|
Motilium dosages: 10 mg
Motilium packs: 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Generic motilium 10 mg otcTrue craniosynostosis occurs in considered one of each 2,000 infants, predominates in males, and manifests in nonsyndromic and syndromic forms. Normally, the metopic, or frontal, suture closes earlier than delivery; the posterior fontanelle, at the union of the lambdoid and sagittal sutures, by 3 months; and the anterior fontanelle on the junction of the coronal, sagittal, and metopic sutures, by 18 months. The most typical premature closure occurs within the sagittal suture, which ends up in scaphocephaly, dolichocephaly, or elongated head. The subsequent most typical untimely closure is discovered in the coronal suture, which may be both unilateral or bilateral. If unilateral, it causes a unilateral ridge, with a pulling up of the orbit, flattening of the frontal area, and prominence close to the zygoma on the affected facet, which produces a quizzical expression. If premature coronal closure is bilateral, brachycephalia, manifested by an abnormally broad cranium, is the end result. Metopic craniosynostosis causes trigonocephaly, with a pointed frontal bone, hypotelorism, and outstanding temporal hollowing. True lambdoid synostosis, which may additionally be unilateral or bilateral, is exceedingly uncommon, with an incidence lower than 1:100,000. Turricephaly, a towering cranial vault due to multiple suture closure, is type of uncommon and disfiguring. Some infants will have outstanding ridges along sutures with out the other typical cranial findings, and these ridges will spontaneously resolve with time. Crouzon illness, with closure of multiple sutures and the related facial anomalies of hypertelorism, proptosis, and choanal atresia, is called craniofacial dysostosis. Intelligence is regular, however premature suture closure may cause elevated intracranial pressure. In acrocephalosyndactyly, or Apert syndrome, the top is elongated, the results of untimely closure of all sutures; the orbits are shallow, causing exophthalmos; and both syndactyly or polydactyly is current. Saethre-Chotzen, Pfeiffer, and Carpenter have also identified syndromes of acrocephalosyndactyly that embrace numerous combos of synostosis, syndactyly, and different anomalies. Conditions that could be confused with craniosynostosis embrace microcephaly and deformational plagiocephaly. Deformational plagiocephaly is very common and at present occurs in approximately 1 in 10 infants. Most infants could have spontaneous improvement with exercises; very extreme circumstances made need therapy with a cranial orthosis. Appropriate radiographic examinations are sometimes only wanted as a roadmap for surgical restore. Treatment for true craniosynostosis is surgical, with either endoscopic or open strategies. Treatment of syndromic and multiple suture craniosynostosis sometimes require multiple procedures by an skilled craniofacial team during early childhood. Plain radiographs show the preliminary fracture after birth, and subsequent skull defect after a quantity of months (arrows). Rarely, they turn out to be diastatic and are related to a leptomeningeal cyst because of related dural and meningeal tears that enlarge with mind development. Most are associated with the use of forceps, however some are related to intrauterine trauma towards pelvic prominences in automobile accidents and falls, and also in energetic labor. Surgical elevation could also be required and often could be performed with minimally invasive methods. The related dural sinuses could additionally be ruptured, causing a subdural hemorrhage of the posterior fossa. Caput succedaneum, an edematous swelling which might be hemorrhagic, is seen in vaginal deliveries. It may transilluminate, is gentle, pits, is normally at the vertex over suture lines, and resolves rapidly. Subgaleal hemorrhage, which normally outcomes from shearing forces tearing veins, happens between the galea aponeurotica and the periosteum of the skull. It spreads widely, crosses suture traces, may dissect over the forehead and even into an orbit, and should take weeks to resolve. Cephalohematoma is a subperiosteal hemorrhage associated with a linear skull fracture in about 5% of instances. It may end result from the utilization of forceps, can also be related to mechanical factors in the pelvis and the shearing forces of energetic labor, and palpates like a depressed fracture. Most calcified hematomas will spontaneously resolve as the skull grows and incorporates the area.
Sorghum bicolor (Broom Corn). Motilium. - Digestive disorders and other uses.
- How does Broom Corn work?
- Dosing considerations for Broom Corn.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Broom Corn?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96592
Purchase motilium 10 mg mastercardIt appears that estriol, an extremely weak estrogen, is as effective as different estrogens in increasing uteroplacental blood circulate. Estrogens might play a job in fetal growth and organ maturation, together with rising fetal lung surfactant manufacturing. These processes could additionally be regulated in an autocrine or a paracrine mode within the placenta. In the absence of enough maternal sources (and despite placental mechanisms), fetal growth follows a lower trajectory, resulting in intrauterine growth restriction. This scientific condition has been related to the "thrifty phenotype" in the adult, a hypothesis first proposed by David J. Individuals with this phenotype are in danger for a selection of continual illnesses, corresponding to sort 2 diabetes, coronary vascular disease, hypertension, and stroke. Although much of the research has been performed in different mammalian systems and will not be immediately relevant to people, main similarities most likely exist in the way development elements function to guarantee persevering with development and growth of the fetus. For humans, most of our information has been restricted to descriptive studies demonstrating localization of many development issue techniques. Table 8-2 is a partial itemizing of development factors which were identified within the placenta. A detailed description of their respective roles is beyond the scope of this chapter. Peripheral glucose uptake is inhibited in the mother but glucose crosses the placenta freely. Amino acids are actively transported to the fetus towards a focus gradient, and transplacental passage of free fatty acids is gradual. As a consequence, when the mom is within the fasting or starved state, glucose is reserved largely for the fetus and free fatty acids are used preferentially by the mother. In 37 -3 8 Endocrine-Metabolic Changes in Pregnancy Pregnancy is accompanied by a sequence of metabolic modifications, including hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, relative fasting hypoglycemia, elevated circulating plasma lipids, and hypoaminoacidemia. The insulin resistance related to being pregnant is accompanied by maternal islet cell hyperplasia. Left, Almost identical curves show disappearance of circulating insulin after a bolus intravenousinsulininjection(0. High-density-lipoprotein cholesterol levels enhance in early pregnancy, whereas low-densitylipoprotein levels of cholesterol improve later in being pregnant. Prolonged fasting in being pregnant is accompanied by exaggerated hypoglycemia, hypoinsulinism, and hyperketonemia. The elevated circulating concentrations of estrogen and progesterone in being pregnant can also be important in the altered glucose-insulin homeostasis present throughout pregnancy. Two totally different subunits have been characterised and have been designated as A and B. The fast return to normal glucose metabolism after delivery in girls with gestational diabetes has been considered the most effective proof that fetoplacental hormones are largely diabetogenic within the mother. Activin is a carefully associated protein that was discovered soon after inhibin and was named because of its capability to stimulate pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone release. Follistatin is a single-chain glycoprotein that can functionally inhibit pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone launch by the binding of activin. High levels of inhibin-like proteins have been reported in patients with fetal Down syndrome92 and in patients with hydatidiform mole93; low levels have been observed in girls with irregular gestations, similar to ectopic pregnancies,ninety four and pregnancies that finish in abortion. These regulatory occasions seem to be parallel to that of the pituitary gland, where activin will increase follicle-stimulating hormone launch, whereas follistatin and inhibin oppose this impact. This 41�amino acid peptide was first isolated from the hypothalamus and is liable for stimulation of adrenocorticotropic hormone and proopiomelanocortin peptides from the pituitary. The content of immunoreactive oxytocin will increase all through gestation and parallels the rise of maternal blood quantity. The placental oxytocin content material is estimated to be fivefold larger than within the posterior pituitary lobe, suggesting that the placenta may be the main supply of oxytocin during pregnancy. Circulating ranges of oxytocin are low all through pregnancy and improve markedly only through the second stage of labor. Relaxin is produced in a number of sites, together with the corpus luteum in pregnant and nonpregnant ladies, the decidua, the placenta, the prostate, and the atria of the heart. Relaxin concentrations are highest through the first trimester and peak at about 1. Available proof suggests that every one relaxin circulating within the mom during pregnancy is of luteal origin.
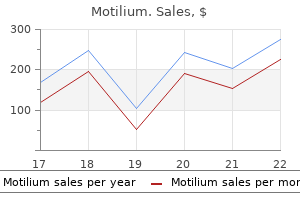
Buy motilium amexA behavioral therapeutic method utilizing habit reversal remedy at its core has been shown to be efficient in a latest large multicenter examine. Thalamic or pallidal deep mind stimulation is a promising technique in refrac tory cases. Symptoms start earlier than age 20 and frequently are associated with tremor, dystonia, and other movement disorders. Cortical myo clonus could additionally be epileptic (as in Baltic myoclonus or pro gressive myoclonic epilepsy, photosensitive myoclonus, epilepsia partialis continua) or part of a neurodegenera tive disorder (corticobasal degeneration, Alzheimer dementia, diffuse Lewy body illness, and others). Myoclonus may be categorized in accordance with etiology as idiopathic/genetic (familial myoclonus, myoclonus dystonia), physiologic (hypnic jerks or diaphragmatic myoclonus/hiccups) or secondary/symptomatic when a trigger for the myoclonus is clearly recognized. Examples of the latter group might embrace encephalitis, hypoxia, toxins, storage illnesses, and basal ganglia degenera tions, as in Huntington disease, Wilson illness, and certain other disorders). Myoclonus may be constructive because of a short muscle contraction or unfavorable when muscle tone is briefly lost, as in asterixis. Anoxic mind injuries might lead to myoclonus, which, in flip, could also be cortical, diencephalic, or reticular in origin; stimulus sensitive or action induced; and segmental, generalized, or multifocal in distribution. This kind of myoclonus could also be focal, preferentially affecting the distal limb muscular tissues, or multifocal with spontaneous, reflexive or stimulussensitive jerks accentuated by movement. Fre quently, anoxicinduced myoclonus is accompanied by secondary seizures, significantly after cardiopulmonary arrest. Status epilepticus is found in 32% of postanoxic sufferers, and in many, multifocal myoclonus alone or together with generalized tonicclonic seizures is regularly observed. The incidence of myoclonic sei zures is bimodal, with the majority of them occurring inside 12 hours after cardiopulmonary resuscitation and the remaining occurring a quantity of days later. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain may show diffusion restriction within the cortical and subcortical gray matter between 24 hours and thirteen days. Myoclonus status is refractory to therapy, could require multiple antiepileptic drugs, and, when accompanied by convul sive standing epilepticus, is best managed with deep anesthesia. Electrophysiologically, myoclonus is characterised by a muscle bursts which are lower than seventy five msec in dura tion. A number of stimuli corresponding to noise, mild, and contact can provoke this sort of myoclonus in a number of areas of the body. Adams reported the first sequence of patients with the syndrome of intention or action myoclonus as a sequel to hypoxic encephalopathy. Limb and truncal ataxia, cerebellar outflow tremor, and dysarthria are different frequent accompaniments. Postanoxic myoclo nus could also be the result of cortical or subcortical injury or be as a outcome of alterations in brainstem serotonergic path methods. Some types of myoclonus, significantly these of sub cortical origin, are believed to come up from the reticular system primarily from the nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis. This reticular reflex myoclonus is characterized by a brief electromyographic burst lasting 10 to 30 msec, with generalized bilateral synchronous activation of muscular tissues following a distribution suggesting unfold up the brainstem and all the means down to the wire. Essential myoclonus may be idiopathic or familial, beginning in the first to second decade of life. In patients with important myoclonus, the neurologic exam ination fails to show different deficits. In a couple of families, decrease verbal scores have been reported and infrequently psychological retardation. Similar to essential tremor, alcohol could assist to ameliorate the symptoms, however the incidence of alcoholism is elevated. Adults extra probably have coarse, proximal "wing beating" or "chest beating" tremor, masked facies, and dysarthric speech. Wilson diseAse Also generally known as hepatolenticular degeneration, Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive dysfunction that occurs in 1 of 30,000 people. Although a neurologic disorder, it affects multiple organs, with the liver being the most common and earliest affected.
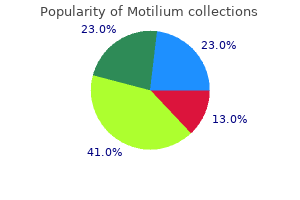
Safe motilium 10mgThe regular twin maintains the acardiac twin by perfusion via two anastomoses, one artery to artery and one vein to vein. The circulation of the acardiac twin is subsequently reversed, and most authors have assumed that this reversal of circulation can also be the cause of the malformation. Two trisomic acardiac fetuses and one triploid acardiac have been described, findings that counsel main errors in fertilization. It is then remarkable that for each acardiac twin for which adequate placental examination has been made, a monochorionic (usually monoamniotic) placenta has been found, thought to be diagnostic of monozygosity. The wide selection of sizes and shapes among acardiac twins has led to a fancy taxonomy. The causes of some anomalies are more readily comprehended than those of others; examples are the discordant growth of conjoined twins and maybe the acardiac anomaly and aplasia cutis which may be related to sudden drops in blood strain before birth. It is plausible that some other disruptions, such as porencephaly, happen as a result of interfetal vascular embolization or coagulation, and that other deformations are caused by crowding. In a lot of structural defects, nevertheless, the pathogenesis seems to be linked indirectly to the twinning process itself. These knowledge suggest that additional studies may present vital perception into not solely the poorly understood twinning process itself but also the pathogenesis of many congenital anomalies. Sixteen such circumstances of divergence in gonadal dysgenesis have been described by Pedersen and colleagues,79 to which cases of discordance for trisomy 21 and some circumstances of acardiac twins have to be added. These are the distinctive occasions, however they indicate the complexities of the twinning course of. A relevant inquiry reported that spontaneous discount occurred in 36% of twin pregnancies observed sonographically, in 53% of triplets, and in 65% of quadruplets. These a quantity of pregnancies are sometimes hormonally induced, and selective discount from triplets to twins improves the finish result of pregnancy. The many problems of selective reduction have been summarized by Berkovitz and associates. This state is referred to as blood chimerism as a result of the stable tissues could not participate in the admixture of genotypes. Blood chimerism is greatest defined by the existence of transplacental anastomoses umbilical twine. The wire is nearly invariably brief, betraying the immobility of the acardiac fetus, and it often possesses only one artery. Occasionally, nonetheless, acardiac fetuses have been witnessed to transfer, and in such circumstances the cord may be quite lengthy. They can now be detected prenatally by the absence of cardiac exercise and reversal of circulate on Doppler sonography. During the early event of manufacturing identical twins, one embryo could obtain extra embryoblasts than the other. This concept and its relevance to acardiacs have been described in some detail by Benirschke. Because blood chimerism occurs so early in embryonic life, this graft is tolerated as "self " and survives permanently with none unwell effect. Although blood chimerism occurs with regularity in marmosets and regularly in twin cattle, where it might cause freemartinism, it is extremely unusual in humans, in whom such anastomoses between presumably dichorionic twins have been recognized solely not often. An try should be made to establish the zygosity at birth and to register the objective findings within the chart. Performing this task on the delivery is particularly applicable because of the supply of the placenta, examination of which might assist materially within the process. The twins must also have a dichorionic placenta, which may be separated or fused. If doubt exists on gross examination of the dividing membranes, a transverse part. Templeton A: the multiple gestation epidemic: the position of the assisted reproductive applied sciences, Am J Obstet Gynecol 190:894, 2004.
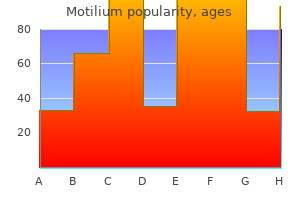
Cheap motilium ukLithium � Used in the remedy of bipolar problems as a result of it decreases the severity of the manic section and elongates the time between manic phases a. Pharmacokinetics (1) Narrow range of therapeutic serum ranges (2) Delayed onset of motion (6�10 days) b. Examples (1) Amphetamine (2) Dextroamphetamine (3) Lysdexamphetamine � A prodrug converted to dextroamphetamine b. Methylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate (more active, d-threo-enantiomer, of racemic methylphenidate) a. Parkinsonism is related to lesions within the basal ganglia, especially the substantia nigra and the globus pallidus. There is a discount in the number of cells within the substantia nigra and a decrease within the dopamine content. The lesions result in increased and improper modulation of motor activity by the extrapyramidal system, resulting in a resting tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia. L-Dopa is all the time given in combination with carbidopa or benserazide; peripheral dopa decarboxylase inhibitors. Severe gastrointestinal issues (1) Nausea (2) Vomiting (3) Anorexia (4) Peptic ulcer c. Dyskinesia (1) Development of irregular involuntary movements (2) Choreoathetosis, the commonest presentation, includes the face and limbs (3) Effects resemble tardive dyskinesia induced by phenothiazines f. The autoxidation of dopamine may contribute to destruction of dopaminergic neurons; this will restrict the therapeutic time window to the effectiveness (3 to 5 years) of L-dopa therapy. CatecholO-methyltransferase is inhibited by tolcapone in both the peripheral tissues and the brain. Mechanism of motion � Agonist that binds to each the dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in the striatum and substantia nigra b. Uses (1) Delays the necessity for L-dopa when used as monotherapy (2) Reduce the "off" symptoms when added on to L-dopa remedy 4. Mechanism of motion � Agonist that acts at each the dopamine D2 and D3 receptors b. Uses (1) Delays the need for L-dopa when used as monotherapy (2) Reduce the "off" symptoms when added on to L-dopa therapy (3) Also, for stressed leg syndrome Pergolide withdrawn from market because of affiliation with valvular coronary heart disease. Mechanism of motion (1) Antiviral agent that releases dopamine (2) May block dopamine reuptake (3) Central cholinolytic effect b. Adverse results (1) Blurred imaginative and prescient, constipation (2) Hallucinations, suicidal ideations (3) Livedo reticularis 6. Mechanism of motion (1) Indirect dopamine agonists that selectively inhibit monoamine oxidase B (2) An enzyme that inactivates dopamine (3) Metabolized to methamphetamine b. Use (1) Most generally given in conjunction with L-dopa (2) May be effective alone as a neuroprotectant as a outcome of its antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects (3) Selegiline can be obtainable as a transdermal formulation 7. These drugs additionally decrease the tremor and signs produced by a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist corresponding to haloperidol. Rapid unfold of the impulse alongside the two branches of the bundle of His and the Purkinje fibers 5. Rapid depolarization (phase 0) (1) Rapid inward motion of Na� due to the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels (2) Variation in resting membrane potential: �90mV to �15mV b. Initial speedy repolarization (phase 1) (1) Inactivation of sodium channels (2) Influx of Cl� c. Plateau phase (phase 2) � Slow but prolonged opening of voltage-gated calcium channels d. Repolarization (phase 3) (1) Closure of calcium channels and K� efflux by way of potassium channels (2) Return of inactivated sodium channels to resting section. Antiarrhythmic medicine produce results by altering a number of of the next components: 1. These brokers have various results on the electrophysiology of the guts (Table 12-1). Antiarrhythmic medicine target automaticity, conduction velocity, refractory interval or membrane responsiveness. Antiarrhythmic Drugs According to the Vaughn-Williams Classification (Box 12-1) A. Procainamide (1) this local anesthetic is equivalent to quinidine as an antiarrhythmic agent and has similar cardiac and poisonous results. Mechanism of motion (1) Bind to inactivated voltage gated sodium channels (2) Decrease the period of the action potential and the efficient refractory period (3) By inhibiting the sluggish Na� "window" current c.
Order motilium 10 mg on lineThis ensures saltatory axonal conduction that jumps from one node of Ranvier to the subsequent. Pre-oligodendrocyte Restoration of Conduction by Remyelination New oligodendrocytes Release of neurotransmitter the Ending of the Relapse. They are curtailed by a traditional feedback loop in which the tip product eliminates the originator. In addition, catabolites derived from the kynurenine metabolic pathway are directly cytotoxic to Th1 effector cells. Th17 effector cells are relatively insensitive to tryptophan hunger and kynurenine toxicity. Kynurenine then back-signals to these identical regulatory T cells instructing them to ship a pro-apoptotic message to Th17 effector cells. Demyelinated segments could additionally be remyelinated by preoligodendrocytes that enter demyelinated plaques from surrounding areas. Remyelinated segments are readily recognized as a end result of internodal distances are shorter, and the myelin sheaths are thinner than their predecessors. Remyelinated areas are seldom shielded from demyelination in subsequent relapses. Perhaps the simplest has been to choose them as acute, chronic lively, or continual silent. The continual lively plaque shows latest disease at its periphery, or elements of it, however continual modifications in its heart. For the higher part, these therapies are directed in opposition to T cells and the peripheral immune element. Gray matter lesions that include few T cells turn into more and more prominent with accompanying damage to cortical axons, to dendrites, and to neuronal cell our bodies. Meningeal inflammation can be in depth and it has been suggested that it could one method or the other contribute to subpial cortical demyelinated plaques and an accelerated scientific course. Since T cells and macrophages are rare in cortical demyelinated areas and activated microglia are ample, a microglia-activating signal delivered from a distance has been proposed. Loss of the trophic assist to axons normally offered by oligodendrocytes may contribute. The spinal twine may present grayish areas on its floor, usually unilateral and slightly depressed. When the cerebral hemispheres are sectioned, the demyelinating lesions become apparent. Recently acquired lesions are gentle and pink, whereas lesions of long standing are inclined to be quite a few, agency, and to have a grayish gelatinous appearance indicative of substantial gliosis. These lesions also are inclined to be scattered asymmetrically via the gray and white matter. Larger lesions form by coalescence of smaller ones and by bouts of relapsedriven enlargement at their edges. Large lesions usually have an irregular form and a pointy outline, provided illness is inactive. A favored web site for plaque location is underneath the ground of the fourth ventricle, as illustrated, however plaques could happen in any location and unfold from their origins at the pial and ependymal surfaces over a bigger or smaller area. In the spinal cord, lesions are once again primarily based on the pial floor and lengthen inward as hemispheric or conical areas. Histologically, plaques are most easily demonstrated in sections stained for myelin, the place they seem as demyelinated areas. The transition from the demyelinated space to intact myelin is demarcated by the arrows. They present as areas of energetic demyelination with ill-defined boundaries, in depth irritation all through, perivascular cuffs, and macrophages engaged in myelin stripping and removing. Chronic lively plaques show current disease at their periphery, or components of it, however chronic adjustments within its middle. Astrocytes now take on a fibrillary morphology and categorical the sinuous processes of continual gliosis. Myelin loss from a nerve fiber is distinct and greatest outlined by toluidine blue stains.
Syndromes - Hard or firm-feeling belly
- Knee that gives way
- Death
- Congenital (present from bith) narrowing of the pulmonary vessels
- Cataracts
- Take the drugs your doctor told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Cortisol level will be high.
- Artificial respiration
- For the first 5 months of life, always place your infant on his or her back to go to sleep. This position has been shown to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Once a baby can roll over by himself, the maturing nervous system greatly reduces the risk of SIDS.
- A level of 100-125mg/dL means you have impaired fasting glucose, a type of prediabetes. This increases your risk for type 2 diabetes.
Buy motilium 10 mg visaSurgeons have operated on protruding aortic atheromas, and sooner or later these lesions could be attacked by endovascular strategies. Arterial lesions are often repaired surgically or utilizing endovascular know-how in the form of angioplasty and/or stenting. Vessel lumen nearly fully obstructed by thickened media and enlarged to about three occasions regular measurement. The commonest locations are the putamen and the pallidum, adopted by the pons, thalamus, caudate nucleus, inner capsule, and corona radiata. Rarer are lacunes in the cerebral peduncles, pyramids, and subcortical white matter. The two most typical pathologies that affect penetrating arteries are lipohyalinosis and atheromatous branch illness. Serial sections of penetrating arteries that provide the territory of lacunar infarcts usually have focal enlargements and small hemorrhagic extravasations via the walls of the arteries. Subintimal foam cells sometimes obliterate the lumens, and pink-staining fibrinoid material lies inside vessel walls. Arterial segments are often changed by whorls, tangles, and wisps of connective tissue that obliterate the standard vascular layers. This vascular pathology has been known as segmental arterial disorganization, fibrinoid degeneration, and lipohyalinosis. The distribution of deep hypertensive hemorrhages is identical as the locations of lacunes (putamen, capsule, thalamus, and pons). Lipohyalinotic arteries may occlude, inflicting lacunar infarction, or rupture, inflicting intracerebral hemorrhage. Intracerebral department atheromatous illness additionally effects brain tissue equipped by penetrating arteries. In this condition, the orifices of penetrating arteries are blocked by atheroma within the parent artery. Atheroma may originate within the parent artery and extend into the branch, or microatheroma could come up on the origin of the branch itself. Pontine infarcts are probably the most frequent neuropathologic lesion found in necropsies of diabetics and, in most cases, are brought on by atheromatous department disease. Multiple bilateral lacunes and scars of healed lacunar infarcts in thalamus, putamen, globus pallidus, caudate nucleus, and inside capsule. Smooth muscle cells in the media are swollen and often degenerated, and the endothelium could additionally be absent and changed by collagen fibers. This hereditary situation causes lacunar infarcts in the basal ganglia and cerebral white matter similar to these present in hypertensive patients. The scientific findings embody perinatal hemorrhages and porencephaly, tendency to brain hemorrhage after trauma, retinal artery tortuosity, cerebral aneurysms, penetrating artery related infarcts, white matter gliosis, and kidney disease. The main essential situation to separate from these "micropathologies" is occlusion of parent arteries blocking move in penetrating artery branches. In sufferers of Asian origin, especially Japan, Korea, and China, small deep infarcts are sometimes attributable to occlusive illness of the large intracranial mother or father arteries. When small deep infarcts are attributable to severe occlusive disease of the intracranial giant mother or father arteries, the infarcts are barely bigger, the neurologic indicators are barely worse, and recurrence is more common than in infarcts caused by intrinsic disease of the penetrating arteries. The most common scientific syndromes attributable to lacunar infarction are pure motor hemiparesis (weakness of face, arm, and leg on one facet of the physique with no sensory, visual, or cognitive abnormalities; pure sensory stroke (hemisensory loss with out other signs); dysarthria�clumsy hand syndrome; and ataxic hemiparesis. When severe and clinically evident, this chronic microvasculopathy is commonly called Binswanger disease. In this situation, the cerebral white matter has confluent areas of sentimental, puckered, and granular tissue. These areas are patchy and predominate within the occipital lobes and periventricular white matter, particularly anteriorly and close to the ventricular floor. The partitions of penetrating arteries are thickened and hyalinized, however occlusion of the small arteries is uncommon. In these sufferers, arteries within the cerebral cortex and leptomeninges are thickened and include a congophilic substance. The scientific picture in sufferers with Binswanger white matter abnormalities is variable. Most patients Cardiac hypertrophy and anteroseptal infact with coronary coronary heart disease 1. Pseudobulbar palsy, pyramidal signs, extensor plantar reflexes, and gait abnormalities are common.

Buy cheap motilium on lineThe nucleus of the solitary tract gives off local connections in the brainstem to reflex pathways for salivation and for regulation of biting, chewing, and swallowing exercise. Ascending axons from the nucleus of the solitary tract travel through the brainstem, and a big proportion of them synapse in the parabrachial nucleus. From there, axons continue on to the thalamus (for conscious appreciation of taste), amygdala (for style associations), and hypothalamus (presumably for regulation of feeding). The inputs to the hypothalamus and amygdala are augmented by a smaller variety of axons that reach these websites instantly from the nucleus of the solitary tract. Taste neurons in the thalamus are positioned adjoining to the tongue somatosensory space, and so they innervate the insular cortex, which is the primary style cortex. The posterior two thirds of the nucleus of the solitary tract receives inputs from other internal organs through the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves. The nucleus of the solitary tract offers native inputs to cell teams in the medulla that control gastrointestinal functions, together with gastric acid secretion and gut motility as properly as cardiovascular and respiratory reflexes. Other axons from the posterior two thirds of the nucleus of the solitary tract terminate within the parabrachial nucleus. Parabrachial neurons then contact the visceral sensory thalamus, which, in turn, projects to the insular cortex, where sensations corresponding to gastric fullness or air starvation attain acutely aware appreciation. Other parabrachial outputs are joined by smaller numbers of axons from the nucleus of the solitary tract itself in projecting to the amygdala, where they might be involved in visceral conditioned reflexes. Parabrachial inputs to the hypothalamus might play a job in a variety of functions, from regulation of behaviors such as feeding and consuming to management of secretion of hormones such as vasopressin (during hypovolemia) and oxytocin (during emesis). The limbic lobe of the brain was first defined by Paul Broca, in 1878, as the cortex surrounding the medial fringe of the cerebral hemisphere, as shown in orange in the higher determine. These limbic areas all receive extremely processed sensory info from the affiliation regions of the cerebral cortex, process that information for its emotional content material, and then project back to the affiliation cortical areas to provide emotional coloring to cognition. The inputs from the cingulate gyrus primarily originate within the infralimbic and prelimbic areas (around and just beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum). These areas primarily ship axons to the lateral hypothalamus, in addition to to parts of the autonomic system within the brainstem and the spinal cord, and are believed to provide a lot of the autonomic part of emotional response. This lengthy looping pathway, shown in yellow within the figure, curves just below the corpus callosum, after which dives into the diencephalon at the foramen of Monro. Many axons go away the fornix in the hypothalamus and provide inputs to the ventromedial nucleus. However, a dense column of fornix axons reach the mammillary body, where they terminate. Although the hippocampus seems to be very important in reminiscence consolidation, isolated damage to the fornix or mammillary bodies has more restricted and inconsistent results on memory, so the operate of this pathway stays enigmatic. The mammillary nuclei provide one other salient bundle of axons to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus. This mammillothalamic tract is closely myelinated and simply seen, however its contribution to reminiscence formation is more subtle, like that of the mammillary body itself. Lesions of the mammillothalamic tract have been reported to forestall the generalization of limbic seizures, nevertheless, and this pathway has been suggested as a goal for deep brain stimulation to stop generalization of seizures. Some axons depart the amygdala in parallel to the fornix, operating along the lateral edge of the lateral ventricle just below the tail and physique of the caudate nucleus in the stria terminalis, proven in blue within the lower determine. Other amygdaloid inputs to the hypothalamus take a method more direct anterior route, operating over the optic tract into the lateral hypothalamus. Many hypothalamic cell teams obtain inputs from the amygdala, which are thought to be important for the visceral parts of conditioned emotional responses. As a outcome, the vary of problems that occur when the hypothalamus malfunctions can be very great. Hence, a affected person with a pituitary tumor or craniopharyngioma impinging on the hypothalamus might have problems extending into many functions. Such patients are sometimes quite somnolent as a outcome of an essential department of the ascending arousal system runs by way of the lateral hypothalamic space.
Generic 10mg motilium with amexBy dividing and branching, the ingrowing mass of ectodermal cells gives rise to the long run lobes and lobules, and much later to the alveoli. The lactiferous ducts and their branches are developed from outgrowth in the lumen. The pit turns into elevated on account of mesenchymal proliferation, forming the nipple and areola. The nipple, areola, and breast bud are important landmarks for the willpower of gestational age within the new child. At forty weeks, the nipple and areola are clearly seen and the breast bud is as a lot as 1. In the primary weeks after supply, the breast bud is visible and palpable; nevertheless, the gland then regresses to a quiescent stage as maternal hormones in the infant diminish. After this, the gland grows only in proportion to the remainder of the body till puberty. The additional growth of the breast includes two distinct processes: organogenesis and milk production. The ductal and lobular growth is organogenesis, and this is initiated before and throughout puberty, ensuing within the progress of breast parenchyma with its surrounding fats pad. The formation of alveolar buds begins within 1 to 2 years of the onset of menses and continues for a number of years, producing alveolar lobes. This menarcheal stimulus begins with the extension of the ductal tree and the generation of its branching pattern. The ducts can develop bulbous terminal finish buds that are the forerunners of alveoli. The formation of the alveolar bud begins within 1 to 2 years of the onset of menses. During this ductal growth, the alveoli enlarge and the nipple and areola turn out to be extra pigmented. The breast continues to enlarge barely with additional division of the ductal system until concerning the age of 28, except pregnancy intervenes. During being pregnant, nevertheless, the dimensions and weight improve to about four hundred to 600 g, and to 600 to 800 g throughout lactation. A projection of mammary tissue into the axilla is known as the tail of Spence and is linked to the central duct system. The breast is often dome shaped or conic, turning into extra hemispheric in the adult and pendulous in the older parous woman. This is referred to as hypermastia, which is the presence of accessory mammary glands which are phylogenic remnants. These remnants might include accessory nipples or accent gland tissue situated anywhere along the milk line. These remnants remain quiet till being pregnant, when they may reply to the hormonal milieu by enlarging and even secreting milk throughout lactation. Major glandular tissue within the axilla may pose a beauty or administration drawback if the tissue enlarges considerably during pregnancy and lactation, secreting milk. Other variations embrace hyperplasia or hypoplasia in numerous combinations, as listed in Box 9-3. Gigantomastia is the extreme enlargement of the breasts in being pregnant and lactation, sometimes to life-threatening 9 the Breast and the Physiology of Lactation 117 proportions. In excessive cases, gigantomastia could require heroic measures, together with emergency mastectomy. Not all abnormalities or variations preclude breastfeeding, and the decision is made on a case-by-case basis. The nipple is a conic elevation in the center of the areola at the stage of in regards to the fourth intercostal space, slightly below the midline of the breast. The nipple accommodates easy muscle fibers and is richly innervated with sensory and pain fibers.
Order cheap motilium on-lineE, With postpartum withdrawal of luteal and placental sex steroids and placental lactogen, prolactin is able to induce full secretory exercise of alveolar cells and launch of milk into alveoli and smaller ducts. This thickened ectoderm becomes depressed into the underlying mesoderm, and thus the floor of the mammary area quickly becomes flat and eventually sinks below the extent of the surrounding epidermis. It has a verrucous floor and has sebaceous and apocrine sweat glands, but not hair. The areola surrounds the nipple and can also be slightly pigmented and becomes deeply pigmented throughout being pregnant and lactation. The average diameter is 15 to 16 mm, however the vary may exceed 5 cm during pregnancy. The nipple and areola are very elastic and elongate into a teat when drawn into the mouth by the suckling infant. The floor of the areola incorporates Montgomery glands, which hypertrophy throughout being pregnant and lactation and resemble vesicles. During lactation, they secrete a sebaceous materials to lubricate the nipple and areola and defend the tissue while the infant suckles. Each nipple incorporates four to 18 lactiferous ducts, of which five to eight are major ducts surrounded by fibromuscular tissue. The corpus mammae is an orderly conglomeration of a selection of unbiased glands often identified as lobes. The morphology of the gland consists of parenchyma that contains the ductular-lobular-alveolar buildings. It additionally consists of the stroma, which is composed of connective tissue, fat tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics. The mass of breast tissue consists of tubuloalveolar glands embedded in adipose tissue, which provides the gland its smooth, rounded contour. The mammary fats pad is important for the proliferation and differentiation of the ductal arborization. Each lobe is separated from the others by connective tissue, and opens right into a duct that opens into the nipple. The primary blood provide comes from the interior mammary artery and the lateral thoracic artery. The main drainage is to axillary nodes and the parasternal nodes along the thoracic artery within the thorax. The lymphatics of the breast originate in lymph capillaries of the mammary connective tissue and drain through the deep substance of the breast. The sensory innervation of the nipple and areola is intensive and consists of both autonomic and sensory nerves. The innervation of the corpus mammae is meager by comparison and is predominantly autonomic. Thus, the conclusion is that secretory actions of the acinar epithelium of the ducts depend on hormonal stimulation, similar to by oxytocin. When sensory fibers are stimulated, the discharge of adenohypophyseal prolactin and neurohypophyseal oxytocin occurs. The areola is most sensitive to the stimulus of suckling, the nipple the least, and the pores and skin of the breast is intermediate. The giant variety of dermal nerve endings ends in high responsiveness to suckling. Breast nerves can influence the mammary blood supply and due to this fact also influence the transport of oxytocin and prolactin to the myoepithelial cells and the lacteal cells, respectively. There is elevated infiltration of the interstitial tissue with lymphatics, plasma cells, and eosinophils. The lactating mammary gland has a lot of alveoli that are made up of cuboidal, epithelial, and myoepithelial cells. The ranges are high during pregnancy, however the affect of prolactin on the breast itself is inhibited by a hormone produced by the placenta, originally referred to as prolactin-inhibiting hormone but believed to be progesterone. Lactogenesis is the initiation of milk secretion, starting with the changes within the mammary epithelium in early pregnancy and progressing to full lactation. Stage I lactogenesis happens during pregnancy and is achieved when the gland is sufficiently differentiated to secrete milk.
|