|
Super P-Force dosages: 160 mg
Super P-Force packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills
Order discount super p-force on-lineThey are expensive brokers and their use is proscribed to sufferers with severe, progressive osteoporosis regardless of exposure to antiresorptive remedy. Teriparatide is licensed to be used in men and women, whereas recombinant parathyroid hormone 1-84 is simply licensed for postmenopausal women. Treatment is currently restricted to 18�24 month durations and most sufferers would require therapy with antiresorptive agents after discontinuation to keep the improvements in bone mass. Alternative agents Strontium ranelate-Strontium ranelate been proven to considerably cut back vertebral and non-vertebral fracture threat in postmenopausal girls. Pain reduction Pain reduction is regularly adequately achieved with analgesics, however physical measures-such as hydrotherapy or transcutaneous nerve stimulators-may be helpful adjuncts to remedy. The ache related to fractures usually resolves inside 6 months, however patients with vertebral fractures could must be given longterm analgesia because of secondary degenerative disease. Monitoring of treatment the rationale for monitoring therapy response is that a proportion of patients fail to reply to treatment, commonly as a result of non-persistence with therapy, poor dosing compliance or, less commonly, as a result of underlying illness. Biochemical markers of bone turnover could offer a extra fast assessment of therapy response-within 3�6 months. The decrease in bone turnover in response to antiresorptive agents could also be a superior predictor of the decrease in fracture threat. Falls prevention Predisposing factors, corresponding to postural hypotension or drowsiness as a result of drugs, should be eradicated the place potential. Patients might benefit from physiotherapy to enhance their steadiness and saving reflexes. Patients ought to be provided with acceptable walking aids, and an environmental evaluation should be manufactured from their accommodation to eliminate hazards corresponding to unfastened rugs and cables. Assessment via specialized falls clinics could additionally be appropriate, significantly in these people with features suggesting a medical trigger for falls, similar to palpitations or blackouts. Education An necessary part of the management of osteoporosis is training and help of the affected person, their carers and their household. Progressive joint destruction and extraarticular manifestations account for the disability and elevated mortality. Early recognition and intervention with diseasemodifying remedy is essential to preventing the progressive incapacity. Geographical variations in disease sample have been reported and attributed to lifestyle differences in populations; nevertheless, genetic differences have additionally been implicated within the severity of the disease. Usually the illness is insidious in nature, hardly ever occurring in males younger than 30 years, with gradually rising incidence with advancing age. In ladies the incidence steadily will increase from the mid-20s to peak incidence between 45 and seventy five years. In the classical presentation, which stays the more common variant, the illness impacts the small joints of the hands and feet in a more symmetrical pattern. Less frequent types of presentation are acute monoarticular, palindromic rheumatism and asymmetrical large joint arthritis. They can have an effect on nearly any system of the body and are mediated by various mechanisms. Immune responses corresponding to immune advanced deposition, cytokine production and direct endothelial injury can produce distant and native results. Also, mechanical causes corresponding to synovial hypertrophy and subluxation of joints could trigger entrapments of the nerves or vessels. The incapacity leads to disuse and irregular mechanics, which outcomes in degenerative changes and osteoporosis. The response has crossreactivity with host tissue, initiating an autoimmune synovitis and subsequent hypertrophy. Synovial hypertrophy is the necessary thing factor that results in cartilage and bone destruction, inflicting progressive joint damage and disability. Other tissues are affected via completely different mechanisms, accounting for the extra-articular manifestations. Atlanto-axial subluxation-This results from involvement of the atlanto-axial joint, which can be clinically asymptomatic till the subluxation develops. Development of pain across the occiput, radiating arm ache, numbness or weak point of the limbs and vertigo on neck movement are warning indicators; if not picked up this will lead to sudden demise, especially if patients endure neck manipulation for endotracheal entubation throughout surgical procedures.
Discount super p-force 160 mg amexDespite stabilization or enchancment in pores and skin sclerosis, internal organ issues could develop at a later stage, and so long-term follow-up is mandatory. The characteristics of sufferers with each subset at completely different occasions in their illness are summarized in Boxes 19. Skin involvement is much much less in depth and could additionally be confined to the fingers (sclerodactyly), face or neck. These include pulmonary arterial hypertension, severe midgut disease and interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. This appears to reflect the immunogenetic background of those people and should explain the medical differences between patients with hallmark reactivity. In addition, the medical affiliation of antibody profiles allows patients at elevated risk of Table 19. Most patients profit from vascular therapy, and a number of brokers that recommend the potential for vascular remodelling have been utilized in trials (Table 19. Cyclophosphamide has been demonstrated to have modest benefit in prospective medical trials (Hoyles et al. High-dose immunosuppression with autologous peripheral stem-cell rescue is currently being evaluated in scientific trials. Some of these are virtually common, similar to oesophageal reflux, whereas most of the extreme problems happen in round 10�15% of instances general. The frequency of the complication is likely to be around 10% overall, although printed prevalence studies have varied largely owing to differences in diagnostic methods and variation in examine cohorts. Diagnosis can solely be made robustly utilizing right-heart catheterization and is set by a mean pulmonary arterial pressure in extra of 25 mm Hg at rest, without elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, but with increased pulmonary vascular resistance. With the advent of contemporary superior therapies, together with endothelin receptor antagonists. Bronchoalveolar lavage is favoured in some centres and certainly correlates with the extent of disease, but not always with exercise. Immunosuppressive remedy with cyclophosphamide has recently been proven to be superior to placebo in a big controlled medical trial, but the effect was modest. Progressive deterioration, even if gradual, is a scientific indicator for lively treatment. In severe advanced illness without main co-morbidity, single lung transplantation has been proven to be helpful. The major drawback is considered one of recognition, and education of both patients and physicians is important. Patients should be admitted for blood strain control and monitoring of renal perform. There could additionally be important recovery in renal operate for as much as 2 years after a renal crisis, and choices relating to transplantation ought to be delayed till that point. Up to 90% of sufferers demonstrate oesophageal dysmotility with reflux, and the proton pump inhibitors have dramatically improved symptomatic disease. Histopathologic subsets of fibrosing alveolitis in patients with systemic sclerosis and their relationship to consequence. The coronary heart and pulmonary vasculature in scleroderma: scientific features and pathobiology. Systemic sclerosis related pulmonary hypertension: improved survival in the present period. Paradoxically, colonic involvement may result in severe constipation, and anorectal incontinence is prevalent. Further randomized controlled trials are needed to enhance the therapeutics of this troublesome condition. It has usually been confused and compared with causalgia, a special situation with similar medical signs. Generally talking, the extra words used within the description of a situation, the less we perceive that condition. This change in nomenclature has carried out little to reassure the nonspecialist that our understanding of the situation has substantially improved. To have the "full house" clinically, the following must be present: (a) severe pain, usually beginning peripherally, and working extra proximally over time in a non-dermatomal trend (allodynia)-the pain is disproportionate to the triggering occasion and clinical findings (hyperpathia); (b) often a previous occasion that might be comparatively trivial in traumatic phrases; (c) irregular blood flow to the affected area (usually a limb), with colour modifications (blues, whites and reds) and oedema; (d) abnormal sweating in the space; (e) adjustments within the motor system, with weakness and generally tremor; (f) eventual structural changes to superficial and deep buildings resulting in atrophic, shiny skin, contractures and patchy osteoporosis round joints on X-rays. Usually one limb is affected, but it may possibly turn into bilateral, or have an effect on another limb. It is usually most evident distally (hand and wrist, or foot and ankle), but a complete limb can be affected, similar to in "shoulder-hand syndrome".
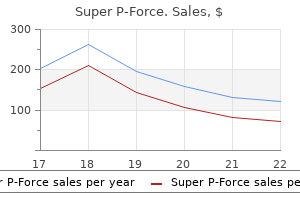
Best buy for super p-forceMacule (L macula = spot) Mycosis (mykes = fungus) (osis = situation of) fungal infection of skin or other fissues. Pediculosis brought on by animal parasites known as pedicull or lice in the hair, physique or pubic region. In the lengthy bones of the extremities the shaft or diaphysis is the hard compact portion, the epiphysis or finish is spongelike and lined by a shell or more durable bone and the metaphysis or rising portion lies between them. Bone cells multiply quickly in early years but in a while only lifeless cells are replaced or injured ones are repaired. Long bones give help, flat bones present protection for delicate organs and irregular bones permit for extra movement. The outer portion of bones is hard, nevertheless the hole internal half is full of soft marrow (Gr. Yellow marrow is present in long bones, whereas purple marrow is found ultimately of lengthy bones in addition to in ribs and our bodies of the vertebrae. The latter is liable for the manufacture of pink blood cells, a few of the white blood cells and platelets. Bones are often fully hardened by about twenty years of age via the deposit of calcium and phosphorus from food. Some stay as cartilage, however, for example, the tip of the nose, the ears and the anterior a part of the ribs attached to the sternum. Inside, the cells of the lining of the joint give out a small amount of slippery fluid (synovial fluid) which retains them lubricated and allows free movement. Joints have: (1) no movement, for instance, the flat bones of the skull; (2) slight motion, for instance, the bodies of the vertebrae; (3) free movement, for example, the joints on the shoulder and hip. Ties of freely movable joints (1) Ball and socket A joint in which a rounded head is received into a cup-like socket, for example, the shoulder joint, fashioned by the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity of the scapula. Bones of the skull Two parietal bones, one occipital bone, and one frontal bone type a overlaying for the mind. Two temporal bones include the ear cavities, the organs of steadiness, and the mastoid cells. Two inferior turbinate bones within the nostrils kind the outer partitions of the nasal cavity. Sinuses Four pairs of cavities in the cranial bones make the cranium lighter and return the sound of the voice. Named after the bones during which they lie, there are 2 frontal sinuses, 2 maxillary sinuses, 2 ethmoid sinuses, and 2 sphenoid sinuses. Sinusitis the impact of swollen epithelial tissue which blocks drainage channels and thereby prevents regular secretions within the sinuses four. These are divided into 5 groups according to their distinguishing characteristics. Pronation (8) Moving to the susceptible position with the arms hanging down and the palms going through backwards. The cranium is made up of twenty-two bones carefully fitted collectively with out movable joints, excluding the lower jaw or mandible. This is connected to the cranium by a hinge joint on both aspect that allows movement of the mandible up and down. It is firmly attached and Medical Terminology Course eleven (2) (3) (4) Thoracic vertebrae (12 in number) the twelve pairs of ribs are hooked up to these. Lumbar vertebrae (5 in number) these are giant vertebrae that enable free movement to the spinal column. The sacrum the sacrum is a single wedge-shaped bone consisting of 5 vertebrae fused together. An arch is formed, providing an opening or spinal canal throughwhich the spinal wire passes (Diag. Fingerlike extensions called transverse course of serve to anchor tendons and ligaments.
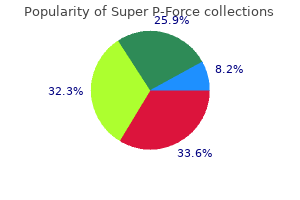
Buy cheap super p-force 160mg on-lineFibers in the ground of the tendon sheaths extending from the basis of the collateral ligaments to the palmar facet. Transversely oriented fibrous tracts on the palmar side of the heads of the metacarpal bones on the degree of the joint areas. Fibers which pass into the floor of the tendon sheaths above the interphalangeal joints. It corresponds to the obturator groove between the 2 obturator tubercles and is traversed by the obturator artery, vein and nerve. Strong ligament that passes to the ilium primarily from the transverse processes of L4 and 5. Strong ligament that extends from the medial margin of the ischial tuberosity to the sacrum and ilium. Superficial bundle of ligaments attached dorsally to the interosseous sacroiliac ligaments between the sacrum and ilium. Fibrous connection between the two halves of the symphysis emanating from the pecten ossis pubis on both facet. Fibrocartilage plate with a synovia-filled median groove, situated between the articular surfaces made of hyaline cartilage on the proper and left pubic bones. It is hooked up anteriorly to the intertrochanteric line, posteriorly above to the intertrochanteric crest. A fracture of the neck of the femur can due to this fact be intracapsular when in the anterior area or extracapsular when in the posterior area. Strong anterior ligament of the hip joint capsule extending from the ilium to the intertrochanteric line. It radiates into the orbicular zone from the posterior margin of the acetabulum and can additionally be attached to the anterior margin of the higher trochanter and to the intertrochanteric line. Ligament that arises medially from the joint capsule of the pubic bone and extends to the orbicular zone and to the a part of the femur proximal to the lesser trochanter. A ring of fibrocartilage and connective tissue that completes and deepens the bony acetabulum. A clean ligament extending from the acetabular notch to the pit on the pinnacle of the femur. Slender extension of fibers from the sacrotuberous ligament to the internal facet of the ischium. It passes from the ischial spine to the sacrum and coccyx and separates the greater from the lesser sciatic foramen. Foramen between the higher sciatic notch, sacrum, sacrospinous ligament and the higher a part of the sacrotuberous ligament. It is traversed by the piriformis muscle, superior and inferior gluteal arteries, veins and nerves, the inner pudendal vein, pudendal nerve, sciatic nerve and posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. Foramen between the lesser sciatic notch and the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments. It transmits the obturator internus muscle as well as the interior pudendal artery and vein and the pudendal nerve to the ischiorectal fossa. Dorsal mass of ligaments that move from the tuberosity of the sacrum to the tuberosity of the ilium. Fibrous band originating in the posterior wall of the capsule, extending upward and outward from the tendon of the semimembranous muscle, thereby reinforcing the capsule. Curved band of fibers extending from the epicondyle, throughout the origin of the popliteal muscle to the pinnacle of the fibula, thus reinforcing the posterior wall of the capsule. Aponeurosis from a half of the vastus medialis muscle that extends medially from the patella and attaches to the medial margin of the tibial tuberosity. It maintains the pathway of motion of the patella by way of muscular contraction and serves as a reserve extension apparatus. Aponeurosis of part of the vastus lateralis lateral to the patella with attachment lateral to the tibial tuberosity. Group of fibers passing anteriorly from the pinnacle of the fibula to the tibia, thus holding the 2 bones collectively.
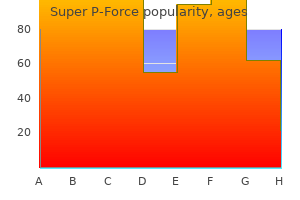
Cheap super p-force 160 mg amexAs we will later see, the stimulation or "trigger" that prompts receptors concerned with listening to and equilibrium is mechanical, and the receptors themselves are called mechanoreceptors. Physical forces that 188 Human Anatomy and Physiology involve sound vibrations and fluid actions are responsible for initiating nervous impulses ultimately perceived as sound and stability. A giant a half of the ear, and by far its most necessary part, lies hidden from view deep inside the temporal bone. The auricle is the appendage on the side of the pinnacle surrounding the opening of the external auditory canal. It extends into the temporal bone and ends at the tympanic membrane or eardrum, which is a partition between the external and center ear. The pores and skin of the auditory canal, particularly in its outer one third, incorporates many brief hairs and ceruminous glands that produce a waxy substance known as cerumen that will acquire within the canal and impair hearing by absorbing or blocking the passage of sound waves. Sound waves travelling through the exterior auditory canal strike the tympanic membrane and cause it to vibrate. Middle Ear the middle ear is a tiny and very thin epithelium lined cavity hollowed out of the temporal bone. The names of these ear bones, called ossicles, describe their shapes - malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The "handle" of the malleus attaches to the inside of the tympanic membrane, and the "head" attaches to the incus. When sound waves trigger the eardrum to one hundred ninety Human Anatomy and Physiology vibrate, that movement is transmitted and amplified by the ear ossicles as it passes via the center ear. A level worth mentioning, because it explains the frequent spread of infection from the throat to the ear, is the reality that a tube- the auditory or eustachian tube- connects the throat with the middle ear. The epithelial lining of the center ears, auditory tubes, and throat are extensions of 1 steady membrane. Consequently a sore throat may spread to produce a middle ear infection referred to as otitis media. Inner Ear the activation of specialised mechanoreceptors in the internal ear generates nervous impulses that lead to listening to and equilibrium. Anatomically, the inner ear consists of three spaces in the temporal bone, assembled in a complex maze referred to as the bony labrynth. This odd formed bony area is full of a watery fluid known as perilymph and is split into the following components: vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. Within each canal is a specialized receptor called a crista ampullaris, which generates a nerve impulse whenever you move your head. The sensory cells within the cristae ampullares have hair like extensions that are suspended within the endolymph. The sensory cells are stimulated when motion of the pinnacle causes the endolymph to transfer, thus causing the hairs to bend. The organ of listening to, which lies in the snail formed cochlea, is the organ of Corti. It is surrounded by endolymph filling the membranous cochlea or cochlear duct, which is the membranous tube inside the bony cochlea. The Taste Receptors the chemical receptors that generate nervous impulses resulting within the sense of taste are known as taste buds. About 10,000 of those microscopic receptors are discovered on the edges of much larger construction on the tongue known as papillae and likewise as portions of other tissues in the mouth and throat. Nervous impulses are generated by specialized cells in style buds, called gustatory cells. All different flavors end result from a combination of taste bud and olfacctory receptor stimulation. For this reason a chilly that interferes with the stimulation of the olfactory receptors by odors from foods in the mouth markedly dulls style sensations. The location of the olfactory receptors is considerably hidden, and we are sometimes compelled to forcefully sniff air to smell delicate odors. Each olfactory cell has a selection of specialised cilia that sense completely different chemical substances and trigger the cell to reply by producing a nervous impulse. To be detected by olfactory receptors, chemical substances should be dissolved within the watery mucus that traces the nasal cavity. After the olfactory cells are stimulated by odor-causing chemical compounds, the resulting nerve impulse travels through the olfactory nerves in the olfactory bulb and tract and then enters the thalamic and olfactory facilities of the brain, where the nervous impulses are 197 Human Anatomy and Physiology interpreted as particular odors.
Super p-force 160mg for saleThe nervous system has been in comparison with a phone trade, in that the brain and the spinal wire act as switching centres and the nerve trunks act as cables for carrying messages to and from these centres. Cells of nervous system and their features the two kinds of cells discovered within the nervous system are called neurons or nerve cells and neuroglia, that are specialised connective tissue cells. Dendrites are the processes or projections that transmit impulses to the neuron cell bodies, and axons are the processes that transmit impulses away from the neuron cell our bodies. The three forms of useful classification of neurons are based on the direction by which they transmit impulses. Sensory neurons transmit impulses to the spinal cord and mind from all components of the physique. Motor neurons transmit impulses within the reverse direction-away from the brain and spinal cord. Sensory neurons are additionally called afferent neurons; motor neurons are referred to as efferent neurons, and interneurons are known as central or connecting neurons. Myelin sheath is a white, fatty substance formed by Schwann cells that wrap around some axons outside the central nervous system. Impulse Generation and Conduction the Nerve Impulse the cell membrane of an unstimulated (resting) neuron carries an electric charge. Because of optimistic and adverse ions concentrated on either side of the membrane, the within of the membrane at rest is unfavorable as in contrast with the skin. A nerve impulse is an area reversal in the cost on the nerve cell membrane that then spreads alongside the membrane like an electric current. This electrical change outcomes from fast shifts in sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane. The reversal occurs very quickly (in less than one thousandth of a second) and is adopted by a rapid return of the membrane to its authentic state so that it may be stimulated again. In different words, how does the axon of 1 neuron make functional contact with the membrane of one other neuron Within the branching endings of the axon are small bubbles (vesicles) containing a type of chemical often known as a neurotransmitter. When stimulated, the axon releases its neurotransmitter in to the narrow gap, the synaptic cleft, between the cells. The neurotransmitter then acts as a chemical sign to stimulate the following cell, described as the postsynaptic cell. On the receiving membrane, usually that of a dendrite, generally one other part of the cell, there are particular sites, or receptors, able to decide up and respond to particular neurotransmitters. Receptors in the cell membrane affect how or if that cell will respond to a given neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine (Ach) is the neurotransmitter launched on the neuromuscular junction, the synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell. All three of the above neurotransmitters operate in the autonomic nervous system. Note, nonetheless, that some of these chemical compounds act to inhibit the postsynaptic cell and hold it from reacting. The axon ending has vesicles containing, neurotransmitter, which is launched across the synaptic cleft to the membrane of the next cell (Source: Carola, R. A complete pathway by way of the nervous system from stimulus to response is termed a reflex arc. Receptor-the finish of a dendrite or some specialized receptor cell, as in a special sense organ, that detects a stimuli. These neurons may carry impulses to and from the mind, could function inside the brain, or may distribute impulses to totally different regions of the spinal cord. Most reflex arcs involve many more, even tons of, of connecting neurons within the central nervous system. Use of the time period peripheral is appropriate because nerves lengthen to outlying or peripheral elements of the physique. Its two major buildings, the mind and spinal cord, are found alongside the midsagittal plane of the body. The brain is protected in the cranial cavity of the skull, and the spinal twine is surrounded in the spinal column.
Diseases - Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: familial
- Marfan Syndrome type IV
- Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
- Myelinopathy
- Hirschsprung microcephaly cleft palate
- Lipomucopolysaccharidosis
Order discount super p-force on lineWeak fibrous band passing from the foundation of the backbone of the scapula to the posterior margin of the glenoid cavity. Strong fibrous band inside and above the articular capsule serving to protect and hold together the clavicle and acromion. The portion of the coracoclavicular ligament taking an upward and lateral course from the coracoid process to the clavicle. Ligamentous union between the first rib and the clavicle lateral to the sternoclavicular joint. Thickened portion of the capsule passing from the root of the coracoid course of to the higher margin of the larger and lesser tubercles. Three thickened bands (superior, middle, inferior) throughout the anterior wall of the capsule. Joint fashioned by the articular circumference of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna. Ligament which spreads from the lateral epicondyle to the annular ligament of the radius and the ulna. It is connected to the anterior and posterior margins of the radial notch of the ulna. Thin band of fibers passing from the distal margin of the radial notch of the ulna to the neck of the radius. Membranous sheet which spreads between the interosseous margins of the radius and ulna. Ligamentous band extending obliquely downward from the ulnar tuberosity to the radius. It is hooked up at the radius and styloid process of the ulna and, as an intra-articular ligament, it connects the radius and ulna. Proximal wrist joint between the proximal row of carpal bones and the radius together with the articular disc. Ligament on the dorsum of the wrist extending from the radius to the triquetrum bone. Ligament on the flexor aspect radiating from the radius to the lunate and capitate bones. Ligament extending from the flexor side of the head of the ulnar mainly to the capitate bone. Groups of fibers radiating to either side of the wrist primarily from the top of the capitate bone. Collateral ligament extending from the styloid process of the ulna to the triquetrum and pisiform bones. External collateral ligament passing from the styloid process of the radius to the scaphoid bone. Ligamentous bands extending between the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones on the dorsum of the wrist. Groups of ligaments between the carpal bones on the palmar facet below the radiate carpal ligament. Ligaments penetrating directly by way of the joint clefts between the carpal bones within a row. Medial continuation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the hook of the hamate bone. Lateral continuation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris to the bottom of the fifth metacarpal. Rigid ligaments on the dorsum of the hand between the distal carpal bones and the metacarpal bones. Ligaments on the palmar facet of the hand between the distal carpal bones and the metacarpal bones. They lie in the intracapsular spaces between the dorsal and palmar metacarpal ligaments. Joints between the heads of the metacarpal bones and the bases of the proximal phalanges.
Buy super p-force 160 mg low costAccording to structure joints may be categorized in to , fibrous, cartilaginous & synovial. The major perform of the skeletal system is: a) Protection b) Storage of minerals c) Support d) Producing movement e) All of the above 2. The two sort of ridged connective tissue found within the human skeleton are: a) Spongy & compact bone b) Bone & cartilage c) Periosteum & endosteum d) Metaphysis & Diaphysis e) Cancellous & bone plate 3. The main bone at the posterior facet of the base of the skull is: a) Sphenoid b) Occiputal c) Temporal d) Lacrimal e) Zygomatic 105 Human Anatomy and Physiology 4. Describe the construction of a muscle Describe the connective tissue parts of skeletal muscle tissue Briefly describe how muscles contract List the substances wanted in muscle contraction and describe the operate of every Differentiate between isotonic and isometric contractions Define the following terms: origin, insertion, synergist, antagonist, and prime mover Define the totally different bases employed in naming skeletal muscle tissue Identify the principal skeletal muscle in several areas of the body by name, action, and innervations. The muscular system, however, refers to the skeletal muscle system: the skeletal muscle tissue and connective tissues that makeup individual muscle organs, such because the biceps brachii muscle. Cardiac muscle tissue is positioned within the heart and is subsequently thought-about a part of the cardiovascular system. Smooth muscle tissue of the intestines is a half of the digestive system, whereas clean muscle tissue of the urinary bladder is a part of the urinary system and so forth. Functions of muscle tissue Through sustained contraction or alternating contraction and rest, muscle tissue has three key features: producing motion, offering stabilization, and producing heat. Motion: Motion is obvious in actions such as walking and working, and in localized movements, similar to grasping a pencil or nodding the top. Stabilizing body positions and regulating the quantity of cavities in the physique: Besides producing movements, skeletal muscle contractions keep the body in stable positions, corresponding to standing or sitting. Postural muscle tissue display sustained contractions when a person is awake, for instance, partially contracted neck muscular tissues hold the top upright. In addition, the volumes of the body cavities are regulated by way of the contractions of skeletal muscles. For instance muscle tissue of respiration regulate the volume of the thoracic cavity through the strategy of breathing. These actions depend on the built-in functioning of bones, 109 Human Anatomy and Physiology Much of the warmth released by muscle is used to maintain normal physique temperature. Physiologic Characteristics of muscle tissue Muscle tissue has four principal traits that allow it to perform its features and thus contribute to homeostasis. Excitability (irritability), a property of each muscle and nerve cells (neurons), is the flexibility to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signal called motion potentials (impulses). For example, the stimuli that set off motion potentials are chemicals-neurotransmitters, released by neurons, hormones distributed by the blood. Contractility is the ability of muscle tissue to shorten and thicken (contract), thus producing pressure to do work. Extensibility implies that the muscle could be prolonged (stretched) with out damaging the tissue. While one is contracting, the other not solely relaxed but in addition normally is being stretched. Elasticity implies that muscle tissue tends to return to its original form after contraction or extension. Connective Tissue Component A skeletal muscle is an organ composed primarily of striated muscle cells and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has two elements; the connective tissue sheath that extend to form specialized structures that help in attaching the muscle to bone and the fleshy part the stomach or gaster. The extended specialized structure might take the form of a wire, known as a tendon; alternatively, a broad sheet called an aponeurosis might connect muscles to bones or to different muscular tissues, as within the abdomen or throughout the top of the cranium. Connective tissue additionally extends into the muscle and divides it into numerous muscle bundles (fascicles). Microscopic structures the muscle bundles are composed of many elongated muscle cells called muscle fibres. Each muscle fibre is a cylindrical cell containing several nuclei situated immediately beneath the cell membrane (sarcolemma). Each myofibril is a thread-like construction that extends from one end of the muscle fibre to the opposite. The ends of a sarcomere are a network of protein fibres, which form the Z-lines when the sarcomere is seen from side.
Order super p-force 160 mg lineThrough interactions on this partnership the promotion of most participation is explored. The shifting bias that exists within the rehabilitation process creates adjustments inside these partnerships. As well as delivering therapeutic intervention and enabling the patient to learn inside their environment, the therapist will also be required to provide steering about other partnership interventions, facilitating one of the best outcome of the rehabilitation process. Opportunities to practise software of expertise into function should be underpinned by the partnerships between the affected person and the related members of the interdisciplinary team. The key members inside the rehabilitation team are nurses and assist workers, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, neuro-psychologists, stroke coordinators, medical staff, and household and associates. They must be informed and supported via the rehabilitation course of and each time potential concerned in decision-making. Application of the Bobath Concept seeks to allow the affected person to interact within their setting, producing an effective, fascinating and appropriate response to their environment. Motor restoration and control is developed via the successful execution of an intended task inside the environment, through the processes of neuroplasticity. Rehabilitation on a stroke unit has been shown to cut back mortality significantly (by approximately 28%) compared to basic medical wards (Langhorne et al. Consistent team input, offering expert 24-hour administration, and therefore carry-over in an organised stroke unit, is the important ingredient for higher survival, restoration and regaining independence to return home (Langhorne et al. Task-specific coaching and repetition have demonstrated cortical functional reorganisation (Nelles et al. Studies show coaching, or rehabilitation, will increase cortical illustration with subsequent functional recovery, whereas a lack of rehabilitation or training decreases cortical representation and delays restoration (Teasell et al. The relevance and appropriateness of the duty makes all of the distinction to the sensory steering required and motor patterns that are produced, due to this fact enhancing motor restoration. Motor studying theories inform therapists about what makes an effective studying setting and the method to design a rehabilitation programme to meet the needs 183 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation of the person. The lively learner must be engaged, challenged and involved in meaningful task training. Practising an exercise of relevance might be the simplest therapeutic approach available for successful rehabilitation (Trombly & Wu 1999). The early days the patient who has neurological dysfunction enters a interval of preliminary cerebral and/or spinal shock and is unable to combine the techniques management of posture and movement. They will have problem in maintaining and sustaining upright posture towards the force of gravity and will be unable to create applicable alignment and activity levels. The presence of hypotonia and weak point automatically gears the neuromuscular system to compensate for lack of postural stability which might lead to fixation. This prevents the recruitment of selective movement to attain functional skills (Edwards 2002). When considering posturing of a person or body half, this is an lively element on which selective movement is predicated. Factors that influence the recovery of postural control, and due to this fact perform, embrace help, seating and appropriate alignment and realignment of the patient (Amos et al. The method the affected person is handled, transferred and enabled to transfer inside their surroundings optimises success at all phases of restoration. Therapeutic use of potential environmental constraints such as plinths, pillows, doorframes and partitions can assist with spatial, visual and perceptual deficits. As motion efficiency improves, the environmental helps can progressively be adapted to create greater challenges. The determination to reduce or withdraw facilitation appropriately throughout task apply permits the patient to make, recognise and correct errors 184 Exploring Partnerships within the Rehabilitation Setting in the means of achieving objectives. The facilitator influences not only the individual and the surroundings but also the choice of functional objective that the patient is working in course of, which have to be sensible and meaningful. Regular early standing within forty eight hours of stroke has been proven to be protected for homeostasis (Panayiotou et al. Positioning and seating for recovery the aim of good seating and positioning is to present adequate postural support to enable applicable alignment and stability of the trunk and limbs, subsequently decreasing the fear of falling and want for compensatory fixation acceptable to that postural set.
Buy discount super p-force 160 mg lineThis small structure is cartilaginous early in life, but gradually becomes ossified beginning during center age. Ribs Each rib is a curved, flattened bone that contributes to the wall of the thorax. The ribs articulate posteriorly with the T1�T12 thoracic vertebrae, and most connect anteriorly through their costal cartilages to the sternum. Instead, the ends of each rib are attached to hyaline cartilage, which might extend for a number of inches. Most ribs are then attached, either instantly or not directly, to the sternum by way of this cartilage. The ribs are categorised into three teams primarily based on their relationship to the sternum. Ribs 1�7 are categorised as true ribs (vertebrosternal ribs) as a end result of the cartilage from every of these ribs attaches directly to the sternum. For ribs 8�10, the cartilages are connected to the cartilage of the next larger rib. Thus, the cartilage of rib 10 attaches to the cartilage of rib 9, rib 9 then attaches to rib 8, and rib eight is connected to rib 7. Instead, their small costal cartilages terminate within the musculature of the lateral abdominal wall. Identify specific bones and bone options of the axial skeleton on an articulated skeleton, on disarticulated bones, bone models, or on a picture/diagram 3. Identify and describe unique features of a fetal skull, together with fontanels, and describe their perform in the fetus Required Materials � Adult articulated cranium � Fetal articulated cranium � Tape � Marker � Phone or other device Procedure 1. Label the following options of an adult articulated cranium with tape and publish an image to Lt: 21. Label the next features within the fetal skull with tape and post an image to Lt: 1. Identify specific bones and bone options of the axial skeleton on an articulated skeleton, on disarticulated bones, bone fashions, or on a picture/diagram Required Materials � Articulated skeleton � Phone or different system Procedure 1. Identify particular bones and bone features of the axial skeleton on an articulated skeleton, on disarticulated bones, bone models, or on a picture/diagram 2. Distinguish amongst vertebrae positioned in different areas of the vertebral column Required Materials � Articulated skeleton � Phone or other gadget Procedure 1. Identify which of the next vertebrae as cervical, thoracic, or lumbar: Lesson 20: Axial Musculature Created by Aimee Williams Introduction the muscular tissues of the top, neck, and trunk provide energy and stability to the trunk of the physique whereas also allowing some special capabilities corresponding to creating facial expressions and respiratory. In this lesson, students will establish choose muscles of the pinnacle, neck, and trunk and work to perceive their perform by way of muscle attachments, actions, and innervation. Note that the origins of the muscular tissues of facial features are on the floor of the cranium and that the insertions of those muscles have fibers intertwined with connective tissue and the dermis of the skin. Because the muscle tissue insert within the pores and skin somewhat than on bone, when the muscle tissue contract the pores and skin strikes extra significantly than seen within the appendages to create our wide number of facial expressions. Accordingly, the orbicularis oris is a round muscle that moves the lips, and the orbicularis oculi is a round muscle that closes the eye. The occipitofrontalis has a frontal belly and an occipital stomach (near the occipital bone on the posterior part of the skull) stomach. Instead, the 2 bellies are linked by a broad tendon referred to as the epicranial aponeurosis, or galea aponeurosis (galea = "apple"), as a end result of the physicians originally learning human anatomy thought the skull resembled an apple. These embody the zygomaticus major and zygomaticus minor, which move the mouth upward and outward, and the risorius, which pulls the angle of the mouth laterally, aiding in actions corresponding to laughing or smiling. Additionally, the levator labii superioris inserts into the skin of the upper lip to raise and protrude the higher lip, showing the higher gums. Located at the tip of the chin is the mentalis which is a deep, paired muscle that causes protrusion of the decrease lip and elevation of the pores and skin of the chin to present stability to the decrease lip (ex: pouting). Overlaying the mentalis, the depressor labii inferioris muscle has an analogous perform and assists in actions corresponding to kissing or playing the trumpet.
|