|
Thomas Zgonis, DPM, FACFAS - Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
- Chief, Division of Podiatric Medicine and Surgery
- Director, Podiatric Surgical Residency and Reconstructive Foot and
- Ankle Fellowship
- The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio
- San Antonio, Texas
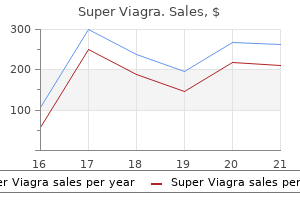
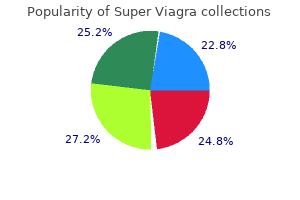
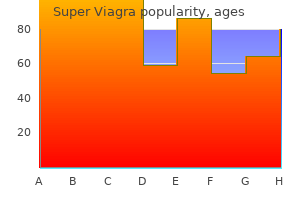
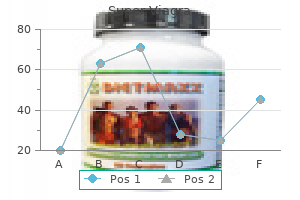
Super Viagra dosages: 160 mg
Super Viagra packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills

Cheap super viagra online visaThe virus produces 4 major forms of warts: common erectile dysfunction medication muse cheap super viagra on line, flat, plantar, and genital (condyloma acuminatum). The length of the wart is variable as nicely; approximately 65% of the lesions resolve spontaneously inside 2 years. Warts could be spread between persons and between physique sites by direct or oblique contact. Most warts are located on the fingers, palms, and elbows because trauma to these sites promotes inoculation of the virus. Warts additionally show the Koebner phenomenon, which leads to linear configurations of lesions at websites of shaving or scratching. Common Warts Verruca vulgaris, or the common wart, is found mostly on the dorsal surface of the hands or fingers, though it might be situated at any body site. The lesions could additionally be solitary or multiple and measure from a quantity of millimeters to greater than 1 cm. Varying in color from yellowish-tan to grayish-black, the common wart has a distinct rough, papillated floor. Punctate thrombosed capillaries, clinically manifested as black dots, could additionally be seen on the floor. They usually seem grouped, especially when the Koebner phenomenon has occurred secondary to shaving or different trauma. These lesions are most often confused with lichen planus or lichen nitidus because these disorders also feature flat-topped papules. Plantar Warts Verrucae plantaris, or plantar warts, develop on the weight-bearing areas of the toes, heels, and the midmetatarsal region. The lesions are pushed into the pores and skin in such a way that the verrucous floor is even with the encircling skin. These warts are sometimes very tender and may produce significant discomfort with ambulation. In early or mild instances, the one physical discovering could also be subtle skin-colored, flat-topped papules. Their development may be exuberant in some patients when untreated, leading to cauliflower-like masses. These genital warts must be differentiated from moist papular or nodular lesions of secondary syphilis (condylomata lata). Although nonvenereal transmission might happen, corresponding to unfold from cutaneous warts, the presence of genital warts in young youngsters is often related to sexual abuse. The vesicles rupture and form a crust over the subsequent 5-7 days and generally heal within 2 weeks. The cutaneous eruption is often accompanied by fever, regional lymphadenopathy, or flulike signs (Table forty eight. Recurrent infections are characterized by localized vesicular eruptions and symptoms such as itching or burning on the similar website. Reactivation of the virus could additionally be triggered by sunburn, cutaneous trauma, febrile diseases, menstruation, or emotional stress. Oral antivirals, if administered through the prodromal period earlier than the onset of lesions, may abort or shorten recurrent episodes. Multiple vesicles and subsequent erosions develop on the lips, gingivae, anterior portion of the tongue, or exhausting palate. The condition may be very painful and is often accompanied by inability to eat and drink. The fever sometimes resolves within 3-5 days, whereas the oral lesions might persist for as a lot as 2 weeks. Enteroviruses could produce comparable oral manifestations; nonetheless, they tend to spare the gingivae and sometimes have an effect on the posterior pharynx. Systemic antivirals could hasten resolution of the lesions and shorten the course of the sickness. Neonatal herpes is a probably fatal infection, typically with severe central nervous system involvement. Vigilant evaluation to decide extent of infection, intravenous acyclovir, and supportive care are required. Immunocompromised youngsters who develop a herpetic infection ought to receive intravenous acyclovir and be monitored rigorously for proof of pulmonary, hepatic, and central nervous system involvement. This situation, referred to as eczema herpeticum or Kaposi varicelliform eruption, could also be accompanied by fever and malaise (see Atopic Dermatitis). Treatment of Warts Treatment of warts is designed to be cytodestructive and varies depending on the sort of wart, site of the lesion, age and immune standing of the patient, and extent of involvement. Topical therapies embrace keratolytic preparations, such as salicylic acid, ammonium lactate, and 5-fluorouracil. In-office remedies embrace topical cantharidin, cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen, or immunotherapy with Candida or Trichophyton antigen. In children with numerous warts, cryotherapy may be limited by discomfort and immunotherapy may be preferable. Cimetidine has been utilized in kids with multiple lesions that have failed different treatment choices. Extremely recalcitrant warts could necessitate surgical or laser (pulsed dye or carbon dioxide) therapy. A conservative method is commonly finest for this self-limited an infection because the therapy could also be worse than the situation. Prolonged periods of applying duct tape to the wart (plantar, finger) have additionally resulted in resolution. The scientific lesions are indistinguishable however could be differentiated by serologic exams. Primary manifestations usually comply with an incubation interval of roughly 1 week. They range from subclinical infections to localized or generalized vesicular eruptions to life-threatening systemic infections. The basic medical manifestation consists of grouped thin-walled vesicles on an erythematous base. The lesions often start Varicella Varicella (chickenpox) is a very contagious, but normally self-limited an infection brought on by the varicella-zoster virus. Transmitted by close contact and respiratory droplets, varicella has an incubation period of 10-21 days. The cutaneous manifestation in healthy children is characterised by crops of lesions (usually 2 or three crops of 50-100 lesions each) that originally appear as 2- to 3-mm purple macules and then evolve by way of papular, vesicular, and at last pustular levels inside approximately 24 hours. The vesicular stage has historically been described as resembling "dewdrops on a rose petal".
Discount 160 mg super viagra amexHowever impotence libido discount super viagra 160mg with mastercard, development attenuation that occurs after a sustained period of normal growth suggests that a disorder has been acquired. Slow improvement or poor school efficiency may indicate a central disorder or could represent part of a syndrome. Chronic illness typically impedes development, as do certain drugs (glucocorticoids). A history of nonendocrine medical problems may also provide clues to the underlying dysfunction. Physical Examination Height and weight ought to each be plotted fastidiously on growth charts. In contrast, a baby who is brief however chubby is more prone to have an endocrine disorder or syndrome. Disproportionate quick stature is attribute of skeletal dysplasias (short limbs within the case of achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia, short trunk in some uncommon types of skeletal dysplasia) and may also be seen in long-standing hypothyroidism. The presence of dysmorphic options is commonly suggestive of a syndrome or genetic dysfunction. Goiter, delayed dentition, bradycardia, dry hair or pores and skin, or delayed reflexes could also be suggestive of hypothyroidism. Bitemporal hemianopsia, papilledema, optic atrophy, or accelerating head circumference in a younger baby is suggestive of a central nervous system abnormality (craniopharyngioma) causing hypopituitarism. Delayed puberty is compatible with constitutional delay in growth and development, hypogonadism, panhypopituitarism, extreme hypothyroidism, or continual illness. What does the child eat in a typical 3-day interval (often greatest described by a formal food plan record) Does the child have belly pain, diarrhea, unexplained fevers, mouth or anal sores, or joint ache Does the child have neck swelling, lethargy, constipation, cold intolerance, or weight acquire with out much improve in peak Complete compensation for growth failure is unlikely to happen if the disorder was many years in period or occurred very close to the onset of normal puberty. Males with delayed puberty may be handled with testosterone enanthate or cypionate (50-100 mg/month intramuscularly or subcutaneously for 3-6 months; smaller doses given more incessantly could additionally be extra physiologic and are most popular by some practitioners) to gradually bring about secondary sexual traits and accelerated linear development. This is usually gratifying for males and is usually followed by spontaneous pubertal development. The low dose of testosterone is designed to keep away from undue development of bone age and lack of development potential. Several small studies report beneficial results of oxandrolone in males with constitutional delay of progress and puberty. Side effects at this dose are uncommon, however indicators of virilization should immediate a reduction in dose. Estrogen-Just as males with constitutional delay are treated with androgens, females with pubertal delay and delicate quick stature could additionally be treated with a brief course of estrogen remedy. However, benign constitutional delay is much less doubtless in females (who are extra likely to have an underlying pathologic trigger such as Turner syndrome) and such therapy is relatively uncommon. Increased intracranial pressure (pseudotumor cerebri) is a rare however severe dose-related aspect effect. It often resolves if remedy is stopped, and after resolution, therapy can frequently be restarted at a lower dose. Because of its growth-promoting results, there has lengthy been concern a couple of attainable increase in the incidence of most cancers. Although all-type cancer-related mortality was not increased within the French cohort, bone tumor�related mortality was increased. Possible unwanted effects embody hypoglycemia, increased intracranial pressure, and adenotonsillar hypertrophy. This is especially true for kids with delayed puberty, in whom the discrepancy in height compared with friends (who have gone via their pubertal growth spurts) is disconcerting. Understanding tips on how to measure a baby accurately, performing simple proportion measurements, and calculating development velocity are expertise that all pediatricians must have so as to diagnose quick stature and determine associated illness states and syndromes. Translating clinical guidelines into apply: the effective and appropriate use of human development hormone. Efficacy and safety of development hormone remedy in children with hypochondroplasia: comparability with an historic cohort. Growth hormone therapy of brief stature: status of the standard of life rationale. Kansra Hypoglycemia, although uncommon in children past the new child period, is an acute, life-threatening medical emergency that may result in seizures, permanent mind injury, and even sudden death. Various pathologic mechanisms, such as abnormal hormone secretion, metabolic defects, and medicines or toxins, have been attributed as causes of hypoglycemia. Therefore, to consider hypoglycemia both in a toddler or newborn, a comprehensive technique for prognosis and remedy is essential. An important underlying explanation for hypoglycemic problems is a disruption within the normal response of the metabolic and endocrine systems in the course of the transition from fed to fasted state. Hypoglycemia results from an imbalance in glucose homeostasis, both excessive glucose elimination from the circulation or poor glucose supply into the circulation, or each. Obtaining plasma and urine specimens to evaluate the crucial ranges of assorted hormones and metabolic merchandise at the time of hypoglycemia are important for diagnosis and must be drawn immediately before therapy begins. Obtaining a "pink prime" and "green top" blood assortment tube will allow for most all studies to be run. Historically, a working definition for significant hypoglycemia was initially developed primarily based on the scientific manifestations of low blood sugars in neonates. Attempts have been made to define hypoglycemia by utilizing operational thresholds or a medical approach. An operational threshold is predicated on the glucose in plasma or entire blood that prompts the intervention and is outlined as blood glucose <40 mg/dL (plasma glucose ranges <45 mg/dL); the scientific approach defines the blood glucose focus threshold at which scientific signs and symptoms appear (and disappear by correcting the low glucose concentration). The wide range of blood glucose concentrations at which clinically overt indicators may appear has led to uncertainty in definition. Regardless of the broad fluctuations in glucose levels (between fed and fasting states), plasma blood glucose is generally maintained inside a really narrow range of 70-100 mg/dL. A plasma glucose worth below 40 mg/dL is usually taken because the medical definition of hypoglycemia. However, subtle signs and symptoms of neuroglycopenia may be documented at plasma glucose ranges beneath 70 mg/dL and are more obvious at glucose levels under 60 or 50 mg/dL. For provocative tests, corresponding to fasting studies, a glucose stage of 50 mg/dL can be taken as sufficiently low for judging gasoline and hormonal responsiveness. The response to a given stage of plasma glucose can differ, relying on the underlying dysfunction. When comparing reported glucose values, the clinician must recognize some technical elements. Unless a free-flow blood pattern is obtained from the toddler with minimal ache, the glucose values are more probably to be unreliable. Second, complete blood glucose values are slightly decrease than these of plasma due to the dilution by the fluid in the red blood cells. This is especially necessary in newborns, whose hematocrit values are higher than older infants and youngsters.
Purchase super viagra 160 mg amexOsteoid osteomas have a extremely vascularized nidus impotence after 60 buy 160 mg super viagra with visa, which incites an intense, painful, inflammatory response that produces sclerosis of the encircling bone. Most benign neoplasms are seen on anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the symptomatic area. Characteristics of benign lesions embody well-circumscribed lesions with out periosteal new bone formation or gentle tissue mass. If a lesion is suspected however not seen on plain radiographs, similar to may happen in an osteoid osteoma, a technetium bone scan could also be helpful. Diagnosis is further aided by surgical biopsy, which may also permit for surgical therapy. Leukemia is the most typical childhood malignancy and is regularly accompanied by musculoskeletal complaints, similar to limping, fever, bone ache, pallor, bruising, and weight reduction. Common malignancies involving the musculoskeletal system embrace osteogenic sarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, and intraspinal tumors, such as astrocytomas (Table 34. Intraspinal tumors are inclined to produce neurologic symptoms, similar to muscle weakness, as the cause for limping. The different lesions might produce a mass, bone weak point, and potential pathologic fractures. A cautious musculoskeletal and neurologic examination is critical for any youngster with a suspected neoplasm. In many circumstances, a mass, either in the concerned bone or in adjoining delicate tissues, could also be palpable. These lesions are frequently adjacent to joints and will end in decreased range of motion. Neurologic evaluation may present evidence of muscle weak point or irregular reflexes, suggestive of spinal twine or peripheral nerve involvement. Anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the concerned area usually reveal the presence of a neoplasm. The preoperative prognosis was Ewing sarcoma, but at biopsy the prognosis was acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Radiographic abnormalities associated with acute leukemia include diffuse osteopenia, metaphyseal bands, periosteal new bone formation, geographic lytic lesions, sclerosis, and permeative distraction. When the an infection is confined to the synovium of a joint, the condition is termed septic arthritis. If the primary focus of the infection is within bone, even when the joint is secondarily concerned, the situation is termed osteomyelitis. Bacterial pathogens are probably the most frequent cause of osteoarticular infections in children, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most frequent etiology. Beyond the neonatal period, Kingella kingae is the second most frequent trigger in youngsters beneath 5 years of age. In older children and adolescents with puncture wounds of the foot, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. Sexually energetic adolescents could develop septic arthritis as a result of gonococcal infections. Patients with sickle cell anemia could develop osteomyelitis on account of Salmonella species or pneumococcal infection. Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis mostly entails the femoral neck, the distal femoral metaphysis, and the proximal tibial metaphysis. Children with these infections could additionally be acutely sick; many could have fever, limp, and localized ache. Subacute osteomyelitis, which has very distinct manifestations, happens most commonly within the knee. Radiographs present sclerotic metaphyseal lesions that sometimes cross the expansion plate into the epiphysis. Children with acute bone and joint infections may exhibit the clinical indicators of bacteremia and an infection, together with elevations in temperature, white blood cell depend, erythrocyte sedimentation price, and C-reactive protein level. When the hip joint is concerned, the kid holds the hip ready of flexion, abduction, and exterior rotation. This position unwinds the hip capsule and allows it to maintain the best volume of intracapsular fluid. This initially decreases pressure, however because the pus continues to accumulate, even this position fails to relieve symptoms. A hip joint effusion is often not palpable, but there may be overlying delicate tissue swelling and tenderness. There is usually a joint effusion and perhaps delicate tissue swelling, erythema, and increased heat over the metaphysis if osteomyelitis is present. Osteomyelitis sometimes manifests with level tenderness over the involved site; with continued bone destruction and rupture of pus into the periosteum, tenderness becomes more diffuse. Infection of the foot is less widespread except as a sequela to puncture wounds through a tennis shoe, producing the classic P. The lesion crosses the epiphysis; that is attribute of a subacute osteomyelitis. B, Anteroposterior tomography clearly demonstrates the lucent nature of the lesion and its surrounding sclerosis. If a septic process concerning the hip is suspected, an ultrasound examine could also be useful in demonstrating an effusion. The synovial fluid evaluation ought to embrace a cell count, measurement of protein and glucose ranges, Gram stain, cultures, and sensitivity studies. Infections of peripheral joints, such because the knee, are extra readily diagnosed by arthrocentesis. If an osteomyelitis of a metaphyseal region is suspected primarily based on imaging studies, the subperiosteal area and bone may be instantly aspirated with a large-bore needle. Despite these interventions, microbiologic research might frequently fail to yield results. Transient synovitis (also generally recognized as toxic synovitis) of the hip is the most typical reason for limping in kids. It can occur in all age groups, however the imply age at onset is 6 years; most patients are between three and 8 years of age. Hip transient synovitis is characterized by acute onset of monoarthritic hip pain, an associated limp, and gentle restriction of hip movement, especially abduction and inner rotation. B, A T1 weighted fat-saturated postgadolinium sagittal view demonstrates a thick, rim-enhancing lesion with a small quantity of nonenhancing fluid in preserving with early abscess formation with epiphyseal extension (arrow) and a small cloaca (arrowhead) extending to the tibiotalar joint. Suspected causes embrace lively or recent systemic viral an infection, trauma, and allergic hypersensitivity. Approximately 70% of affected kids have had a nonspecific viral upper respiratory infection 7-14 days before the onset of symptoms. Lateral spine radiographs show narrowing of the T12-L1 intervertebral disk house (arrow in A). An axial bone window from a noncontrast computed tomography scan of the spine demonstrates irregularity to the vertebral finish plates (arrows in B). A sagittal T2 weighted image (C), a sagittal fat-saturated T1 weighted postcontrast picture (D), and an axial T1 weighted postcontrast picture (E) of the thoracolumbar junction show lack of height of the T12-L1 intervertebral disk area with adjoining T2 prolongation of the adjacent end plates (arrows in C), with corresponding abnormal enhancement in the same areas (arrows in D), and surrounding masslike delicate tissue enhancement (arrowheads in E).
Cheap generic super viagra ukThis is a result of duplication of the ureteric bud throughout embryogenesis impotence surgery purchase generic super viagra from india, inflicting a double amassing system, or 2 ureters. Duplicated ureters can open separately inside the bladder, but in rare instances, an ectopic ureter can finish in the vagina, urethra, or vestibule, resulting in dribbling and incontinence. Normal insertion of the ureter into the bladder submucosal wall types a flap-valve mechanism that forestalls urine backup during filling and contraction. Urine move mechanics are disrupted by the constant filling of the bladder with urine that has flowed backward and then returns to the emptied bladder. This is an uncommon electrolyte dysfunction in children but could be noticed in main hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D intoxication, immobilization, Williams syndrome, malignancy, and idiopathic hypercalcemia of infancy. This results in renal sodium and water losses and thus to polyuria and quantity contraction. In persistent hypercalcemia, increased calcium excretion over time can lead to nephrocalcinosis, tubular injury, and poor urinary concentrating capability, thus enhancing polyuria. In youngsters, it happens clinically as a outcome of diuretic use, aldosterone excess states, Cushing syndrome, and intrinsic renal issues that affect potassium dealing with. This results in distortion of regular neural tissues within the spinal cord or nerve roots. The vary of anomalies contains meningocele, lipomeningocele, major tethered wire, dermoid cyst, syrinx, and sacral agenesis. Hypokalemia interferes with water reabsorption in the accumulating duct of the kidneys. Polyuria and urinary incontinence may be the first signs of diabetes mellitus and are secondary to hyperglycemia and the osmotic diuresis resulting from chronic glycosuria. The renal threshold for reabsorption of glucose is exceeded when the blood glucose stage is higher than roughly one hundred eighty mg/dL. If oral intake of fluid decreases, as happens when diabetic ketoacidosis causes anorexia and emesis, vital dehydration and shock frequently develop. The defect could be full or partial, and thus the diploma of polyuria is variable. In the idiopathic form, infiltrative ailments similar to Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe syndrome) must be sought. The resultant decreased capacity to focus leads to a higher incidence of nocturnal enuresis in affected patients. Juvenile nephronophthisis is an autosomal recessive disorder that leads to end-stage renal failure between preadolescence and early maturity. Patients have excessive urine output because of poor renal concentrating ability and renal salt losing. The salt losing causes salt craving, and sufferers have a desire for salty meals or even eat salt instantly from the saltshaker. A small share of these patients have retinitis pigmentosa, which can cause blindness at birth or later in life. Infants might present with poor development, extreme dehydration, seizures, and central nervous system harm or dying. In households by which the diagnosis has already been made, early intervention in infants can forestall these symptoms and result in a superb consequence. In youngsters, the presentation contains failure to thrive, polyuria, and polydipsia. Hypercalciuria and low urine citrate excretion mix to produce nephrocalcinosis. The autosomal recessive type of the disease is incessantly related to hearing loss. This autosomal recessive disorder outcomes from a defect in cystine transport and results in the lysosomal accumulation of cystine throughout the body. Acidosis, rickets, polyuria, and severe failure to thrive are hallmarks of the illness. Early intervention with oral cysteamine to bind cysteine has dramatically improved the end result in affected sufferers. Hemoglobin S is a genetic defect in hemoglobin A that ends in red blood cells that deform underneath low oxygen tension (see Chapter 37). The renal medulla is a website with excessive osmolality, low oxygen tension, and relative acidosis, all situations that promote sickling. This leads to occlusion of blood vessels and injury Primary Nocturnal Enuresis Establishing whether or not the first nocturnal enuresis is the one symptom or whether or not there are associated symptoms such as diurnal incontinence, constipation, sleep problems, or behavioral issues, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity dysfunction, is important before a treatment technique is developed. It is also useful to let the family and baby know that virtually all sufferers "outgrow" primary nocturnal enuresis. If therapy is sought, the enuresis alarm has a high success price, however affected person selection is essential. These gadgets are designed to awaken sufferers when micturition begins and end result within the improvement of elevated bladder capacity. Its effect may not be seen for up to 12 weeks, and due to this fact the household and patient must be highly motivated. Its safety profile has been glorious, but patients ought to be given careful instruction on restricting fluid consumption after the bedtime dose. Imipramine, a tricyclic antidepressant, has been proven to be effective, however its side effects and toxicity have restricted its use for this benign situation. Red Flags Dysfunctional Voiding Treatment of gentle voiding dysfunction ought to begin with nonpharmacologic administration. This encourages voiding when the affected person is relaxed and will result in fewer contractions of the external sphincter throughout micturition. Keeping a diary of the voiding schedule involves the child in management and makes him or her extra conscious of bladder habits. Aggressive administration of constipation (see Chapter 16) improves good bladder emptying and decreases bladder instability. When incontinence continues regardless of nonpharmacologic strategies, anticholinergic remedy ought to be added within the treatment of a kid with an overactive or unstable bladder. Oxybutynin should be began at a low dosage and titrated to its most dosage if necessary. This might maintain the kid freed from an infection and will forestall the painful urination that reinforces exaggerated external sphincter contraction and urine holding. Biofeedback is reserved for patients with average to extreme dysfunctional voiding. Patients can learn to enhance bladder capability and inhibit detrusor contractions by way of this method. Polyuria Polydipsia Failure to thrive Poor urinary stream Encopresis Secondary enuresis Abnormal gait, together with toe walking Recurrent urinary tract infections Cutaneous lesions over lumbosacral spine Diminished lower extremity reflexes Abnormal genitalia Palpable bladder Hypertension Headache Visual disturbances Obstructive sleep apneas Neuropathic Bladder and Anatomic Disorders the therapy of these disorders is dependent upon the particular defect.
Purchase super viagra overnight deliveryLess particular however still helpful clues are a history of autoimmune issues erectile dysfunction after testosterone treatment purchase 160mg super viagra with mastercard, jaundice, anemia, cholecystectomy, or splenectomy in different relations. Physical Examination Some patients current with previously unidentified chronic liver illness. The clinician should focus on indicators of portal hypertension: spider angiomas, palmar erythema, dilated stomach veins, ascites, and splenomegaly with a small liver. Cutaneous excoriation as proof of pruritus, xanthomas, and jaundice assist cholestasis. A large, tender liver is suggestive of acute viral hepatitis or congestive heart failure. Abnormal neurologic findings, including tremor, nice motor incoordination, clumsy gait, and choleriform actions, recommend Wilson illness. A slit-lamp examination should be included to search for the Kayser-Fleischer rings (a brownish discoloration at the periphery of the cornea) of Wilson disease. Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia Most causes of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia within the child and adolescent are secondary to hemolysis (Table 15. A full blood count with evaluation of the smear, reticulocyte rely, and Coombs test can differentiate hemolytic from nonhemolytic disorders. This is necessary in considering how rapidly the evaluation should proceed or how closely the patient should be monitored. Patients with coagulopathy, hyperammonemia, encephalopathy, or hypoglycemia must be admitted to the hospital and noticed very closely. Gallstones are notably widespread in children with hemolytic issues, similar to sickle cell disease, thalassemia, erythrocyte membrane defects, erythrocyte enzyme defects, and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Gallstones are additionally associated with anatomic abnormalities of the biliary tract, cystic fibrosis, ileal dysfunction, weight problems, parenteral vitamin, sepsis, prematurity, and being pregnant. Stones may be discovered by the way on abdominal radiographs or ultrasound research in asymptomatic people. Alternatively, gallstones might manifest with symptoms of biliary colic: nausea, vomiting, proper upper quadrant or nonspecific belly ache and jaundice. Steathorrhea, weight loss, and symptoms of fat-soluble deficiency could be current in some sufferers. Liver transplantation is out there as curative intervention as soon as disease progresses to end-stage liver disease. Acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia is characterised by pallor, stomach ache, fever, and dark urine in addition to jaundice. Hemolytic anemia may be associated with infection, immunodeficiency, malignancy, hemolytic uremic syndrome, or other autoimmune issues, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune hepatitis. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia could be caused by congestive heart failure and infection ought to in such circumstances extrahepatic symptoms, cardiac failure, or sepsis dominate the image. Multiple biliary strictures have additionally been found in affiliation with Langerhans cell histiocytosis, congenital hepatic fibrosis, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney illness, following ischemic/hypoxic harm, and in immunodeficiency states. Overlap syndrome with features of both sclerosing cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune cholangitis with irritation centered on small bile ducts has been described as variants of the disease. The most important step is to consider sufferers for 272 Section three GastrointestinalDisorders vertically during childbirth; and from occupational exposure. Infection in the new child could be prevented by administration of hepatitis B immunoglobulin within 12 hours of birth and a series of three hepatitis B vaccinations. In developed countries, hepatitis B must be suspected in children born from mothers with preexisting hepatitis B or mothers with no prenatal care. The majority of children with hepatitis B are asymptomatic; few develop signs of acute or chronic hepatitis. Extrahepatic signs of arthritis, polyarteritis, urticaria, and nephritis from circulating immune complexes may be current. Children with continual energetic hepatitis B can be treated with interferon 2b or antiviral brokers. Chronic infection develops in 40-60% of affected children, in distinction with as much as 80% of contaminated adults, and might progress to cirrhosis. Patients with artificial liver failure must be referred for pressing evaluation by the liver transplant middle. In the absence of an identifiable viral agent, idiopathic acute hepatitis may be recognized solely after the complete resolution of irregular bilirubin and aminotransferases is documented. If abnormalities persist, a work-up for continual liver ailments must be initiated. However, in nearly 66% of infected patients between 5 and 17 years of age, a symptomatic illness with jaundice develops. Small percentages develop both a relapsing or protracted cholestatic illness lasting up to 8 months. Transmission is by the fecal-oral route, which may embrace contaminated water and food, especially shellfish. The greatest fecal excretion is earlier than the onset of jaundice when the illness has not yet been recognized. Transmission rates are excessive in daycare centers and establishments with developmentally delayed kids. After publicity, an infection can be prevented in 85-90% of circumstances by giving intramuscular immunoglobulin to contacts within 2 weeks of publicity. It is a rapidly evolving space; nevertheless, pediatric expertise with direct-acting antiviral regimens is restricted. Other viruses together with herpes simplex, human herpesvirus 6, parvovirus B19, and norovirus also can trigger hepatitis, significantly in the immunosuppressed affected person. Copper is then released into the circulation and is in the end deposited within the central nervous system, kidneys, and cornea. The hepatic manifestation predominates in childhood; a neuropsychiatric manifestation becomes extra widespread later, in adolescence and adulthood. The liver involvement could manifest as acute hepatitis, fulminant hepatic failure, continual hepatitis, cirrhosis, or asymptomatic elevation of serum aminotransferases. Neurologic signs similar to dysarthria, clumsiness, tremor, and mood problems 273 could or is most likely not current. The prognosis is supported by documenting a low serum ceruloplasmin stage, excessive urinary copper excretion, and elevated hepatic copper concentrations on liver biopsy. Wilson illness is a doubtlessly deadly treatable dysfunction that must be promptly diagnosed. Patients presenting with synthetic liver failure should be promptly referred for liver transplant analysis. In the latter case, this can be related to both unintended or purposeful overdose.
Syndromes - Fainting or feeling light-headed
- Excessive sweating (night sweats)
- Cancer
- Washing of the skin (irrigation) -- perhaps every few hours for several days
- Has it increased recently?
- Weakness
- Sweating
- Loss of appetite
Buy super viagra 160mg amexIt was once common practice to settle for lower standards for glucose ranges in newborns due to the excessive frequency of low plasma glucose levels on the day of delivery erectile dysfunction essential oils purchase super viagra 160 mg. Specific maturational delays in a quantity of of the fasting methods (metabolic, endocrine) adequately clarify why neonates have such a excessive risk of hypoglycemia through the first 12-24 hours after delivery. However, during the period of starvation it could additionally use ketones another (but not sole) supply for energy production. Glucose is derived either from the intestinal absorption of dietary carbohydrates (exogenous source) or endogenous manufacturing (glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis). Within 2-3 hours after a meal, glucose absorption from the intestine ceases, and the liver becomes the main supply of glucose for the brain and different tissues. The liver produces glucose via a mixture of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis provides roughly 25% of hepatic glucose manufacturing within the early phases of fasting; the rate of gluconeogenesis is determined largely by charges of proteolysis and remains fixed throughout fasting. Hepatic glycogenolysis offers the vast majority of glucose production early in a quick, however by 12 hours, liver glycogen shops turn out to be depleted. Most tissues can oxidize free fatty acids immediately and thus decrease their use of glucose. Partial oxidation of free fatty acids in the liver produces ketones (-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate), that are readily oxidized by the mind, thus sparing cerebral glucose consumption. Metabolic methods and hormones normally stop hypoglycemia during fasting (Tables 44. The integration of these systems is demonstrated by the modifications in plasma concentrations of the major fuels and hormones during the course of fasting. Plasma glucose concentrations gradually decline over the course of the fast as liver glycogen reserves are depleted. Plasma levels of lactate, a representative gluconeogenic precursor, decline in the course of the course of fasting as hepatic gluconeogenesis is stimulated and protein turnover slows. Plasma free fatty acid ranges start to rise rapidly after 12-20 hours of fasting in response to the fall in insulin concentrations as glucose ranges decline. The elevated availability of fatty acids is accompanied by a 10- to 20-fold rise in plasma 813 ketone levels as hepatic oxidation of fatty acids is activated. Determining the circulating levels of those fuels and hormones on the level of hypoglycemia supplies crucial data for diagnosing the purpose for hypoglycemia. Those within the 1st class outcome from activation of the autonomic nervous system and release of the counter-regulatory hormone epinephrine. Those within the 2nd category are secondary to inadequate supply of glucose to the brain (neuroglycopenia). The majority of cases are transient, though the neonatal period can additionally be the time when inherited problems are most likely to manifest. Plasma levels of lactate, a consultant gluconeogenic substrate, decline steadily through the quick as hepatic gluconeogenesis is activated. In addition, the enzymes needed for gluconeogenesis may be much less developed than in regular full-term infants. Infants of Diabetic Mothers Infants born to mothers with any kind of diabetes, including gestational diabetes, are in danger for hypoglycemia because of oversecretion of insulin in the course of the first few days after delivery. This transient neonatal hyperinsulinemia occurs as a outcome of maternal hyperglycemia stimulates fetal insulin secretion and, after supply, affected infants have difficulty in downregulating insulin secretion to adapt to the withdrawal of the hyperglycemia. Because of the growth-stimulating effects of insulin on the fetus, infants of diabetic mothers are often massive for gestational age. Blood glucose levels must be monitored after start till they stabilize in the normal range. Enteral feedings should be initiated as quickly as possible to stop fasting hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia should be treated with intravenous glucose; the issue ought to resolve promptly, within 1-2 days. Perinatal Stress-Induced Hyperinsulinism Some infants with start asphyxia or intrauterine progress restriction may have extreme issues with hypoglycemia for prolonged periods, ranging from a few days to a few months after birth. The low blood glucose levels in these infants have been attributed to high plasma insulin concentration. The current prevention and management of Rh sensitization have markedly lowered the incidence of erythroblastosis and of fetal and neonatal anemia. Nonetheless, such infants require cautious monitoring of plasma glucose focus soon after birth. By the 2nd day of life, the frequency of plasma glucose concentrations below 50 mg/dL decreases to less than 1%, which indicates a fast maturation of fasting metabolic adaptation. The extraordinarily poor fasting tolerance on the day of delivery could be explained by lack of development of key enzymes in the pathways of each hepatic gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis. Transcription of those genes is delayed until after supply however becomes well activated by the end of the first 24 hours. Glucagon and cortisol could additionally be essential for activation of enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis. Thus, on the day of start, all newborns may be considered as having impaired fasting adaptation. Breast-fed infants are at particular threat for hypoglycemia when there are problems initiating milk manufacturing. Intrapartum Maternal Glucose Administration Administration of excessive glucose quantities to the mother during labor leads to maternal as nicely as fetal hyperglycemia. In addition, excessive fetal blood glucose and insulin ranges can also cause a rise in fetal blood lactate concentration and metabolic acidosis. These effects are extra pronounced if the mother has obtained infusions of glucose for a prolonged time. Maternal Drug Therapy the assorted pharmacologic agents administered to the mother for the treatment of medical problems that may affect blood glucose ranges in the newborn could be divided into 2 broad classes: 1. Some medicine, together with oral hypoglycemic agents, can immediately have an effect on blood glucose. Oral hypoglycemic agents, such as chlorpropamide and sulfonylureas, are administered by some physicians for the therapy of gestational diabetes. Because these medication are simply transported throughout the placenta, the infant is born with a sure quantity of drug present within the circulation. These drugs, significantly these with prolonged effects, may end in profound hypoglycemia that tends to persist till the drug is eliminated, both by its personal clearance or by change transfusion. Some drugs are administered to the mom with oblique effects (the extra common contributor to neonatal hypoglycemia). Affected infants are usually massive for gestational age and present with symptoms of hypoglycemia within the 1st days after delivery. The hypoglycemia is often extremely severe, and treatment may require intravenous glucose infusions at 20-30 mg/kg/min (4-6 occasions normal) to keep plasma glucose within the normal range of 70-100 mg/dL.
Purchase super viagra mastercardFluoxetine and citalopram are present in comparatively high concentrations in breast milk erectile dysfunction drugs and medicare generic super viagra 160 mg with visa. Iron and folate dietary supplements (and prevention towards hookworm and malaria) are recommended in plenty of creating nations. Parenteral iron may be given (to these with iron deficiency anaemia not tolerating oral iron) as iron dextran or iron sucrose. Hb rises by 8g/L /week over 6 weeks, so late extreme anaemia (Hb <90g/L) might have blood transfusion. Prenatal analysis is possible by chorionic villus sampling (p15) for thalassaemias anticipated by parental blood research. They are nonetheless prone to sickling crises in being pregnant and the puerperium, so antenatal analysis is essential. Transmission also with viral load >400 copies/mL, seroconverision during pregnancy, superior disease, preterm labour, hepatitis C. Premature labour If membranes rupture >34wks expedite delivery, whatever the maternal viral load. Assess renal operate; check with nephrologist if creatinine >120mol/L, protein excretion >2g/24h (use thromboprophylaxis if >5g/24h). Postnatal � Encourage breastfeeding (insulin, metformin, and glibenclamide are suitable with breastfeeding) � Encourage pre-pregnancy counselling earlier than next pregnancy � If preproliferative retinopathy evaluate ophthalmologically for 6 months � Discuss contraception. Withdraw remedy after 6�12 months for four weeks to see if long-term remedy is required. Hypothyroidism may be related to postpartum despair, so verify thyroid status of women with postpartum despair. Viral hepatitis and gallstones could cause jaundice in being pregnant and investigation is similar to the non-pregnant. Bile acids are a test usually solely requested in being pregnant and if raised, diagnose obstetric cholestasis. Plasmodium falciparum malaria is dangerous (and complicated) in being pregnant, significantly in these with no malaria immunity. Other associations between falciparum malaria and being pregnant are anaemia, miscarriage, stillbirth, low birth weight, and prematurity. Non-resistant vivax, ovale, and malariae are treated with chloroquine orally over three days with weekly dose to stop relapse during being pregnant. If an infection peripartum, anticipate fetal misery, fluid-balance problems, and hypoglycaemia in labour. Mothers residing in endemic areas Chemoprophylaxis improves birthweight (by ~250g, with fewer very low birthweight babies). Glycosuria in being pregnant often displays altered renal physiology somewhat than hyperglycaemia. Trimethoprim and nitrofurantoin are protected options but avoid trimethoprim in the 1st trimester (antifolate action) and nitrofurantoin within the third (neonatal haemolytic anaemia). Acute cystitis affects 1%, characterised by urinary frequency, urgency, dysuria, haematuria, and lower stomach pain. Pyelonephritis Affects 1�2% of pregnant girls and is more common due to dilatation of higher renal tract in pregnancy. Patients with marked anaemia, hypertension, retinopathy, or heavy proteinuria should avoid pregnancy as additional deterioration in renal perform could additionally be anticipated. Pregnancy for these on dialysis is fraught with issues (fluid overload, hypertension, pre-eclampsia, polyhydramnios). Outcome is better for these with renal transplants, however as much as 10% of moms die inside 7 years of giving birth. It is categorized in accordance with seizure type: main generalized epilepsy (tonic�clonic seizures, absences, myoclonic jerks), and partial or focal seizures which may progress to secondary generalization (complex partial seizures) of which temporal lobe epilepsy is part. Those with poorly managed epilepsy are most probably to expertise a deterioration (check drug compliance). Obstetrics Respiratory disease in pregnancy Oxygen demand will increase considerably in pregnancy, because of raised metabolic fee and consumption. Asthma is common, affecting up to 7% of ladies in pregnancy and is due to reversible bronchoconstriction of airways from smooth muscle spasm, together with inflammation and increased mucous manufacturing. For most girls bronchial asthma remains unchanged or improved, but it might worsen (especially if poorly controlled to start with). Severe and/ or poorly managed bronchial asthma could result in fetal development restriction and preterm labour. Onset is insidious, with cough, haemoptysis, weight reduction, and evening sweats, and may cause coarse crackles within the upper lobes and lymphadenopathy. Treat with rifampicin, isoniazid (plus pyridoxine), and pyrazinamide and/ or ethambutol. Most are gentle to moderate involving skin, however these with renal involvement and hypertension could deteriorate and are vulnerable to pre-eclampsia. Aspirin 75mg day by day ought to be began prior to conception and continued throughout pregnancy, and the fetus must be carefully monitored. Postpartum, use either heparin or warfarin (breastfeeding contraindicated with neither) as danger of thrombosis is excessive. It tends to fall once more after delivery (often leading to an enchancment and tricking medical doctors into stopping antihypertensives too early) peaking again at day 3�4 postpartum. Remember to use the correct cuff size-using a small cuff on a large arm results in a falsely elevated studying. These ladies have the next danger of developing pre-eclampsia (double if on treatment), fetal development restriction, and placental abruption. If hypertension is secondary to another disorder contain a specialist in hypertensive disorders. Change methyldopa to one other antihypertensive publish supply as threat of postnatal melancholy. Avoid diuretics if breastfeeding (labetalol, atenolol, metoprolol, captopril, and enalapril are safe). There is an elevated danger of growing pre-eclampsia (15�26%) especially with earlier onset of hypertension. Management: Assessment in secondary care, with urine testing for proteinuria with automated reagent strip readings or urine protein/creatinine ratio testing to rule out pre-eclampsia. If treatment continues to be needed at 6 weeks arrange evaluate with specialist in hypertensive disorders. Other postpartum danger elements include mid-cavity or rotational instrumental delivery, postpartum haemorrhage and blood transfusion. Postnatally, enoxaparin can be given as quickly as possible so long as no ongoing postpartum haemorrhage, and >4h since epidural sited or eliminated. Obstetrics Thrombophilia in pregnancy Thrombophilia is the tendency to elevated clotting and there are many underlying causes.
Discount super viagra on lineFurthermore erectile dysfunction treatment time order online super viagra, it should accomplish this task with out excessive irritation or the event of autoimmunity. Antibody-mediated immunity (humoral or B cell immunity) is mediated by bone marrow-derived B lymphocytes and plasma cells (differentiated antibody-producing cells), which release antibodies (immunoglobulins) into secretions, plasma, and interstitial areas. Antibodies work to opsonize and promote phagocytosis of organisms, neutralize toxins, and lyse pathogens (with the help of complements). Cell-mediated immunity (T cell immunity) is mediated by thymus-derived T lymphocytes. The phagocytic system consists of tissue macrophages and dendritic cells, as properly as blood-borne monocytes and neutrophils. In response to specific alerts, phagocytes ingest and kill invading microorganisms. The complement system acts synergistically with antibodies and the rest of the immune system to help clear microbial infections each directly (complement-mediated cytolysis) and indirectly (recruitment of phagocytic cells, opsonization of microbes). The differential diagnosis for patients with recurrent infections is formidable in view of the complexity of the immune system. The completely different arms of the immune system are interconnected, thus related infections may happen as a manifestation of phagocyte, humoral, cellmediated, or complement disorders that may be inherited or acquired (Table 41. Alternatively, extremely attribute infections can level to a defect in a selected arm of the immune system (Table forty one. Because of the low chance of identifying a discrete immune defect, the first physician faces the difficult determination in regards to the extent of the evaluation and which patients merit a whole evaluation. In addition, different genetic defects within the immune system lead to recurrent episodes of spontaneous inflammation. A single continual an infection could wax and wane with intermittent, insufficient remedy and will manifest as a sequence of infections. Furthermore, a detailed history can elucidate different danger components for recurrent infections. Many nonimmune problems are characterised by an elevated susceptibility to infection that must even be considered (see Table 41. A detailed historical past can provide clues as to the probability and nature of a major immune deficiency (Table 41. Infants previously placed on ventilators could develop persistent obstructive lung disease (bronchopulmonary dysplasia), predisposing them to recurrent pulmonary infections. Attention ought to be paid to the time of umbilical twine separation since infants with a history of delayed umbilical cord separation and recurrent episodes of sepsis or pneumonia should be evaluated for leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Medical History A variety of nonimmune medical issues can end result in recurrent infections (see Table forty one. Approximately 30% of youngsters with recurrent sinopulmonary symptoms can be categorized as atopic (allergic on a hereditary basis). The bodily examination of allergic school-aged youngsters may reveal typical characteristics including the following: dark circles underneath the eyes; open mouth with dry lips; coated tongue; proof of nasal obstruction; transverse nasal crease; boggy, pale nasal mucosa; mucus within the pharynx; posterior pharyngeal "cobblestoning"; and postnasal drip. Chronic treatment with corticosteroids and different immunosuppressants may end up in acquired immunodeficiency and recurrent infections. Anatomic Abnormalities Recurrent infections in primary immune deficiencies usually have an effect on totally different anatomic areas. Structural or anatomic defects usually end in recurrent infections which may be generally localized to the affected organ system. Approximately 10% of children with recurrent infections have an underlying continual disease or a structural defect that predisposes them to recurrent infections (see Table 41. Bacteria Escherichia coli (sepsis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis) Klebsiella pneumoniae (sepsis, pneumonia) P. Chronic Granulomatous Disease Bacteria (soft tissue, lymphadenitis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis) Catalase-positive organisms. Other Phagocyte Defects (Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency Hyperimmunoglobulin E, Ch�diak-Higashi syndrome, specific granule deficiency, Rac-2 deficiency) Bacteria (soft tissue, pneumonia, lymphadenitis) Pseudomonas species, S. Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (sepsis, sinopulmonary infection) Haemophilus influenzae (sepsis, meningitis, arthritis, sinopulmonary infection) Streptococcus pneumoniae (sepsis, meningitis, arthritis) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (sepsis, pneumonia) Mycoplasma species (arthritis, pneumonia) Salmonella species (enteritis) Campylobacter species (enteritis) 2. Viruses Enterovirus, together with polio vaccine (encephalitis, paralysis, myositis, arthritis) Rotavirus (enteritis) three. Combined B and T Cell Defects (Congenital, Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, Immunosuppression Malignancies) A. Fungi Cryptococcus neoformans (sepsis, meningitis) Histoplasma capsulatum (pneumonia, disseminated disease) Coccidioides immitis (pneumonia, meningitis) C. Right middle lobe syndrome and sequestered lung can appear as recurrent pneumonia in the same anatomic location. Any direct communication to the cerebrospinal fluid that bypasses the blood�brain barrier predisposes patients to a central nervous system infection. Basilar cranium fractures and dermal sinus tracts or fistulas may communicate with the subarachnoid area or neural tissue. Other conditions predisposing patients to opportunistic infections of the central nervous system embody penetrating international physique, cerebrospinal fluid shunts, myelomeningocele, and encephalocele. Local infections of the sinuses or of the center ear may spread to contiguous structures to kind cerebral abscesses or subdural-epidural empyema. Intravenous drug abuse, bacterial endocarditis, and heart illness with right-to-left shunt are associated with an elevated danger of central nervous system infections. Genetic defects of immunity could be inherited as X-linked, autosomal recessive, or autosomal dominant problems. A household history of unexplained toddler deaths or serious an infection must be sought, particularly in male infants since a selection of necessary immune deficiencies are X-linked. Evidence of consanguinity ought to be sought as many serious primary immune deficiencies are autosomal recessive. Since allergic diseases can appear as recurrent infections, a family history of atopy is necessary. A baby who has 1 allergic father or mother or 2 allergic parents is predisposed to allergic reactions by 25% and 50%, respectively. Environmental History the incidence of respiratory disease is elevated in kids exposed to cigarette or marijuana smoke or different noxious fumes (woodburning stove) within the house. Respiratory and dermatologic findings are seen because of publicity to environmental allergens and toxins. A travel history might counsel exposure to uncommon organisms that are regionally endemic, corresponding to certain parasites and particular insect or animal bites, or to contaminated water. A transfer to a brand new home or to a new nursery school or publicity to a new babysitter, pet, or housekeeper may suggest attainable allergic and infectious risks. Physical Examination Eustachian tube abnormalities or cleft palate result in recurrent or persistent otitis media; congenital heart disease ends in an increased danger of endocarditis; and posterior urethral valves, vesicoureteral reflux, or ureteral pelvic junction obstruction ends in recurrent urinary tract infections. Recurrent pneumonia might end result from congenital malformations (trachea-esophageal fistulas, cystic adenomatoid malformation, or sequestration), from aspiration of a international physique (peanut, small toys) or persistent aspiration (gastroesophageal reflux or swallowing disorders), and from bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Repeated pneumonias in dependent lobes warrant evaluation for recurrent aspiration. Chronic sicknesses that lead to recurrent pulmonary infections embrace cystic fibrosis, primary ciliary dyskinesia, or 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Recurrent sinus infections can happen due to anatomic defects of the sinuses (polyps, stenotic os).
Buy generic super viagra 160 mg on lineVitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that induces the post-translational -carboxylation of the vitamin K-dependent substances (factors 2 erectile dysfunction treatment new york order 160 mg super viagra with visa, 7, 9, and 10; protein C; and protein S). This carboxylation step occurs after the protein is synthesized within the liver and should occur for the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor to bind calcium, the bridge to the membrane surface on which these proteins type complexes with different members of the clotting cascade and catalyze subsequent reactions. Vitamin K deficiency successfully renders these proteins unable to bind to a surface. Most of the vitamin K in adults originates from the food regimen and from bacterial production within the gut. Such infants might expertise diffuse bleeding and even central nervous system hemorrhage at 3-5 days of life. In the analysis of bleeding in a new child, the clinician should Physical Examination crucial dedication is whether or not or not the patient appears acutely or chronically unwell, together with important indicators and progress parameters. The nose must be examined for ulcers or anatomic bleeding websites, and the heart must be examined for the presence of murmurs (as occur in anemia and endocarditis). Joints should be examined for chronic arthropathy (as happens in hemophilia) or joint laxity (as happens in Ehlers�Danlos syndrome), and the extremities are examined for thumb or radial anomalies (thrombocytopenia�absent radius syndrome, or Fanconi anemia). The stomach and lymph nodes must be examined for the presence of hepatosplenomegaly and adenopathy. The examination of the skin ought to embrace a search for pallor, hematomas, petechiae, ecchymoses, telangiectasias, poor wound therapeutic (large or abnormal scars), lax (loose) skin, and varicose veins (possible deep venous thrombosis). Petechiae are pinpoint, flat, darkish red lesions brought on by capillary bleeding into the skin. All data are expressed as the imply adopted by the higher and decrease boundaries encompassing 95% of the traditional inhabitants. All values presented as the mean by the higher and decrease boundaries encompassing 95% of the inhabitants. Hematomas are accumulations of blood within the pores and skin or deeper tissues; in the skin, hematomas are raised and palpable. Bruises ought to be described intimately, including whether hematomas are related to bruises and whether or not petechiae are present. Purpura refers to any group of issues characterised by the presence of dark-red, purplish, or brown lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. The discoloration is brought on by the leakage of purple blood cells from affected vessels. Purpuric lesions could be attributable to abnormalities of the platelets, of coagulation proteins, or of vessel partitions. Coagulation Screening Tests After obtaining a history and performing a bodily examination, the clinician should decide the necessity for a hemostatic analysis. The history is prone to be the most sensitive screening device for a significant bleeding disorder, though its use in a very younger baby, particularly before toddler age, is proscribed and a focus should shift to the perinatal and family historical past. For patients with medical clues of a coagulation dysfunction, the preliminary screening studies should assess the clotting factors and platelet perform. When insensitive laboratory reagents fail to detect clinically vital deficiencies (most frequent in delicate factor 9 deficiency). Epistaxis (1) Duration, frequency, seasonal tendency (2) Associated trauma (nose selecting, allergy, infection) (3) Resultant anemia, emergency division evaluation, cautery b. Oral (gingiva, frenulum, tongue lacerations, bleeding after tooth brushing, after dental extractions requiring sutures/ packing) c. Bruising (number, websites, size, raised [other than extremities], spontaneous versus trauma, knots inside center, skin scarring) d. Musculoskeletal (1) Hemarthroses, unexplained arthropathy (2) Intramuscular hematomas b. Deep (1) Circumcision (2) Central nervous system bleeding (3) Gastrointestinal bleeding (4) Cephalohematoma (5) Unexplained anemia or hyperbilirubinemia (6) Delayed wire separation, bleeding after cord separation c. Onset, length, quantity (number of pads), frequency, persistence after childbirth b. Bleeding at childbirth (onset, length, transfusion requirement, historical past of traumatic supply, recurrences with subsequent pregnancies, spontaneous abortions) E. The objects simply listed ought to be applied to instant members of the family, particularly a history of easy bruising, epistaxis, extreme bleeding after surgical procedure, menorrhagia, excessive bleeding after childbirth, or a family history of others with recognized or suspect bleeding issues. Bleeding Time the bleeding time is an oblique measure of platelet number and a extra direct measure of platelet function, vascular integrity, and platelet interplay with the vascular subendothelium. As such, the bleeding time ought to be abnormal in patients with thrombocytopenia, platelet operate abnormalities, irregular collagen (Ehlers�Danlos syndrome), and von Willebrand illness. Platelet Function Analysis Platelet function evaluation was originally recommended as a screening take a look at for von Willebrand illness and platelet perform defects. Its sensitivity and specificity are inadequate for diagnosis, but it could have utility as a display for extreme platelet perform defects in very small infants where rapid outcomes are needed and size prohibits collection of huge volumes of blood needed for platelet aggregation testing. Thrombin Time and Reptilase Time the thrombin time and reptilase time are tests that measure the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. The thrombin time is sensitive to heparin impact, whereas the snake venom reptilase time stays regular in the presence of heparin. Both the thrombin time and the reptilase time are prolonged by uremia, by dysfibrinogenemia, and by low fibrinogen levels (<75 mg/dL). Common complaints embrace prolonged, frequent nosebleeds; gum bleeding; prolonged bleeding after tooth extraction; menorrhagia; and straightforward bruising with or with out petechiae formation. Mucocutaneous bleeding is usually associated with abnormalities of platelet number or perform, of platelet cofactors, or of the vessel wall. After publicity to the viral an infection, an antibody that binds to the platelet membrane develops, resulting in the untimely destruction of the antibody-coated platelets in the spleen. To rule out heparin effect, the thrombin time is in contrast with the reptilase time. If the thrombin time is considerably longer than the reptilase time, heparin is current in the sample. The family should be advised that the kid should avoid actions that increase the danger of head injury. Treatment ought to be reserved for kids at excessive risk for medical bleeding (platelet depend <20,000/mm3 and kids with petechiae and mucosal hemorrhages). Some authorities argue that patients with mucous membrane purpura are at larger risk and undoubtedly require treatment. Options for preliminary therapy for sufferers careful history aimed at detecting symptoms. The bodily examination must be detailed and include a search for signs of malignancy. The presence of enormous platelets on the smear or measured as a excessive mean platelet quantity suggests accelerated thrombopoiesis and increased platelet destruction. Sequestration Specific to the neonate *These hereditary thrombocytopenias can be related to normal or increased bone marrow megakaryocytes. Transfusion of platelets ought to be reserved for lifethreatening bleeding, as a outcome of transfused platelets are rapidly destroyed. These patients usually have a tendency to be older (adolescent) girls or to have had an insidious onset of symptoms. Neonatal Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is common, especially in sick newborns.
Effective super viagra 160mgThis happens in states of extreme potassium depletion (H+ strikes in erectile dysfunction pump.com best 160mg super viagra, whereas K+ exits the cell, to keep electroneutrality). One of the components answerable for this sort of alkalosis is the associated volume contraction, which outcomes in elevated bicarbonate reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the kidney. Failure of Acid Excretion In both acute and continual renal failure, the kidneys fail to excrete the acid produced from normal daily metabolism. Both H+ and anions accumulate in the physique, leading to slow consumption of bicarbonate stores. However, the acidosis is usually not extreme except a markedly catabolic state happens or different related conditions coexist. Increased mineralocorticoid ranges directly improve H+ secretion within the outer medullary accumulating duct. Hypokalemia promotes hydrogen ion secretion in the distal nephron and stimulates ammonia genesis in the proximal tubular cells. The alkalosis in sufferers with low urinary chloride is maintained by quantity depletion; quantity repletion is needed to right the alkalosis. In the process of volume depletion, there are losses of sodium, potassium, and chloride, however the lack of chloride is often larger than the losses of sodium and potassium mixed. Since chloride losses are the main cause of the amount depletion, these patients require chloride to appropriate the volume deficit and metabolic alkalosis; these sufferers have chloride-responsive metabolic alkalosis. Although that is the initiating factor, the alkalosis is sustained by concomitant Cl- and K+ losses. Secondary hyperaldosteronism, ensuing from quantity contraction, promotes further urinary potassium and H+ excretion, worsening the hypokalemia and alkalosis; urine is the supply of most of the potassium losses attributable to emesis. The diploma of metabolic alkalosis related to vomiting is mostly mild except in conditions during which gastric secretions are greatly stimulated. Metabolic alkalosis may additionally be seen in newborns of mothers with eating problems (bulimia). The baby displays the electrolyte modifications of the mom and sustains alkalosis due to the Cl- deficiency. This is a rare congenital syndrome characterised by a defect in small- and large-bowel chloride absorption that leads to a continual diarrhea with high chloride losses in the stool. The alkalosis is sustained because of hypochloremia, hypokalemia, and volume contraction with resultant secondary hyperaldosteronism. The metabolic derangements brought on by loop diuretics are identical to these seen in Bartter syndrome. Chronic hypercapnia, as seen in bronchopulmonary dysplasia or cystic fibrosis, leads to an elevated serum bicarbonate concentration from metabolic compensation. Affected sufferers have chloride depletion, which may be worsened by concomitant diuretic use. With resolution of the hypercapnia, the bicarbonate concentration stays high until the chloride depletion is corrected. Urinary Chloride Level Higher Than 20 mEq/L with Hypertension Pediatric sufferers with hypertension either have elevated levels of aldosterone or act as in the event that they do. Increased aldosterone "results" trigger renal retention of sodium, which ends up in elevated blood stress. The problems of mineralocorticoid extra are characterised by quantity expansion and hypertension (see Table 46. The mineralocorticoid excess stimulates the renal excretion of H+ and K+, resulting in metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia. The numerous causes could be differentiated by evaluating the renin-aldosterone axis. Treatment is aimed toward removing or correcting the supply of the mineralocorticoid extra. Urinary Chloride Level Higher Than 20 mEq/L with Normal Blood Pressure Bartter syndrome and Gitelman syndrome. These uncommon autosomal recessive disorders end result from defects in varied ion transporters within the nephron. Affected sufferers current with a history of failure to thrive, polyuria, polydipsia, and a tendency for dehydration. Children with Gitelman syndrome, however, are more prone to febrile seizures and tetanic episodes (Table forty six. Treatment of Metabolic Alkalosis Treatment focuses on correcting the underlying disorder and is decided by the pathophysiologic mechanisms of the alkalosis. Patients with a chloride-responsive metabolic alkalosis (urine Cl- <15 mEq/L) reply to volume repletion; both sodium and potassium chloride are needed. In rare cases, if alkalosis persists regardless of chloride supplementation, the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor acetazolamide can be utilized to increase urinary bicarbonate losses. In patients undergoing persistent gastric drainage, administration of either an H2 blocker or H+ pump inhibitor could be beneficial by reducing the gastric H+ secretion. The diploma of hypercarbia drives the signs in a affected person with respiratory acidosis. Patients with acute respiratory acidosis have extra signs than patients with chronic respiratory acidosis. The administration of respiratory acidosis is directed toward enhancing alveolar air flow and treating the underlying dysfunction. In a spontaneously breathing baby, this will outcome from fever, sepsis, delicate asthma, panic assault, or central nervous system issues. In the intensive care unit, the most common cause is mechanical overventilation of an intubated child. A metabolic response to an acute respiratory alkalosis is mediated by hydrogen ion launch from nonbicarbonate buffers and happens within minutes. Metabolic compensation for a respiratory alkalosis develops gradually and takes 2-3 days. Chronic respiratory alkalosis is the one acid�base disorder in which the pH may be completely normalized by the compensatory mechanisms. Symptoms of acute respiratory alkalosis could also be chest tightness, palpitations, lightheadedness, circumoral numbness, or extremity paresthesias. Respiratory acidosis may result from both pulmonary disease, such as in extreme bronchiolitis, or nonpulmonary illness, corresponding to a narcotic overdose. The parethesias, tetany, and seizures are thought to be associated to the lower in ionized calcium that occurs because alkalemia causes extra calcium to bind to albumin. The deviations in pH are more marked when 2 main events block the compensation of one another, similar to the mix of a metabolic acidosis and a respiratory acidosis seen in a patient with shock and respiratory failure. In distinction, within the presence of two opposing primary events, the pH may be normal or only minimally abnormal, as may be seen with combined vomiting and diarrhea. A mixed acid�base disorder is usually seen when neonates with respiratory acidosis brought on by persistent lung illness additionally receive diuretics, which can cause a metabolic alkalosis. The prognosis of blended acid�base disorder must be suspected within the following situations: If the compensation for the first occasion is absent or is out of the expected range.
References - Brizel DM, Wasserman TH, Henke M, et al: Phase III randomized trial of amifostine as a radioprotector in head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:3339, 2000.
- Johnson PC, Rolak LA, Hamilton RH, Laguna JF. Paraneoplastic vasculitis of the nerve: A remote effect of cancer. Ann Neurol. 1979;5:437-444.
- Kucher N, Koo S, Quiroz R, et al. Electronic alerts to prevent venous thromboembolism among hospital patients. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):969-977.
- Parke RL, McGuinness SP. Pressures delivered by nasal high flow oxygen during all phases of the respiratory cycle. Respir Care. 2013;58(10):1621-1624.
- Wright MF, Scollay JM, McCabe AJ, et al: Paediatric femoral hernia-the diagnostic challenge. Int J Surg 9:472-474, 2011.
- Trudel G, Marchand A, Ravart M, et al: The effect of a cognitive-behavioral group treatment program on hypoactive sexual desire in women, Sex Relation Ther 16(2):145n164, 2001.
|

