|
Samir A Abdulla MBChB FRCS - Associate specialist in general surgery with
- interest in upper GI and laparoscopic surgery
- Queens Hospital, Burton on Trent, UK
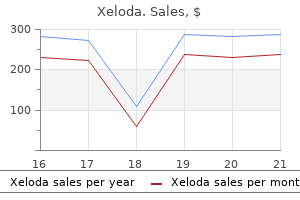
Xeloda dosages: 500 mg, 500 mg
Xeloda packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 40 pills

Trusted xeloda 500 mgNote the herniated liver is slightly larger in signal compared to menstrual cramps 9dpo order xeloda cheap online the stomach portion suggesting edema. The heart is displaced slightly superiorly, but the axis was normal on the standard 4chamber view. Developing hydrops portends a very poor prognosis, so the affected person was handled with betamethasone. If hydrops is progressive regardless of therapy, think about referral to a fetal surgical procedure middle. This was monitored intently for development of hydrops, but on subsequent scans, it grew to become much less apparent. The primary differential for this look is a congenital diaphragmatic hernia. It is important to document an intact diaphragm and normal position of the stomach. Color Doppler is extremely helpful in conditions like this because the feeding vessel is usually straightforward to discover. This arises from the aorta, or different systemic vessel, and is usually readily identifiable by colour Doppler. The mass is triangular and hyperechoic, with the conventional lung floating posteriorly. The authentic communication with the foregut sometimes involutes, leading to a blind-ending pouch or cyst. High airway obstruction causes retention of fetal lung fluid and subsequent overdevelopment of the lungs. The right lung was regular and there was no proof of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia. This fetus survived but had sudden coarctation of the aorta with a stormy postop course due to pulmonary hypertension. Multiple cysts along the left chest, neck, and arm have fashioned due to congenital lymphatic obstruction. Normal lymphatic drainage anatomy with a patent jugular lymphatic connection is shown on the fetal right. The supply was uncomplicated, and intubation was not required, as suggested by the prenatal imaging. Arisoy R et al: Prenatal analysis and consequence of lymphangiomas and its relationship with fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Masslike areas of anechoic septated cysts are present within the subcutaneous tissues, distinguishing lymphangioma from pores and skin edema, which is usually diffuse and uniform. The medial portion of the mass abuts the airway, however the airway is broadly patent, and intubation was not required. There is compression of the guts resulting in hydrops with skin edema and ascites. At delivery, an endotracheal tube was positioned and the mass, a wellencapsulated teratoma, was immediately resected. Even when efficiently resected, there can be long-term morbidity from tracheomalacia. Simoncic M et al: Mediastinal teratoma with hydrops fetalis in a newborn and growth of chronic respiratory insufficiency. The echogenicity is closer to liver than lung, and there are fantastic linear striations. The anterior location and imaging look are classic for a normal thymus, which can be quite prominent in a fetus. The thymus shall be flanked on both side by the internal mammary arteries creating what has been referred to because the thybox. Bronchopulmonary Sequestration Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (Left) Axial ultrasound by way of the chest in a fetus with a left-sided diaphragmatic hernia reveals the liver showing as a uniformly echogenic chest mass, which is compressing the heart in opposition to the proper chest wall. Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Mediastinal Teratoma (Left) Coronal ultrasound through the anterior chest shows a large complicated mass. A teratoma can grow at a really rapid rate and shortly result in fetal decompensation. Congenital High Airway Obstruction Sequence Congenital High Airway Obstruction Sequence (Left) Axial ultrasound by way of the fetal chest shows hyperexpanded lungs with compression of the guts in the midline. Tracheal obstruction causes retention of fetal lung fluid and subsequent overgrowth. The abdomen is the obvious fluid assortment, but the small bowel is also herniated with the multiple interfaces creating a fancy appearance. The heart is displaced to the best, and the compressed proper lung is being measured by the calipers. Lymphangioma Lymphangioma (Left) Axial ultrasound shows bilateral, large, advanced, multiloculated chest wall masses. Lymphangiomas are typically soft tissue masses but can lengthen into the mediastinum. Bronchogenic Cyst Neurenteric Cyst (Left) Axial ultrasound via the chest exhibits a centrally located, small, unilocular cyst, which remained stable throughout gestation. The secondary heart field lying contiguous with, but medial to , the first cardiac crescent populates the outflow tract and primordium of the best ventricle. As the embryo elongates and folds, the limbs of the crescent come collectively within the midline and fuse, creating the heart tube (which moves into the thorax). The proximal, venous pole remains anchored dorsal and will turn into a part of the atria, whereas the arterial pole bends rightward and ventral and can turn out to be the outflow tract. The right and left ventricles are proven in addition to the eventual right atrium and great vessels. The left ventricle is derived from the primary heart subject (red), the right ventricle, and outflows from the secondary heart subject (blue). The tertiary subject (orange) contributes to formation of the atria and offers mobile components to the ventricles. Note the moderator band within the trabeculated proper ventricle; this can be used to determine the morphologic right ventricle, which ought to always be the anterior ventricle. Note that the flap of the foramen ovale is within the left atrium, which signifies right-to-left circulate with the oxygenated stream of blood from the umbilical vein and ductus venosus crossing to the left to present oxygenated blood to the mind. The tricuspid valve is seen in cross part in the middle of the right ventricular cavity. A defect on this space could simply be an isolated perimembranous ventricular septal defect but can also be present in association with proper ventricular outflow tract or conotruncal lesions, similar to tetralogy of Fallot or double outlet right ventricle. It permits one to lay out the main pulmonary artery and the ductus arteriosus because it runs posteriorly, toward the spine, to join the descending aorta. The regurgitation is secondary to myocardial ischemia and impaired ventricular contraction. Note the right vein is blue, so the probe is anterior and to the right of the fetus. The left superior vena cava drains into the proper atrium through the coronary sinus, which is enlarged due to the increased quantity of blood entering it. Be careful to examine for anomalous pulmonary venous return to the coronary sinus, one other essential cause of dilation of this construction.
Purchase xeloda visaThe left ventricular wall has been completely destroyed women's health evergreen order xeloda from india, leaving 1 giant, irregular, porencephalic cyst. The thalami are preserved and there are fragments of medial cerebral hemisphere tissues. The lack of a normal cortical rind is the hallmark statement in hydranencephaly. The falx divides a fluid-filled calvarium with no cerebral tissue however preserved thalami. With the proper diagnosis of hydranencephaly (with dismal prognosis) labor was induced at 32 weeks to avoid operative delivery. The mass impact of the supratentorial ventricular dilatation is compressing the cerebellum. The posterior fossa is normal, including a well-seen normal 4th ventricle and vermis. Corral E et al: Prenatal three-dimensional ultrasound detection of adducted thumbs in X-linked hydrocephaly: two case reviews with molecular genetic studies. Even at this early gestational age, the top was measuring 10 days forward of the other measurements. This situation is related to extreme mental impairment and carries a 50% recurrence threat in male fetuses. Other findings embrace callosal dysgenesis, tectal beaking, an enlarged massa intermedia, and a medullary spur on the cervicomedullary junction. Progressive ventriculomegaly is common with Chiari 2, most probably because of progressive compressive pressure on the 4th ventricle. It is crucial to notice the dearth of fluid within the cisterna magna as a clue to Chiari 2 and never anticipate the banana signal to make the correct analysis. The future cisterna magnum is a 2nd lucency behind the echogenic linear choroid plexus throughout the 4th ventricle. Chapman T et al: Diagnostic imaging of posterior fossa anomalies in the fetus and neonate: part 2, posterior fossa problems. The temporal horns of the lateral ventricles are dilated as properly as the third ventricle. Similar views can be obtained prenatally using an endovaginal probe if the fetus is in a cephalic presentation. A cerebellar hemisphere has rotated into the position of the inferior vermis, just like the prior path specimen. This resolved in follow-up, in preserving with interval fenestration of the foramen of Magendie. Plane A will present the vermis however airplane B will show an obvious vermian defect because it goes via the cyst. One prenatal collection showed an obvious association between congenital coronary heart illness and Blake pouch cyst. The cavum septi pellucidi is visible, confirming the correct scan aircraft for measurement of the cisterna magna depth. These represent remnants of the partitions of Blake pouch, which enlarges when fenestration is delayed. There is elevated cerebrospinal fluid volume in the posterior fossa, but the vermis is structurally normal and not rotated. The vermis was present on this case however rotated superiorly, ensuing in the keyhole look seen between the cerebellar hemispheres. Data summarized from Sherer et al 2007, Zalel et al 2002, and Malinger et al 2001. Measure craniocaudal diameter (red line) from culmen superiorly to uvula inferiorly. Kobayashi Y et al: G�mez-L�pez-Hern�ndez syndrome in a Japanese patient: a case report. In this case, the malformation drains into the straight sinus, as depicted previously. Subsequent analysis for indicators of high-output cardiac failure ought to be carried out. There are diffuse ischemic changes (R > L) with areas of hemorrhage, that are widespread problems, particularly with giant shunts. The mind seems regular in this case and the toddler was developmentally regular on follow-up. Corral E et al: Thrombosis of the torcular herophili in the fetus: a sequence of eight circumstances. Because of compression of regular buildings, benign intracranial tumors are equally as deadly as malignant ones. The grayscale appearance overlaps with that seen with intracranial hemorrhage, so cautious analysis with Doppler is needed. This was a craniopharyngioma, however the imaging characteristics are indistinguishable from a teratoma. Hydrocephalus in this case may be from a mix of obstruction and overproduction. Note absence of the corpus callosum, which would usually be seen as a band of tissue connecting the 2 cerebral hemispheres. Also note the teardrop-shaped ventricles (colpocephaly) typical of agenesis of the corpus callosum. Colpocephaly, with the pointed anterior frontal horns, is nicely demonstrated in this case. Note the gap between the cerebral hemispheres the place the normal corpus callosum should be visible. In this case, agenesis of the corpus callosum was isolated and the infant did nicely. The measurement (calipers) was taken at the degree of the atrium where the dorsal choroid plexus (the glomus) resides. The findings, together with amniocentesis results, have been diagnostic of a 2nd child affected with X-linked aqueductal stenosis. Superior frontal horn is considerably "squared", and the inferior frontal horns level down. Essential to have a look at cranium vault from a number of scan planes Refraction of beam might create artifactual defect Must know normal anatomy 216 radiologyebook. The correct scan airplane exhibits the cavum, thalami, and central midline echo, and the head form is oval appropriately. Lemon-Shaped Lemon-Shaped (Left) Axial ultrasound exhibits bifrontal concavity in a 19week fetus. While a lemon-shaped head can be a normal variant, it ought to set off a cautious analysis of the fetus. Lemon-Shaped Strawberry-Shaped (Left) Axial ultrasound shows the typical configuration of the strawberry-shaped head, which is extensive side-to-side and shortened front-to-back. Note the big cavum septi pellucidi; this has been observed in aneuploid fetuses. Strawberry-Shaped Craniosynostosis (Left) 3D surface-rendered ultrasound exhibits a outstanding frontal "bulge" and broad flat nose in a fetus ultimately identified with Beare-Stevenson cutis gyrata syndrome.
Diseases - Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Petit Fryns syndrome
- Common variable immunodeficiency
- Urocanase deficiency
- Alport syndrome, dominant type
- Chondrosarcoma (malignant)
- Mastocytosis, short stature, hearing loss
- Epilepsy telangiectasia
- Non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder
Buy generic xeloda canadaRetrogastric adhesions are taken down to women's health center uiuc order generic xeloda online permit complete mobilization of the stomach, get rid of any redundant posterior wall of the pouch, and exclude the fundus from the gastric pouch. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Stomach pouch End-to-side sort of anastomosis between gastric pouch and Roux-en-Y limb B. Stomach musculature Longitudinal muscle of esophagus Outer longitudinal muscle layer of stomach (concentrated chiefly at lesser and larger curvatures and at pyloric part) Bypassed portion of abdomen Middle circular muscle layer of stomach Duodenum Jejunum Longitudinal muscle of duodenum C. Retrocolic retrogastric is the shortest path to the gastric pouch (tension free), whereas antecolic antegastric is the only of the three approaches. The higher omentum is divided vertically in the midline, starting from the inferior fringe of the omentum to the transverse colon. The ligament of Treitz is recognized to the left of midline, with the inferior mesenteric vein to its left. On making a retrocolic path for the Roux limb, a defect within the transverse mesocolon must be anterior and to the left of ligament of Treitz to avoid harm to the center colic vessels and to the pancreas. The left gastric artery is the main arterial provide to the gastric pouch, which arises from the celiac artery. Initially, it runs superiorly and to the left to approach the gastroesophageal junction, where it provides rise to esophageal branches, turns inferiorly to observe the lesser curvature of the abdomen, and terminates by anastomosing with the much smaller right gastric artery. In 25% of circumstances, the left gastric artery also provides rise to the left hepatic artery (or accessory left hepatic arteries), which runs via the superior a part of the gastrohepatic ligament. During Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, several inside defects should be closed with working nonabsorbable suture to keep away from inner hernia. Bleeding and leakage may also happen however are minimized with good surgical approach. Late fistulization from the small gastric pouch remnant to the massive residual stomach is an uncommon reason for failure. Cross section of stomach vasculature (coronal view) Common hepatic artery Left hepatic artery Proper hepatic artery Right hepatic artery Gastroduodenal artery Left gastric artery Celiac artery Superior mesenteric artery Splenic artery B. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid weight problems: approach and preliminary results of our first 400 sufferers. Omental wrap: a easy approach for reinforcement of the gastrojejunostomy during Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. More than 650,000 cholecystectomies are carried out each year, with the bulk accomplished by laparoscopic methods. By far probably the most frequent indication for cholecystectomy is symptomatic gallstone disease. This represents the commonest anatomic variation but is current in only 50% to 70% of patients. Replaced widespread hepatic artery taking origin from superior mesenteric artery Left gastric artery Splenic artery Gastroduodenal artery 2. Proximal bifurcation of hepatic artery or right and left hepatic arteries originating individually from celiac trunk 3. Pain classically happens 30 minutes to 2 hours after the ingestion of a fatty meal and varies in severity. This presentation as biliary colic might progress to an acute inflammatory state promoted by the impaction of a stone in the neck of the gallbladder. In one other complication of gallstone disease, gallstone ileus, the stone erodes through the gallbladder wall and passes into the duodenum or colon. If the stone turns into impacted in the duodenum, it manifests as gastric outlet syndrome (Bouveret syndrome). More typically, if it becomes caught within the terminal ileum, the stone manifests as small bowel obstruction with pneumobilia. Sites of pain in biliary colic Ampullary stone Persistent obstruction (acute cholecystitis) Edema, ischemia, and transmural irritation Sites of pain and hyperesthesia in acute cholecystitis Parietal epigastric or right higher quadrant pain outcomes from ischemia and inflammation of gallbladder wall caused by persistent calculous obstruction of cystic duct. The creator recommends starting the planned procedure laparoscopically, but with a low threshold for conversion to open cholecystectomy in patients with suspected Mirizzi syndrome, gallbladder most cancers, or unusual anatomic variation and sufferers with severe portal hypertension. Pneumoperitoneum is achieved by the placement of a 10-mm umbilical trocar using the open technique or by the use of the Veress needle. The Critical View Ideal retraction of the gallbladder is exercised by its fundus in a cephalad trend and by its neck in a lateral manner. Position of the affected person with the pinnacle up (reverse Trendelenburg) and the proper facet up, along with a decompressed stomach, is really helpful. Once this important view is confirmed, the cystic artery and the cystic duct are controlled and ligated. Some surgeons are "routine cholangiographers," whereas others make use of selective cholangiography. Cystic duct divided between ligatures and transfixed with further suture Cystic artery Transfixion suture Cholangiocatheter Common duct 1. Gallbladder retracted towards fundus Peritoneal edge Gallbladder mattress in liver Critical view in open and laparoscopic cholecystectomy the critical view in open cholecystectomy. The creator uses a dynamic cholangiogram with fluoroscopy to observe the infusion of 50% diluted contrast through a preflushed soft, 5-Fr tube with a 1-mL occlusion balloon. In some patients, the administration of intravenous glucagon is required to achieve passage of distinction into the duodenum. If segmental biliary duct injury is suspected, identification of all intrahepatic segmental ducts is obligatory. Gallbladder Removal and Extraction the gallbladder is dissected from the liver bed with cautery, reaching complete hemostasis and guaranteeing no other tubular buildings are divided. The gallbladder specimen is opened within the working room and verification of proper anatomy established. Cholecystography, cholangiography, portal venography 2 Cholecystography�routes of dye and possible factors of blockage: 1. Failure of gallbladder (diseased) to focus B four 5 Oral route three Intravenous route 1 Cholecystogram C Cholangiogram (through biliary fistula) Portal venogram (into spleen through abdominal wall) D B-D. Cholangiogram Cholangiogram (into gallbladder via laparotomy or peritoneoscope) Portal venogram Routes for cholangiography and portal venography Portal venogram (into mesenteric vein via laparotomy) E E. The dissection begins exactly as described for the laparoscopic method until the critical view is achieved. The fundocystic approach also has been suggested as a safer method in tough laparoscopic cholecystectomies. If the affected person is unfit for surgical procedure, resuscitation and percutaneous drainage can arrest the systemic inflammatory response to permit for an elective method later. In these populations the acute irritation of the gallbladder could be the results of stone pathology or ischemia (acalculous cholecystitis). Symptomatic gallstone illness is a standard surgical consultation in pregnant ladies. In basic, surgical procedure should be avoided in the course of the first and final trimesters if possible. Less frequently (17% to 23%) the cystic duct runs parallel to the hepatic duct for a distance and should even enter the duodenum separately. In 8% to 13% of individuals the cystic duct may enter the hepatic duct on the left aspect after passing in front of or behind the widespread hepatic duct.
Order xeloda 500mgOther contrast enhancement patterns include ovoid or punctate homogeneous enhancement menstruation yoga practice discount 500 mg xeloda with visa. Diffusion restriction is an uncommon imaging discovering and is related to a worse prognosis. Multifocal petechial microhemorrhages are present in the occipital cortex together with a quantity of areas of focal encephalomalacia secondary to infarction. Brewer J et al: Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in 46 of 47 patients with eclampsia. All findings resolved when the affected person was taken off chemotherapy and blood pressure normalized. Note the clotted blood extending outward from the left lateral ventricle into the medullary veins. On follow-up at 2 years old, this youngster has delicate spastic diplegia and delicate language delay. Chau V et al: Postnatal infection is related to widespread abnormalities of brain growth in untimely newborns. Ligam P et al: Thalamic injury in periventricular leukomalacia: novel pathologic observations related to cognitive deficits in survivors of prematurity. Kidokoro H et al: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in infants with periventricular leukomalacia. The lesions progressed to large areas of cavitation in the injured white matter during the next week (not shown). This is the most common location (deep white matter), which is why the term periventricular leukomalacia has been replaced. Note the small cerebellum (normal), which grows extra in later gestation and postnatally. Iron deposition from repeat transfusions also can contribute to marrow signal abnormality. Note the presence of "ivy" signal, branching abnormal hyperintensity within the cerebral sulci. The "ivy" signal is believed to happen secondary to slow collateral flow in engorged pial vessels. Thangarajh M et al: Magnetic resonance angiographydefined intracranial vasculopathy is associated with silent cerebral infarcts and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mutation in youngsters with sickle cell anaemia. Khademian Z et al: Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in youngsters with sickle cell disease. Such patients often have delicate cognitive impairment and are at increased risk of stroke. The vessels are mildly enlarged and tortuous, thought to happen as a pathophysiologic response to anemia and cerebral perfusion. This progressive vasculopathy finally leads to giant and small vessel injury. The patient offered 12 hours after symptom onset and was handled with aspirin solely. Encephalomalacia developed, however the affected person had a normal neurologic exam 6 months later. Children typically have a a lot higher capability for neurologic restoration than adults, even with related imaging findings. I 1 146 Demographics � Age Incidence/mortality biggest in infants < 1 year old � Gender Boys > girls pdf-radiology. Diagnosis was vasculopathy secondary to current an infection, exacerbated by minor trauma. The cerebral hemispheres are practically absent, however the thalami, brainstem, and cerebellum are intact. The posterior fossa and diencephalic constructions equipped by the posterior cerebral circulation are intact. Cecchetto G et al: Looking on the missing mind: hydranencephaly case sequence and literature evaluation. Note hemorrhagic foci involving gray matter of several contused gyri, axonal and deep gray accidents, and traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage in basal cisterns and sylvian fissure. The commonest areas of all are the anteroinferior frontal and temporal lobes. I 1 150 (Left) Gross pathology of the brain from a patient who died with closed head damage reveals bifrontal, temporal hemorrhagic contusions, as properly as traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage within the suprasellar cistern. Diagnostic Checklist Top Differential Diagnoses (Left) Sagittal graphic illustrates a number of diffuse axonal damage hemorrhagic foci within the corpus callosum and brainstem. There can additionally be a proper temporal lobe hemorrhagic contusion, in addition to subarachnoid hemorrhage inside most of the sulci and the interpeduncular fossa. Not proven are further lesions of the midbrain, right thalamus, and corpus callosum, as properly as bifrontal and left occipital lobe contusions. The lack of surrounding edema and superficial location is typical for ganglioglioma. The temporal lobe is the most typical location (> 75%) adopted by the frontal and parietal lobes. Deling L et al: Intraventricular ganglioglioma prognosis and hydrocephalus: the largest case collection and systematic literature review. Adachi Y et al: Gangliogliomas: Characteristic imaging findings and role within the temporal lobe epilepsy. The lack of surrounding edema and lack of great mass impact is typical of ganglioglioma. This mass confirmed a cyst with an enhancing mural nodule, classic for ganglioglioma. Thin section T2 imaging may be very useful for analysis of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Differential considerations would come with hemangioblastoma and pilocytic astrocytoma on this young grownup. Note the dominant cystic element with a dural-based plaque of desmoplastic stroma. Enhancement of the cortically primarily based strong portion with involvement of the adjoining pia and dura is characteristic of these rare tumors. Desmoplastic childish astrocytoma and ganglioglioma presents in infants as large tumors, typically approaching 13 cm. The glioneuronal parts are somewhat viscous areas intermixed with single or a number of firmer nodules. Note the cortically primarily based, sharply demarcated, wedge-shaped mass with a hyperintense rim. Daghistani R et al: Atypical characteristics and conduct of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. Bird-Lieberman G et al: Diffuse hemispheric dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a model new radiological variant related to early-onset extreme epilepsy. Bilginer B et al: Surgery for epilepsy in kids with dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: clinical spectrum, seizure consequence, neuroradiology, and pathology. The mass is general mildly hypointense relative to gray matter, though areas of hemorrhage are hyperintense.
Purchase xeloda australiaTerlipressin and albumin vs albumin in sufferers with cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome: A randomized examine rural women's health issues in canada order xeloda 500 mg online. Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome as outlined by the International Ascites Club by albumin and furosemide infusion according to the central venous pressure: A prospective pilot research. Vasopressin, not octreotide, could also be beneficial in the treatment of hepatorenal syndrome: A retrospective research. Noradrenalin vs terlipressin in patients with hepatorenal syndrome: A prospective, randomized, unblinded, pilot study. Russ Renal impairment can alter drug pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, and consequently patients with renal impairment are susceptible to opposed effects. In addition, these patients take multiple drugs and are at excessive danger of drug interactions and drug-related issues. This chapter describes pharmacokinetic principles and highlights frequent prescribing points in patients with renal impairment, dialysis, and transplantation. Increased absorption in patients with renal impairment from reduced first-pass metabolism is seen with some -blockers, dextropropoxyphene, and dihydrocodeine. Comorbidities in renal sufferers also have an effect; for instance, absorption could be erratic due to diabetic gastrointestinal neuropathy. If protein binding is decreased, a larger free fraction is available for any given whole drug focus, which may enhance drug activity. Organic acids normally have a single binding web site on albumin, whereas organic bases have multiple binding sites on glycoproteins. Protein binding may be altered in sufferers with renal impairment, particularly when serum albumin is low. Predicting the impact of modifications in protein binding is difficult as a outcome of although extra free drug is available at the website of motion, more is out there for metabolism or renal excretion. Hence, lower plasma concentrations can occur and drug half-life may decrease somewhat than improve. Phenytoin, for example, has marked decreases in protein binding in sufferers with renal impairment, and toxicity can happen regardless of normal or low complete plasma concentrations due to an increase in free fraction. With albuminuria, bound drug can also be lost, which can partially explain the refractoriness of nephrotic patients to diuretics. Volume of Distribution Bioavailability (F) is the portion of a drug dose that appears within the systemic circulation after administration by a nonintravenous route. Whereas medicine given intravenously have 100% bioavailability, medicine given by different routes cross via a collection of biologic membranes earlier than getting into the systemic circulation so that solely a fraction could attain the circulation. The gastrointestinal mucosa also acts as a barrier to absorption by metabolizing drugs or retarding absorption. Nausea and vomiting from uremia can impair absorption and contact time between the drug and gastrointestinal mucosa. In patients with superior uremia, the alkalinizing impact of salivary urea may lower absorption of medication optimally absorbed in an acid milieu. Metabolism Drug metabolism is primarily a hepatic perform by which drugs are converted to extra water-soluble entities to promote elimination by the kidneys and bile. Despite the assumption that nonrenal clearance is unchanged, renal impairment can alter and sluggish drug metabolism. Physicians should use medical judgment to evaluate each scenario individually, choose a dosage regimen based mostly on components in that affected person, and continually reevaluate response to therapy. Initial Assessment and Laboratory Data A targeted history is necessary in assessing dose in sufferers with renal impairment. Previous drug efficacy or toxicity should be decided and the present drug record reviewed for potential interactions or nephrotoxins. Physical and laboratory parameters point out volume status, height, weight, and extrarenal illness. Estimating Renal Function for Drug Dosage Table 77-3 Protein binding of drugs in renal illness. Quantitation of drug elimination by the kidney is expressed as renal clearance, which is dependent upon renal blood flow and the power of the kidney to remove the drug. Glomerular filtration is decided by molecular size (<10 kd), cost, and protein binding (increased when binding decreases). Secretion of medication eradicated by tubular transport might change with renal illness, but measurement of tubular perform is tough. The higher the degree of renal impairment, the higher the potential for dose modification. The Cockcroft-Gault equation has been essentially the most widely used and accepted technique for drug dosage calculation. An essential limitation of many renal perform estimates is inaccuracy of singlepoint estimates when renal operate is quickly altering. This may result in overestimation or underestimation of renal operate and underdose or overdose. Activity and Toxicity of Metabolites It is important to contemplate the activity (or toxicity) of drug metabolites along with that of the parent drug itself. Renally cleared metabolites can accumulate, leading to enhanced drug action or toxicity (Table 77-4). It is normally clinically essential to modify doses provided that the fe is bigger than 25% to 50%. The contribution of inactive nontoxic metabolites to overall renal drug elimination could exaggerate the potential for hurt. In this hypothetical example, 10% of the dose is excreted unchanged in urine (fe = 10%); 50% of the dose is metabolized to inactive metabolite M1, which is then all renally excreted; 30% of the dose is metabolized to inactive metabolite M2, which is all renally excreted; and the remaining 10% is excreted unchanged in bile. However, this 90% includes 10% as father or mother drug and 80% as inactive metabolites, and dose modification is probably not essential even in severe renal impairment. Total renal excretion of the dose is 90%; however, the clinically important fraction of active drug excreted in urine is 10%. Two examples of medicine with, on the left, a slim therapeutic index, and on the best, a large therapeutic index. Therapeutic Index of the Drug or Metabolites A wide selection of drugs may cause nephrotoxicity (Table 77-5). Obstructive uropathy can happen with tubular crystallization of acyclovir, statin-induced rhabdomyolysis, or tricyclic antidepressant use. In dialysis patients with no important residual renal perform, use of nephrotoxic medication could additionally be acceptable. The decision to modify dosage for patients with renal impairment is influenced by the therapeutic window or index of the drug. The therapeutic window is the vary of plasma drug concentrations spanning the minimal concentration for scientific efficacy and toxicity.
Buy xeloda 500 mgThe incontrovertible reality that a short-axis view of the ventricles is visible in this plane indicates that the guts can be rotated women's health center southern pines generic 500mg xeloda overnight delivery. The toddler had extended cardiac dysfunction after resection of the teratoma however finally recovered totally. Chamber Asymmetry Chamber Asymmetry (Left) Four-chamber view shows an abnormal axis secondary to dramatic proper atrial enlargement in a fetus with Ebstein anomaly. Conotruncal Malformation Heterotaxy, Cardiosplenic Syndromes (Left) In a fetus in cephalic presentation with backbone to the maternal proper, the fetal left aspect is anterior. The liver is anterior to the center due to diaphragmatic elevation, not a diaphragmatic hernia. Pulmonary Agenesis Pulmonary Agenesis (Left) Axial view of the chest in the identical case exhibits the cardiac apex directed posteriorly. The unilateral left lung agenesis was isolated on this case and the kid is alive and properly. In this case, there was mitral atresia so all the blood circulate from the lungs was going left to right on the atrial level. It is essential to take a glance at the relationship of the nice vessels to avoid missing related transposition. Both the primum atrial septal defect and inlet ventricular septal defect are seen. Ebstein Anomaly Ebstein Anomaly (Left) Four-chamber echocardiogram reveals a mitral valve within the normal position with a standard left heart. This is noted by the difference in arrow areas, which mark the hinge point of each valve. These patients sometimes do nicely after birth when the pulmonary vascular resistance falls. The roof of the yolk sac becomes incorporated in the form of a tube as a half of the primitive gut. Errors in development include communication between the foregut branches, such as a tracheoesophageal fistula. The arterial supply to the intestine is already outlined: Celiac artery (foregut), superior mesenteric artery (midgut), and inferior mesenteric artery (hindgut). The dorsal mesogastrium elongates, forming the left and caudal portions of the lesser sac. The gut continues to elongate and rotates counterclockwise (as viewed from the front) around the superior mesenteric artery throughout the dorsal mesentery. Common developmental errors include midgut malrotation, omphalocele, and imperforate anus. The leaves of the greater omentum elongate to the left and caudally, increasing the lesser sac and masking the transverse colon and small intestine. The yolk stalk, which linked the yolk sac to the primitive gut, is disintegrating. The cecum is the final half to return and continues to rotate in a counterclockwise path until reaching the proper lower quadrant. Errors in growth embody persistence of a half of the yolk stalk (Meckel diverticulum) and errors of bowel rotation. The small bowel and transverse and sigmoid colon remain intraperitoneal, suspended by their respective mesenteries. These are areas of mesodermal deficiency, which upon disintegrating turned the oropharyngeal cavity and space of the urethra and anus, respectively. This graphic reveals the start of disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane in the 4th week. It fuses with the cloacal membrane, dividing it into the anal and urogenital membranes, and types the perineal physique. They unite again to type the proximal vitelline veins, which be part of with the (initially) paired umbilical veins to enter the sinus venosus of the center. The left umbilical vein sends a large branch to the liver, which anastomoses with the plexus derived from the vitelline veins. The extrahepatic (distal) vitelline veins type the precursors to the portal venous system. The proximal components of the vitelline veins have become the hepatic veins, returning blood from the liver to the heart. The distal components have developed into the portal venous system, returning blood from the intestine to the liver sinusoids. Fluid-filled buildings, including the bladder, abdomen, & small bowel, are very excessive sign depth. The higher oblique axial image exhibits the lungs are mildly hyperechoic compared to the liver and spleen. Changes in echotexture often present clues regarding any pathologic course of in a given organ. Following the colon on ultrasound (top right) is somewhat harder, however the anal dimple image (bottom right) of the perineum should be performed in any case of suspected anorectal malformation. It has a classic doughnut or target look with a thick, hypoechoic sphincter and hyperechoic mucosa. Structures that should specifically be evaluated embody the stomach, kidneys, bladder, umbilical twine insertion website, and umbilical cord vessel quantity (the regular look of the kidneys and bladder are reviewed within the method to the genitourinary system). The abdomen modifications in size and form during the exam; fluid might intermittently be seen to enter the duodenal bulb however ought to never persist. Fluid should be visualized on each side of the umbilical twine in a transverse part of the fetal stomach to find a way to contemplate the insertion web site intact. Stimulation of fetal motion may be essential to create a more favorable acoustic window, particularly in the third trimester when the fetal knees are often tucked up towards the stomach wall. These could also be seen at the wire insertion web site, but the easiest way to verify a threevessel wire is to use color Doppler to document the umbilical arteries as they run on either facet of the bladder. If only viewed in the anterior coronal plane, a congenital diaphragmatic hernia could also be missed. In the setting of esophageal atresia, a fluid-filled tubular construction could additionally be seen within the fetal neck. Remember to use shade Doppler to ensure that the fluid-filled structure is between the neck vessels. Also be aware that standard fetal swallowing may trigger intermittent distension of the oropharynx. In the early midtrimester, bowel loops might not resolve as distinct "tubes"; the bowel is seen as the intermediate echogenicity "filler" between the stable organs, bladder, and stomach. The anal dimple may be seen on an axial view through the perineum; the anal mucosa is echogenic and is surrounded by the hypoechoic muscular tissues of the anal sphincter.
Standardized Extract of Grapefruit (Grapefruit). Xeloda. - How does Grapefruit work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Asthma, lowering cholesterol, hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), preventing cancer, weight loss, psoriasis, muscle fatigue, promoting hair growth, toning the skin, reducing acne and oily skin, treating headaches, stress, depression, infections, digestive complaints in people with eczema, yeast infections (as a vaginal douche), and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Grapefruit.
- What is Grapefruit?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96909
Buy xeloda 500 mg low priceSimilarly menstrual endometrium purchase xeloda toronto, there are many totally different polymicrogyria syndromes that depend upon the situation of the polymicrogyria. Bilateral frontal polymicrogyria is a unique entity than bilateral perisylvian polymicrogyria or bilateral parasagittal parietooccipital polymicrogyria; you will want to be specific in reporting the placement of the abnormality. If the cortex is abnormally thin and related to diminished underlying white matter, one should consider a prenatal injury (infectious or ischemic), particularly if the thinning is focal or multifocal. Make positive myelination is acceptable for age (there are many sources of regular myelination charts, together with journal articles and textbooks). Diffuse layers of hypomyelination or amyelination related to overlying polymicrogyria ought to elevate suspicion for congenital cytomegalovirus an infection. Also, search for nodules of heterotopic grey matter in the periventricular or deep white matter. Subcortical heterotopia typically extends from the cortex all the way to the lateral ventricular wall, whereas periventricular nodular heterotopia is more localized to the quick subependymal/periventricular region. Heterotopia might be difficult to differentiate from unmyelinated or injured white matter on T1-weighted images, so remember to look pdf-radiology. In specific, the basal ganglia are most likely to be dysmorphic in look in patients with subcortical heterotopia. In addition, the hippocampi are often abnormal in malformations of cortical growth. In sufferers with lissencephaly specifically, the hippocampi are incompletely folded. Look on the septum pellucidum; absence of the septum is seen in corpus callosum dysgenesis/agenesis, septooptic dysplasia, and in some circumstances of schizencephaly or bilateral polymicrogyria. Abnormally enlarged trigones and temporal horns are sometimes associated with callosal anomalies and pachygyria. In newborns, the vermis ought to extend from the inferior colliculi to the obex, whereas infants and older children should have a vermis that extends from the intercollicular sulcus to the obex. If the fissuration of the vermis seems irregular, take a look at an axial or coronal image to ensure the vermis is present; if the cerebellar hemispheres are steady and not using a vermis between them, make a analysis of rhombencephalosynapsis. If the 4th ventricle has an abnormal rectangular form (with a horizontal superior margin) with a slim isthmus and small vermis, take into consideration a molar tooth malformation. To confirm this diagnosis, look for the "molar tooth" signal of the lower midbrain, consisting of enormous, horizontal superior cerebellar peduncles extending posteriorly toward the cerebellum, and a longitudinal cleft within the superior vermis. Make positive that the components of the brainstem are of normal measurement; in a toddler, the height of the pons should be double that of the midbrain on the midline sagittal image. An important clue can be offered by wanting at the size of the pons compared to that of the cerebellar vermis. Since a lot of the anterior pons is composed of the decussation of the center cerebellar peduncles, growth hypoplasia of the cerebellum is kind of always associated with hypoplasia of the ventral pons. Remember that in a small posterior fossa, intracranial hypotension, or intracranial hypertension may end up in descent of the cerebellum beneath the foramen magnum. Look for causes of a small posterior fossa (clival anomaly, anomaly of the craniovertebral junction), intracranial hypertension (space-occupying mass, hydrocephalus), or evidence of intracranial hypotension (large dural venous sinuses, giant pituitary gland, "slumping" brainstem) earlier than making a prognosis of Chiari 1 malformation. A large anterior commissure is present, probably partly compensating for the small corpus. The affected cortex is undulating, establishing a analysis of proper frontal polymicrogyria. The overlying cortex can additionally be hyperintense in this case of focal cortical dysplasia. Note the absence of the midline septum pellucidum, a standard finding in bilateral schizencephaly. Looking on the (commonly affected) hypothalamus permits diagnosis of ectopic posterior pituitary gland. This discovering, plus the absence of frontal horns, offers the diagnosis of holoprosencephaly. Careful evaluation exhibits a very small vermis with a large, almost rectangular 4th ventricle. These findings, plus a very small isthmus, assist to set up the diagnosis of molar tooth malformation. Lami F et al: Holoprosencephaly: report of four cases and genotype-phenotype correlations. A single ventricular cavity is present, and not using a septum pellucidum or forniceal columns. No frank callosal splenium can be seen, although some white matter fibers appear to be crossing the midline simply above the lateral ventricles. In the world of interhemispheric continuity, grey matter encroaches on the ventricular lumen. Interhemispheric fissure was regular in the anterior frontal and the parietooccipital areas. Note the heterotopic gray matter on the ventricular roof and the poorly developed hippocampi. Note the verticalposterior course of the anterior cerebral artery and the radiating cingulate sulci. The ventricular lumen is compressed medially by the leaf of the septum pellucidum that contains rerouted callosal fibers (Probst bundle) above and forniceal column beneath. Demographics � Age Any age, classically identified in early childhood, most typical malformation present in fetuses � Gender M > F, if isolated discovering � Epidemiology 0. The posterior portion of the corpus callosum is missing, but the junction with the fornix appears preserved. Posterior coronals would present Probst bundles, whereas anterior pictures would appear normal. Probst bundles (uncrossed callosal fibers) type a thick dorsoventral bundle on both sides of the midline, medial to the corona radiata and lateral to the cingulum. Note the small residual islands of cerebral tissue from the frontal and temporal lobes. Heterogeneity of pathology is characteristic of this entity, making the etiology uncertain. Hemimegalencephaly is the only dysfunction that enlarges each the cerebral hemisphere and the ipsilateral ventricle. The "dirty" look of the unmyelinated white matter within the left hemisphere reflects the presence of heterotopic and dysplastic neurons. A hyperintense cell-sparse zone separates the skinny cortical ribbon from the thicker band of disorganized neurons, which is in flip separated from the ventricles by white matter. I 1 24 Demographics � Age Usually diagnosed early in life Mild/partial instances may have delayed presentation pdf-radiology. Note the refined low attenuation of the cellsparse zone in the proper occipital pole. The slightly hyperintense sign deep to the cortex represents the deep zone of disorganized neurons. Bright sign may be seen in the cellbetween the sparse zone thick subcortical band of disorganized neurons & thin superficial cortex. Bahi-Buisson N et al: New insights into genotype-phenotype correlations for the doublecortin-related lissencephaly spectrum.
Discount 500mg xeloda amexAntigen reacts with antibody (IgE) on membrane of sensitized mast cells and/or basophils women's health issues in sri lanka cheap xeloda uk, which respond by secreting pharmacologic mediators Vagus nerve Mast cell degranulation blockers Histamine Mucous gland hypersecretion Smooth muscle contraction Increased capillary permeability and inflammatory reaction Eosinophil attraction F. Both medication, usually inhaled as aerosols, can be used for intrinsic (antigen-induced) or extrinsic (non�antigen-induced) asthma. Nedocromil enhances corticosteroid results and is more potent than cromolyn in patients with extrinsic bronchial asthma (especially exercise induced); even when given after reexposure to antigen, it blocks delayed irritation. Both medicine are poorly absorbed, so antagonistic effects (eg, chest tightness, cough) are restricted to deposition web site. Both drugs alter Cl- channel perform, which (1) on airway neurons underlies cough inhibition, (2) on mast cells delays antigen-evoked bronchoconstriction, and (3) on eosinophils prevents inflammatory responses to antigens. Some agents, especially theophylline and 2-adrenergic agonists, inhibit late response inflammation. These medication are normally used when a persistent cough and bronchial constriction are current. In addition to enjoyable clean muscles and lowering airway reactivity, bronchodilators cut back coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Agents are normally given via inhalation, however some can be given orally or parenterally (intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous route). Most medication have a fast onset of motion (within minutes), but the effect normally wanes in 5 to 7 hours. The commonest bronchodilators are methylxanthines (eg, theophylline, caffeine), -adrenergic agonists (eg, isoproterenol, albuterol, epinephrine), and cholinergic antagonists (eg, atropine, tiotropium). Or, theophylline may block cell floor receptor effects of adenosine, which can induce bronchoconstriction and irritation. Theophylline, the most broadly prescribed and of low price, comes as short-acting tablets and syrups, sustained-release capsules and tablets, and intravenous doses. Even at low to reasonable doses, these medicine improve cortical arousal and application and defer fatigue. Methylxanthines reduce blood viscosity, improve blood flow, increase cardiac output, and induce tachycardia in wholesome subjects. These medication chill out bronchial easy muscle, inhibit mediator launch, enhance transport of mucus, and alter composition of mucus by stimulating adrenoceptors. Bronchodilation is mediated by 2 adrenoceptors which may be located on easy muscle cells in human airways. Nonselective -adrenoceptor agonists (eg, epinephrine, ephedrine, isoproterenol) stimulate all adrenoceptors (1 and a couple of classes). Selective drugs that activate solely 2 receptors (eg, albuterol, terbutaline, salmeterol) are the most commonly prescribed sympathomimetic agents. If preliminary response is insufficient, repeat at 30 to 60 minute intervals as wanted; oxygen as indicated. If response to epinephrine is insufficient or if affected person turns into refractory, give aminophylline intravenously very slowly; administer oxygen. These medication are potent, rapidly appearing bronchodilators, however their stimulation of the cardiac system is a critical disadvantage. Epinephrine is either inhaled or given subcutaneously and is the lively agent in lots of over-the-counter preparations. Maximal bronchodilation is achieved quarter-hour after injection and lasts approximately 90 minutes. Because this drug stimulates cardiac output, increases heart rate, and exacerbates angina, physicians not often prescribe it. Ephedrine, utilized in China more than 2000 years ago, has the longest history of use of any antiasthmatic. It has a longer duration of action, decrease efficiency, and larger oral exercise than epinephrine. Isoproterenol is characterized by a rapid onset of motion, with peak bronchodilation occurring inside quarter-hour of injection. The main drugs-metaproterenol, terbutaline, albuterol, salmeterol, and formoterol-have minimal 1-mediated effects on the nervous and cardiac techniques. The inhalation route allows the best native effects with the fewest adverse results. Inhaled brokers trigger bronchodilation that equals that of isoproterenol and persists for 4 hours. Terbutaline, the only drug that can be utilized subcutaneously, is given for extreme asthma assaults or if insensitivity to inhaled agents exists. Two new medication, salmeterol and formoterol, have an extended period of motion and high lipid solubility. Both medicine at excessive concentrations move slowly into airway clean muscle, so effects can last up to 12 hours. When stimulated, muscarinic receptors cause muscle contraction, which finally ends up in narrowing of the airways and bronchoconstriction. Muscarinic antagonists, or anticholinergics, prevent acetylcholine from producing smooth muscle contractions and extra mucus within the bronchi. However, these medication enhance bronchodilation induced by 2-adrenoceptor agonists, so patients often take both anticholinergics and a pair of agonists. Dry mouth, bitter taste, scratchy throat, and headache are the major adverse results. Corticosteroids Plasma clearance In chronic steroid administration, if dosage is withdrawn or suboptimal, extreme asthmatic exacerbations may happen. Lysosome stabilization Antiinflammatory impact Inhibition of antibody formation Possible inhibition of histamine formation/storage Steroid-resistant sufferers might require greater and steady dosage. Treatment with these agents improves signs of bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis. Corticosteroids inhibit late part allergic reactions (including late asthmatic response to antigen challenge) by varied mechanisms, eg, lowered (1) number of mast cells lining the surfaces of airway mucosal cells; (2) chemotaxis and activation of eosinophils; and (3) cytokine manufacturing by eosinophils, monocytes, mast cells, and lymphocytes. Corticosteroids taken often scale back bronchial reactivity, enhance airway quality, and decrease the severity and frequency of asthma attacks. Commonly used brokers are prednisone, methylprednisone, beclomethasone, flunisolide, budesonide, and mometasone. Intranasal corticosteroids relieve stuffy nostril, nasal irritation, and different discomforts. Spacers (chambers) may be attached to metered-dose inhalers to cut back the rate and particle size of the drug; the quantity of drug reaching the lungs is maximized, and the amount of drug deposited in the mouth is minimized. Spacers are crucial for therapy with corticosteroids, which have many opposed effects. The smaller, regular doses cut back facet impact risk and should remove a necessity for aerosol steroids. Short-term use (days) of prednisone can result in elevated appetite, weight gain, diarrhea, headache, mood modifications, and insomnia, and presumably hyperglycemia and hypertension. Cessation of shortterm corticosteroid use or taking smaller doses of these brokers normally minimizes or eliminates the consequences. Efforts to develop safer corticosteroids with antiinflammatory properties however lacking antagonistic effects are ongoing.
Discount xeloda 500mg fast deliveryInitially women's health clinic rockingham purchase 500 mg xeloda with mastercard, the femur size is normal with shortening turning into obvious within the third trimester. Additional spine findings in achondroplasia include decreased interpedicular distance in the lumbar backbone, but that is difficult to detect prenatally. Another bony protuberance is noted over the sacral area corresponding to the truncated distal backbone. Skin edema can be seen related to hydrops, a standard discovering in many deadly chondrodystrophies. Of all these features, micrognathia is essentially the most constant and most simply seen all through gestation on prenatal ultrasound. The tapered humerus is difficult to see by prenatal ultrasound the place the bone could appear brief. Although nonspecific, a cystic hygroma (or elevated nuchal translucency) is a comparatively widespread finding in 1sttrimester skeletal dysplasias. In pregnancies in danger for this dysfunction due to a earlier child and autosomal recessive inheritance, the prognosis could be made, or at least strongly suspected, even within the 1st trimester. Confirmation of the prenatal findings was potential on this case, even on a nonintact specimen. Careful evaluation of the hands and ft on prenatal ultrasound can help make this analysis in a fetus at increased threat. This is a comparatively extreme instance of the appearance of the foot in this situation. Hypertelorism is noted with a flattened midface, brief nose, and small mouth with outstanding lips. Jo A et al: the versatile capabilities of Sox9 in improvement, stem cells, and human illnesses. The scapulae are considerably hypoplastic, a classic discovering in > 95% of infants with campomelic dysplasia. There are segmentation abnormalities in the cervical spine and hypoplastic transverse processes of the thoracic backbone. The thoracic cavity is often not as severely affected as in a few of the other skeletal dysplasias. This can be seen on ultrasound and is a crucial clue within the prenatal diagnosis of this disorder. A deep skin dimple is usually seen in the infant over the protuberance of the tibia. In the analysis of the scapula in a fetus, the backbone of the scapula and acromion are sometimes current and near regular in size. The scapula must be measured in a sagittal or coronal aircraft from superior to inferior, as shown. Note the intensive punctate calcifications involving the proximal ribs, backbone, and pelvis. Ca�ueto J et al: the role of the abnormalities in the distal pathway of ldl cholesterol biosynthesis within the Conradi-H�nermann-Happle syndrome. Chondrodysplasia Punctata Musculoskeletal (Left) 3D ultrasound reveals fetus at 31 weeks with vital nasal hypoplasia. Shortened limbs (4-5 commonplace deviations below the mean) have been apparent from the midtrimester. Note the low-set, posteriorly rotated ear with overfolded helix and prominent antihelix. Epiphyseal calcifications can be troublesome to visualize and must be particularly targeted. Kosnik-Infinger L et al: Enzyme substitute therapy for congenital hypophosphatasia permits for surgical remedy of associated complicated craniosynostosis: a case sequence. The femur is bowed, short, and poorly mineralized, particularly the metaphyseal ends. Note the extreme lack of ossification and irregular morphology of the lengthy bones and the extremely thin ribs. The metaphyseal irregularities are less pronounced than in the perinatal deadly type. The arms and legs are quick due to angulation and deformity resulting from the fractures. Cozzolino M et al: Management of osteogenesis imperfecta sort I in being pregnant; a evaluation of literature utilized to medical apply. Osteogenesis Imperfecta Musculoskeletal (Left) Coronal ultrasound by way of the thorax and one higher extremity of a midtrimester fetus reveals a small chest and irregular ribs with a number of fractures. Multiple fractures are noted within the extremities, giving the legs, specifically, a bowed appearance. Note the hanging pseudarthroses, that are a results of multiple fractures in utero. Micromelia can be obvious when comparing the near normal foot length to that of the long bones. The suspected diagnosis of Jeune asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy was confirmed after birth. Note the brief horizontal ribs with broad ends, protuberant abdomen, and irregular scapulae with multiple bony spurs. The vertebral our bodies are small and irregular and the metaphyses of the upper extremity bones are broad and irregular. The chest virtually has a pinched look and is in sharp distinction to the protuberant stomach. The small chest ends in pulmonary hypoplasia with a 70% mortality rate in the neonatal/infant interval. This is a standard related finding in a number of of the short rib-polydactyly syndromes and may result in oligohydramnios if extreme. Short and mildly curved lengthy bones, especially the femur, are frequent on this situation. Demographics � Epidemiology Most widespread deadly osteochondrodystrophy � 1st described as distinct entity by Maroteaux in 1967 728 5. Frontal bossing with a depressed nasal bridge, short nostril, and low-set ears are seen. Platyspondyly is clear in the lumbar backbone, and the spiculated appearance of the iliac wing is shown. Kleeblattsch�del calvarium with its complex pattern of craniosynostosis ends in the strikingly abnormal form. Proptotic eyes as a result of shallow orbits and frontal bossing with a depressed nasal bridge may also be seen. The sharp angulation of the extremities was mistaken for campomelic dysplasia on ultrasound. Normally, the metatarsals must be seen within the brief axis when the tibia and fibula are seen in the coronal airplane. Varus angulation of the forefoot is also present with the long axis of the talus being very lateral to the first metatarsal. Being in a position to depend metatarsals and toes is essential for ruling out amniotic bands or ectrodactyly.
Discount xeloda 500 mg mastercardThe inside structure of the mass and its caudal extent are better shown on the T2weighted picture encyclopedia of women's health issues order xeloda overnight. Note the standard intense enhancement of the nodule with no enhancement of the cyst wall. Sadighi Z et al: Pilocytic astrocytoma: a illness with evolving molecular heterogeneity. Mazloom A et al: Outcome of sufferers with pilocytic astrocytoma and leptomeningeal dissemination. Qaddoumi I et al: Pediatric low-grade gliomas and the necessity for new options for therapy: Why and the way St�er C et al: Frequent recurrence and development in pilocytic astrocytoma in adults. Within the supratentorial brain, pilocytic astrocytomas are generally adjoining to the third ventricle. The massive dimension and heterogeneous enhancement would possibly counsel a more aggressive histology. Yamashita Y et al: Minimum obvious diffusion coefficient is significantly correlated with cellularity in medulloblastomas. This "plastic" sample of growth is typical of ependymoma in this location and will increase the problem of surgical resection. Note the "upstream" ventricular obstruction with an enlarged cerebral aqueduct, dilated third ventricle, and tumor extruding via the foramen of Magendie into the cisterna magna. The tumor exhibits inhomogeneous excessive sign with multiple foci of low signal depth. Note the heterogeneous enhancement of the solid tumor parts with marginal enhancement in the cyst walls. Preoperative prognosis was choroid plexus papilloma; at surgery, mobile ependymoma was discovered. Lobulation is regular, however vermian craniocaudal height measures small when in comparability with regular controls. Adachi Y et al: Posterior fossa in major microcephaly: relationships between forebrain and mid-hindbrain dimension in one hundred ten patients. A giant nodule of heterotopic gray matter is situated within the hypoplastic hemisphere. The anterior lobe, usually the biggest part of the vermis, is especially disproportionately small. The transverse sinuses angle upward towards the torcular as the cyst has prevented regular fetal torcular descent. Again, discover that the transverse sinuses are angled upward toward the torcular herophili. The primary fissure and the vermis are compressed by the wall of the retrocerebellar cyst. This must be differentiated from a cerebellar tumor, by which the parenchyma sometimes enhances. Natural History & Prognosis I 4 28 Treatment � Options, risks, issues pdf-radiology. The small measurement of the posterior fossa has allowed inferior displacement of the occipital lobes, which lie lateral to the cerebellum on the level of the medulla. The supratentorial abnormalities associated with rhombencephalosynapsis could also be more clinically vital than the cerebellar malformation. Note the superior tenting of cerebellar white matter tracts which might be continuous across the midline. Thickened superior cerebellar peduncles across the elongated 4th ventricle kind the classic "molar tooth" seen in this anomaly. It is flanked on both sides by thick, elongated, in-plane superior cerebellar peduncles, forming the "molar tooth. The 4th ventricle is massive and upwardly convex; the midbrain seems skinny and elongated. Note additionally the ventriculomegaly, with persisting cavum vergae between the corpus callosum and the hippocampal commissure. Demographics � Age Infancy and childhood; isolated oculomotor apraxia could present later � Gender M=F Natural History & Prognosis � Early dying in affected infants � Older children problems with temperament, hyperactivity, aggressiveness, and dependency Most affected children are severely impaired 15. Note the small dimension of the posterior fossa, giant foramen magnum, and thinning of the brainstem. Note the abnormal foliation within the small affected hemisphere in comparison with the normal right facet. Subsequently, the central lumen of the neural tube enlarges to type the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain vesicles, which is able to turn into the lateral, third, and 4th ventricles. At concerning the 2nd gestational month, neuroependyma and a few mesenchyme from the growing leptomeninges invaginates into the lumen of the 4th ventricle to type the epithelium (from the neuroependyma), stroma and vasculature (from the leptomeninges) of the choroid plexus, soon adopted by comparable invaginations into the 3rd and lateral ventricles. In addition, the choroid plexuses secrete multiple proteins which might be postulated to stimulate proliferation of the neuroependymal cells, stimulating mitosis to generate the cells that would be the building blocks of the growing cerebral hemispheres. Although the choroid plexuses initially occupy > 70% of the ventricular lumen, their relative sizes diminish with progress of the mind and ventricular system. The manufacturing, circulation, and resorption of cerebrospinal fluid are key features of the ventricular system. These embody the realm postrema, the organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis and the subforniceal organ, which are sensory organs, and the subcommissural organ, the neurohypophysis and median eminence of the hypothalamus, and the pineal gland, which are secretory organs. All permit the brain to sense noxious stimuli or disrupted physique regulation (osmoregulation, electrolyte regulation, polypeptide regulation, cardiovascular regulation), circadian oscillations, patency of the sylvian aqueduct, and different features underneath investigation. Imaging Anatomy the traditional anatomy of the cerebral ventricles in kids is sort of consistent. The lateral ventricles are composed of the frontal horns, bodies (in the posterior frontal and parietal regions), occipital horns, temporal horns, and trigones (also known as atria, where the bodies, occipital and temporal horns intersect). Several options of the anatomy of the traditional pediatric cerebral ventricles are necessary. The medial and lateral partitions of the frontal horns and bodies are parallel and straight, not rounded. The temporal horns are quite narrow and their anteromedial borders (in entrance of the hippocampi) type a pointy level. Other necessary features of ventricular anatomy are the 3rd ventricular recesses: the chiasmatic recess between the inferior border of the lamina terminalis and the optic chiasm, the infundibular recess extending into the proximal pituitary stalk, and the suprapineal recess. When regular, these are sharply pointed; rounding or expansion suggests hydrocephalus. Another essential function of the ventricular system is the cerebral aqueduct, the narrowest portion of the ventricular system. Also because of its slim diameter, the aqueduct is the section of the ventricular system mostly narrowed or obstructed by intrinsic and extrinsic processes. Blockage in the ventricles results in "intraventricular obstructive hydrocephalus.
References - Svensson LG, Labib SB, Eisenhauer AC, et al. Intimal tear without hematoma: an important variant of aortic dissection that can elude current imaging techniques. Circulation. 1999;99:1331.
- Kuri, M., Nakagawa, M., Tanaka, H., et al. Determination of the duration of preoperative smoking cessation to improve wound healing after head and neck surgery. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102(5):892- 896.
- Diblasio CJ, Snyder ME, Russo P: Mini-flank supra-11th rib incision for open partial or radical nephrectomy, BJU Int 97:149n156, 2006.
- Metz D, Vakily M, Dixit T, et al: Review article: Dual delayed release formulation of dexlansoprazole MR, a novel approach to overcome the limitations of conventional single release proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29:928, 2009.
- Hoashi T, Bove EL, Devaney EJ, et al. Outcomes of 1- or 2-ventricle conversion for patients initially treated with singleventricle palliation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 141:419- 24.
- August P: Initial treatment of hypertension, N Engl J Med 348:610, 2003.
- Lodise TP, Patel N, Lomaestro BM, et al. Relationship between initial vancomycin concentration-time profi le and nephrotoxicity among hospitalized patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:507-514.
|

