental Mesenchymal Dysplasia Placental mesenchymal dysplasia is a rare disorder character� ized by (a) tortuous chorionic plate vessels with aneurysmal dilatation and thrombosis. The ultrasonographic find� ings of the placenta in this disorder may resemble a partial mole. However, the presence of a weU�formed fetus and the similar old presentation within the third trimester help to distinguish this process from a molar gestation. Histologically, the edematous villi in placental mesen� chymal dysplasia could present focal cistern formation, and their admixture with small villi causes additional resemblance to partial mole. The vascular sample within the edematous villi in placental mes� enchymal dysplasia ranges from avascular to regular to cho� rangiomatous, and there could additionally be an associated chorangioma. Cases by which a molar being pregnant has been excluded with confidence could be diagnosed as irregular villous morphology suggestive ofa nonmolar cytogenetic abnotmality. Ifchromosomal analy~ sis was perfotmed, the histologic findings should be com:latcd with karyotypic results. In exceptional instances, a complete mole associated with a standard twin gestation can even cause diagnostic difficulties, as mentioned Twin Gestation with Simultaneous Complete Mole and Nonnal Pregnancy Twin gestations that represent a whole mole occurring in conjunction with a normal twin are quite uncommon, however have been reported. In difficult cases, one should submit all of the villous tissue for histologic evaluation in the hope of uncovering extra readily apparent diagnostic options. Enlarged, avascular villi with edematous fibromvxoid stroma are seen adjacent to normal third-trimester villi. Several of the cytotrophoblastic and villous stromal cells exhibit nuclear immunoreactivity, however the mildly hyperplastic syncytiotrophoblastic cells are adverse. Thus, for tissue varieties during which the gene bas been imprinted, the p57 gene product is entirely dcrMd from the maternal allde, and its detection by nuclear immunoreactivity serves as a marker for the maternal genome. In partial moles, hydropic abortions, and instances with abnormal villous morphology, many of the cytotropboblastic and villous stromal cells arc p57�positive. A: Many decidual cell nuclei are p57-positive� B: Islands of intervillous intermediate trophoblast. Other instances suggestive of hydatidiform mole in which the p57 immunostain is positive or equivocal should be subjected to molecular genetic evaluation, which is in a position to allow identification of partial moles (diandric triploids), nonmolar mimics similar to hydropic abortions and abnormal villous morphology associated to nonmolar cytogenetic abnormalities (biparental diploids), and the exotic instances of full mole with aberrant p57 expression (androgenetic diploids with retained genetic material from maternal chromosome 11). For example, when attempting to distinguish abnormal villous morphology or hydropic abortus from partial mole, p57 positivity is kind of assured and performing this stain solely serves to delay the diagnosis and improve the worth of the c:valwarion. In this sitwarion, I would prefer to proceed directly to genotyping or ploidy evaluation. The sectioned floor of this uterine choriocarcinoma demonstrates its characteristic gross look as a hemorrhagic nodule. The sectioned surface of the kidney is situated at the prime of the image, and is dwarfed by the big hemormagic tumor with nodular somewhat than infiltrative borders. As anticipated from the gross look of choriocarcinomas, giant portions of the tumor, particularly centrally, are hemorThagic and necrotic. Choriocarcinoma also can current as a complicap tion ofa regular pregnancy, a spontaneous abortion, or an octop pic pregnancy. The estimated frequency of choriocarcinoma is 1:a hundred and sixty,000 for nonnal gestations, 1:16,000 fOr spontaneous abortions, 1:5,000 for ectopic pregnancies, 1:1,000 for parp tial moles, and 1:forty for full moles. Although abnormal uterine bleeding is commonly current, the 6rst manifestations of the disease could also be related to hemorrhagic occasions from metastatic deposits in such areas because the lung, mind, or liver. Grossly, choriocarcinomas are circumscribed, hemorp rhagic plenty at each main and metastatic sites. Microscopically, choriocarcinoma consists of nests and sheets of mononudeate trophoblastic cells interlaced with syncytiotrophoblastic cells in a distinctive biphasic sample. Intermediate trophoblastic cells represent a lot of the mononucleated cells in this field. There is comingling of choriocarcinoma with third-trimester chorionic villi at the fringe of the cancerous nodule. Choriocarcinomas lack chorionic villi by definition, aside from the intraplacental variant, which is discll88ed within the following paragraph. Documented intraplacental choriocarcinomas are terribly rare, and are nearly always present in near-term or term gestations. In general, those who arc recognized as a lesion arc grossly thought to be an inkrct or intervillous thrombus quite than a tumor. Maternal metastatic disease is present at the time of analysis of the intraplacental choriocarcinoma in about 60% ofcases. This low-magnification view demonstrates a portion of acancerous nodule with extensive hemorrhagic necrosis. Viable tumor is current surrounding vessels and at the tumor interface with third-trimester chorionic villi. Aggregates of intermediate trophoblasts embedded within deposits of perivillous fibrin. In slightly extra advanced gestations, villi could have shaped but they might be overshadowed by fragments of the trophoblastic: shell. The dimorphic: proliferation of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast in these conditions c. Multiple histologic sections ought to be examined in an attempt to fUrther exclude choriocarcinoma by discovering chorionic villi � & discussed above, rare choriocarcinomas have been reported in association with villi from term or near-term plac:entas. However, the presence of villi in a first- or second-trimester placenta excludes the potential of choriocarcinoma, even when the trophoblastic: proliferation. Differential Diagnosis It is necessary to distinguish early types of intraplaccntal chop riocarcinoma from the variably mobile aggregates of intermcP diate trophoblasts that are usually incidentally found embedded inside perivillous deposits of fibrin. Oa:asionally; degenerative nuclear atypia could be seen in these trophoblastic elements, resulting in a resemblance to sopcalled c:horiocarp cinoma in situ. A resemblance to choriocarcinoma is apparent but this was a focal microscopic finding unassociated with tissue necrosis. Even then, the potential of an uncommon carcinoma with trophoblastic differentiation must be thought-about. Unlike choriocarcinomas, these tumors will show proof of transition between their ordinary and chorio� carcinomatous parts. Note the characteristic sample of myoinvasion, with tumor cells splaying apart and dissecting between muscle fibers, quite than destroying them. The most typical medical presentation is amenorrhea or abnonnal vaginal bleeding in a 20� to 40-year-old girl with uterine enlargement and sligbdy elevated ranges of serum Jj. Microscopically, the tumor recapitulates the traditional growth sample of implanta� tion�type intermediate trophoblasts infiltrating the myome� trium and vessels. Neoplastic cells with features of the hyperchromatic variant of intermediate tro-phoblast are additionally current in variable numbers. The mitotic index averages 2 mitotic figures per 10 high-power fields, and the imply Ki-67 proliferation index is 14%.
References - Cooper GM, Johnson JA, Langaee TY, et al: A genome-wide scan for common genetic variants with a large influence on warfarin maintenance dose, Blood 112:1022-1027, 2008.
- Sheth SB, DiCicco RA, Hursting MJ, et al: Interpreting the International Normalized Ratio (INR) in individuals receiving argatroban and warfarin, Thromb Haemost 85:435-440, 2001.
- Scott RA, Bridgewater SG, Ashton HA: Randomized clinical trial of screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm in women, Br J Surg 89(3):283-285, 2002.
- Antonarakis ES, Armstrong AJ, Dehm SM, et al: Androgen receptor variantdriven prostate cancer: clinical implications and therapeutic targeting, Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 19:231n241, 2016.
- Jacks T, Fazeli A, Schmitt EM, et al. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature 1992;359(6393):295-300.
- Nandan MO, Yang VW: The role of Kruppel-like factors in the reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells, Histol Histopathol 24(10):1343-1355, 2009.
- Cotter G, Kaluski E, Milovanov O, et al. LINCS: L-NAME (a NO synthase inhibitor) in the treatment of refractory cardiogenic shock: a prospective randomized study. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1287.
- Addis BJ, Corrin B. Pulmonary blastoma, carcinosarcoma and spindle-cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study of keratin intermediate filaments. J Pathol 1985;147:291-301.
|

