|
Cystone dosages:
Cystone packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 120 pills, 240 pills, 300 pills, 10 tabs, 20 tabs, 30 tabs, 60 tabs, 90 tabs, 120 tabs, 180 tabs, 270 tabs, 360 tabs

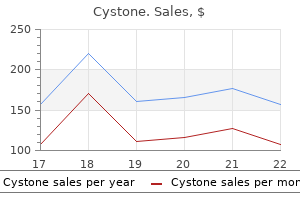
60caps cystone mastercardVarious visceral organs, including the intestines, omentum and ovaries, may be incarcerated in a hernia. Strangulation of the bowel results in ischaemia of its wall that will result in perforation and sepsis. Intestinal obstruction, then again, may initially occur with or without strangulation and compromise of blood move. Pain can accompany even a non-strangulated hernia and by itself is a symptom and not a pathophysiological mechanism. Incarceration of the omentum can cause important pain however is otherwise not associated with critical antagonistic sequelae. In any affected person presenting with an acutely incarcerated groin hernia (inguinal or femoral), an try at mild discount must be made. If the hernia is irreducible and accommodates bowel or ovary, pressing surgical intervention have to be instigated. Patients presenting with symptomatic hernias should be questioned about the length and nature of their signs, looking particularly for evidence of intestinal obstruction. The dimension of the hernia contents is by itself not the criterion for urgency of intervention. Incisional hernias, especially those with a large hernial defect within the absence of obstructive signs and with a benign abdominal examination (no concern for strangulation), may be noticed. Asymptomatic and minimally symptomatic inguinal hernias in adults, even if bilateral, may be noticed. Inguinal hernias in children ought to all the time be repaired, but this can be carried out electively if the hernia is reducible. Acquired umbilical hernias develop in adults due to progressive stretching of the umbilical scar (typically in its weaker higher portion) due to chronically elevated intra-abdominal pressure. Symptomatic hernias must be considered for repair to improve the quality of life and keep away from problems. Congenital umbilical hernias outcome from a failure of the umbilical ring to heal and are fully coated by umbilical pores and skin. They hardly ever incarcerate, resolve spontaneously in most patients and wish repair in only a minority of sufferers. The examination of a painful groin mass of pain should embody which of the next Examination of the groins should be performed with the affected person in the upright and supine positions. The abdomen, groins and upper thighs must be examined utilizing visual inspection and palpation. The location of the hernia, mass or area of tenderness must be famous in relation to the anatomical landmarks (specifically the umbilicus, pubic tubercle and inguinal ligament). Examine the testicles and spermatic cords in males and the labia majora in females. A differentiation must be made between a hernia, lymphadenopathy and a scrotal mass. The presence of inguinal lymphadenopathy mandates an examination of the extremities, lower torso, external genitalia and anorectal region. Avoid repeated and aggressive makes an attempt to reduce an incarcerated groin hernia; immediate surgical session should be obtained. No try should be made to cut back a hernia with overlying inflammatory adjustments that counsel an underlying strangulated hernia. Obturator hernias could additionally be difficult to diagnose until they prolong onto the thigh or may be palpated via the vagina. Alternatively, they may manifest with intermittent signs of ache and thigh paraesthesias. The peritoneal sac of an oblique inguinal hernia emerges lateral to the epigastric vessels by way of the internal inguinal ring (where they might turn into incarcerated) and travels along the testicular vessels or round ligament. Spigelian hernias originate a few centimetres beneath the umbilicus alongside the lateral edge of the rectus abdominis muscle at the web site of its intersection with the arcuate line. Sliding inguinal hernias include viscera as part of their wall and will involve the caecum, sigmoid colon or urinary bladder. Costly imaging is usually reflexively ordered for these sufferers only to reveal � several hours later � a diagnosis that could have been elucidated with correct scientific evaluation, such as an incarcerated hernia. On the other hand, when belly pathology is recognized early, steps for additional treatment can be expedited.
Syndromes - Complete blood count (CBC) to check for signs of anemia
- Time it was swallowed
- Inherited -- due to changes in your genes
- Examination of the inside of the lower large bowel (sigmoidoscopy)
- Obesity
- Chest x-ray
- Swelling
- Men who do not have testicles or whose testicles are under-developed
- A number of different medications can help with your back pain. See also: Medicines for chronic pain
Generic 60caps cystoneThe patellar compression syndrome: surgical treatment by lateral retinacular release. Preoperative computed tomography scanning and arthroscopy in predicting outcome after lateral retinacular release. If the knee remains flexed, the patella could stay dislocated over the lateral femoral condyle. The historical past of damage may be unclear, particularly if the patella rapidly and spontaneously reduced. In one cohort of 189 sufferers, 61% of first-time dislocations occurred throughout sports activity. On the opposite hand, sufferers presenting with recurrent patellar instability are more likely to proceed experiencing additional dislocations than sufferers who current with their first dislocation. The danger of a repeat dislocation in patients presenting with a history of prior patellar dislocation is about 50% over a 2- to 5-year interval. Crosby and Insall3 reported that degenerative changes were uncommon after patellar dislocation. In a more recent study, nonetheless, the incidence of degenerative changes was significantly greater at 6- to 26-year follow-up in first-time dislocators treated nonoperatively. The patellotibial and patellomeniscal ligament advanced play a secondary position in restraining lateral patellar displacement, whereas the medial patellofemoral retinaculum contributes little to patellofemoral stability. Patients could report that one thing "popped out" medially, because the uncovered medial femoral condyle becomes outstanding. The knee normally offers method secondary to pain inhibition of the quadriceps and disruption of the mechanical advantage of the extensor mechanism, and the patient falls down. Increased laxity is signified by more than two quadrants of translation; 10 mm or extra of lateral translation; or the absence of an endpoint. Inability to fully translate the patella laterally due to affected person guarding might lead to a falsenegative end result. The patella abruptly translates laterally as the knee is absolutely extended, transferring in an upside-down "J" sample. A tense effusion or hemarthrosis (on aspiration) after an acute dislocation raises suspicion for an osteochondral fracture. Pivot shift also could also be tried, but may be tough to perform on an acutely injured knee. Medial patellar instability can occur following prior lateral retinacular launch. Medial patellar instability may be distinguished from lateral instability by the DeLee sign. The DeLee signal is positive if the applying of a laterally directed force on the patella (which reduces the patella from its subluxated position) eliminates the pain caused by flexion of the knee. Diagnosis of extensor mechanism disruption must be obvious based mostly on an lack of ability to straight-leg elevate and actively extend the knee. On the lateral radiograph, patellar peak is measured according to the method of Caton and Deschamps (ie, the ratio between the gap from the lower edge of the patellar articular surface to the higher edge of the tibial plateau and the length of the patellar articular surface). Trochlear morphology can be assessed on the true lateral radiograph (the posterior borders of both femoral condyles are strictly superimposed). The axial patellar view could demonstrate lateral patellar subluxation and even frank dislocation. It may demonstrate medial patellar avulsion fractures, although these may be missed on plain radiographs. With the knee flexed to 30 levels, an axial patellar view is taken with a laterally directed pressure applied to the medial side of the patella. Lateral offsets of 20 mm or extra should be corrected with medialization of the tibial tubercle. On a true lateral radiograph, trochlear dysplasia is obvious when the ground of the trochlea crosses the anterior borders of each femoral condyles (ie, the "crossing" sign). Measurement of the trochlear prominence on the lateral view based on Dejour et al. X and Y are strains tangential to the anterior and posterior cortices of the distal femoral metaphysis, respectively.
Best buy for cystoneApproach Elbow arthroscopy has made open resection of olecranon osteophytes primarily some extent of historic curiosity. The determining factor in the decision-making process is whether a contraindication to elbow arthroscopy is present. Examination Under Anesthesia Examination under anesthesia is important to develop a feel for the character and explanation for any extension block. Anterior capsular contracture usually has a slightly softer feel at terminal extension. The surgeon confirms that the ulnar nerve is certainly positioned throughout the groove and remains so with range of motion of the elbow. The lateral "delicate spot" portal location is recognized and 20 cc of saline is injected into the elbow joint. Diagnostic arthroscopy should embody an entire inspection and analysis of the elbow. The olecranon fossa of the humerus should be evaluated for hypertrophy, chondromalacia, and spur formation. A systematic examination of the entire elbow joint is important to identify and take away any unfastened our bodies present. The arthroscopic valgus instability test is performed to assess for important opening in the ulnohumeral articulation. A direct posterior or triceps-splitting portal is established for entry of the motorized resector or burr. When resection is complete, the surgeon should assess elbow extension and valgus instability with a repeat arthroscopic valgus instability take a look at. A cautious take a look at before and after spur excision helps stop unrecognized ulnar collateral ligament instability. Motorized shavers, even when used correctly, present a major risk of damage to the ulnar nerve. After the first week, sufferers are inspired to use the elbow normally for activities of day by day residing, they usually can start strengthening and range-of-motion workout routines. We embody flexor�pronator mass strengthening to enhance dynamic valgus instability. When sufferers attain a pain-free plateau, they can be superior via an interval-throwing program. Use of a motorized shaver within the medial gutter to d�bride olecranon osteophytes in close proximity to the ulnar nerve does warrant excessive warning. One reoperation was required in a affected person with severe chondromalacia of the olecranon articular surface. Bartz et al1 reported on a collection of 24 baseball pitchers treated with a mini-open technique. Nineteen of the 24 obtained complete aid and had been in a place to equal or exceed their preoperative throwing velocity. A lack of compensatory biomechanical operate (ie, the scapula for the shoulder) makes elbow stiffness poorly tolerated. Flexion loss is less tolerated than extension loss, but loss of extension is more frequent. The anterior capsule is taut in extension and lax in flexion, with the energy of the capsule supplied from the cruciate orientation of the fibers of the anterior capsule. The anterior capsule distally extends to the coronoid medially and annular ligament laterally. There is loss of joint quantity (20 mL to 6 mL) and thickened capsular width (from a traditional width of approximately 2 mm). Patients most in danger are those with mixed head and elbow trauma, burn patients, and folks who have undergone surgical approaches to the elbow. Hildebrand et al6 have discovered increased numbers of myofibroblasts in the anterior capsule, a cell line that may lead to collagen cell contraction. Increased matrix metalloproteinases and collagen disorganization have also been described in the contracted capsular tissue.
Discount cystone 60caps otcBecause sciatic nerve accidents are frequent, motor and sensory examination of the affected extremity is critical, with specific consideration paid to strength grades (1�5) and sensation in the peroneal and tibial nerve distribution. Additional vascular assist is equipped by the lateral femoral circumflex artery and the foveal artery within the ligamentum teres. The acetabular labrum increases the coverage of the femoral head, however could also be damaged throughout hip dislocation. Associated injuries corresponding to femoral neck fractures, acetabular fractures, or pelvis fractures might require extra devoted hip, Judet view, or pelvic inlet and outlet radiographs. Posterior dislocations, the most common type, occur when the hip is in a flexed, adducted, and internally rotated position. Decreased femoral anteroversion leads to reduced femoral head protection by the acetabulum and increases the danger of hip dislocation. Injury to the articular cartilage of the femoral head is frequent with femoral head fractures, and posterior wall fractures also can happen with this injury. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head may develop in 20% of patients with femoral head fractures despite anatomic reduction. It travels around the posterior facet of the proximal femur, traveling deep to the quadratus femoris and penetrating the joint capsule just inferior to the piriformis tendon. Nonoperative administration is used solely in Pipkin type I fractures with small articular fragments with an related concentric discount of the hip. Femoral head fracture plus acetabular fracture B No quality clinical research can be found to outline the quantity of displacement of the fragment that can be tolerated. The accepted guideline is that the fragment must be congruent with the intact femoral head. Small impaction injuries associated with anterior dislocation additionally could additionally be handled nonoperatively in plenty of circumstances. Patients managed nonoperatively ought to remain toe-touch weight bearing for eight to 12 weeks. For posterior dislocations, hip flexion beyond 70 degrees ought to be avoided for six weeks to protect the posterior capsule. Most patients with femoral head fractures require surgical procedure to provide an anatomic discount of the femoral head, take away osteochondral unfastened our bodies, or acquire a concentric reduction of the hip joint. Hip arthroplasty is another good remedy possibility in elderly sufferers, especially with giant head fragments. Although their significance is unknown, labral tears often can be evaluated and handled surgically. Algorithm for surgical administration: Nondisplaced fracture or small impaction harm Nonoperative therapy Displaced fragment Small: surgical excision Large: surgical fixation Elderly affected person Small fragment with proof of related femoral head impaction: surgical excision Large fragment or vital femoral head impaction: hip arthroplasty For a posterior Kocher-Langenbeck approach, the patient is placed susceptible on a radiolucent fracture desk with a distal femoral traction pin and the knee flexed to 90 levels to relieve sciatic nerve tension. For a Ganz surgical dislocation, the affected person is placed on a radiolucent table with a beanbag within the lateral decubitus position and the affected leg draped free. Approach the most tough choice is willpower of the best operative method. Epstein2 originally argued that each one femoral head fractures should be approached posteriorly, as a outcome of the posterior blood supply to the femoral head had already been damaged throughout hip dislocation. However, the anterior capsule and anterior femoral neck present very little vascular supply to the femoral head. In addition, visualization of the anteriorly positioned femoral head fracture often is insufficient. This strategy is greatest used when massive femoral head fragments stay dislocated posteriorly after reduction of the hip or with an related posterior column or posterior wall fracture. However, visualization of the anterior head fragment is tough by way of a posterior approach, and such a fracture could additionally be higher handled with a surgical dislocation (see Techniques section). No increased incidence of osteonecrosis was seen, although a barely greater danger of heterotopic ossification was noticed. A Smith-Peterson approach is at present the most generally used methodology for fixation, and is the popular approach for excision of the fragment.
Discount cystone 60caps with amexThe conoid may be seen as a broad ligament that followers out, attaching to the clavicle in a posteromedial place. The width seen on radiographs is influenced by the person variability of obliquity of the joint in relation to the x-ray beam. For optimum visualization of the acromioclavicular joint, the x-ray supply is directed 10 degrees cephalad with lowered penetration energy in comparability with a normal radiograph. It is helpful when a coracoid fracture is suspected with a standard coracoclavicular interspace. Treatment begins with a sling, ice, and a quick interval of immobilization just for ache control. The rehabilitation program consists of 4 phases:four Pain management, quick protecting range of movement and isometric exercises Strengthening workout routines using isotonic contractions Unrestricted functional participation with the aim of increasing strength, energy, endurance, and neuromuscular management Return to activity with sports-specific useful drills Surgical intervention should be thought-about after rehabilitation if pain persists for larger than three months. Objective studies showed that sufferers had no limitation of shoulder motion in the injured extremity and no distinction compared with the unaffected extremity in rotational shoulder muscle power. If signs persist for larger than 3 months, including increased pain, impingement as a end result of scapular dyskinesia, decreased power, lack of ability to get the arm right into a cocking position in throwing, and painful instability, especially posterior instability with the clavicle abutting the anterior portion of the backbone of the scapula, then operative intervention may be indicated. Some sufferers handled nonoperatively will have persistent ache and an inability to return to their sport or job and would require surgical stabilization. This method has been studied in our biomechanics laboratory and is in scientific trials. A description of an arthroscopic process using a highstrength suture and endobutton device is supplied. Preoperative Planning A profitable end result depends on cheap affected person expectations and compliance with the postoperative regimen, together with postoperative sling immobilization for six weeks. We choose a regular table that provides posterior support and stabilization of the scapula. A small bump is placed on the medial scapular edge to stabilize it and elevate the coracoid anteriorly. Full-thickness flaps of the deltotrapezial fascia during the approach are important for closure. Tagging sutures may be placed through the approach to enable for fast and efficient delicate tissue protection over the repair. The head must be mobile to enable repositioning if needed throughout clavicle reaming. The head is cell as a end result of repositioning is sometimes needed throughout medial clavicle drilling. Wide draping is done to expose the sternoclavicular joint and posterior clavicle for full visualization of the shoulder girdle. Superficial skin bleeders are controlled down to the fascia of the deltoid with a needle-tip Bovie. Traction on the tagging sutures or a Gelpi retractor under the flaps is used for visualization. The tagging sutures are used for simple and exact closure of the fascia on the finish of the procedure. The distal end of the clavicle may have to be freed from the trapezius muscle, beneath the acromion, or coracoid. The deltotrapezial fascia is break up alongside the midline of the clavicle and elevated as two fullthickness flaps. A whipstitch or grasping suture is positioned in the two free ends of the tendon for graft passage via bone tunnels. The graft is ready for use if the surgeon is performing our most popular looping method. However, an alternate technique is interference screw fixation to the coracoid course of. In this selection, the graft is folded with one short limb (about three inches) and a limb containing the remaining size of the tendon. Grafts need tendon-grasping sutures at both ends for ease of passage around the coracoid and thru bone tunnels. Standard looping method A graft could be looped across the base of the coracoid process utilizing an aortic cross-clamp (Stanitsky clamp) or a suture-passing system (Arthrex, Inc. A suture passer can be utilized to safely loop the graft and a nonabsorbable suture across the coracoid base. In the choice method, a bone tunnel that approximates the diameter of the graft (usually 6 to 7 mm) is made within the coracoid.
Framboise (Red Raspberry). Cystone. - Dosing considerations for Red Raspberry.
- Stomach problems, heart problems, lung problems, diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, fluid retention, skin rash, sore throat, and other conditions.
- What is Red Raspberry?
- Making labor and delivery easier (red raspberry leaf).
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Red Raspberry work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96330
Buy cystone american expressThe anterior humeral head floor is inspected for any reverse Hill-Sachs lesions, which may indicate macroinstability. A full avulsion of the labrum off the posterior glenoid is visualized from the posterior portal. An arthroscopic rasp or chisel is used to mobilize the labrum from the glenoid rim. The rasp is then used to d�bride the capsule to create an optimal environment for therapeutic. A motorized shaver or burr can be used on the glenoid rim to obtain a bleeding floor for healing. A variety of different commercially obtainable anchors can be used similarly. The anchors are evenly spaced on the posterior glenoid margin to provide a symmetric and balanced repair. The suture hook is delivered through the capsule (if a plication is warranted) and under the torn labrum on the articular margin of the glenoid. An inferior-to-superior path is used for this maneuver to obtain a small capsular plication. This path of suture passage is aimed at restoring pressure to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament. Patients with vital instability clinically may require a more aggressive plication than those with isolated pathology to the glenoid labrum. A suture hook is used to shuttle the anchor limb by way of the capsulolabral complex. The sutures are tied using arthroscopic knot-tying strategies through the posterior portal, and the capsulolabral plication is finished. We favor to start our restore inferiorly and advance superiorly up the posterior glenoid rim. A crescent Spectrum suture passer is used to penetrate one facet of the capsule by the posterior capsular incision, and the suture is threaded into the joint. Varying the space of the suture from the portal incision allows extra tension to be applied to the posterior capsule. If extra plication is warranted (such as in multidirectional instability), extra sutures may be placed within the rotator interval or anterior capsule as described elsewhere in this textual content. The skin portals are closed with interrupted nylon suture and the patient is positioned in a sling that enables slight abduction. Patient positioning Debate exists as to which position permits higher exposure of the posterior glenoid. The surgeon ought to really feel comfy with whichever position is chosen; nevertheless, we feel that the lateral decubitus position provides better visualization. Placing the posterior portal barely lateral to the standard portal allows for simpler placement of the anchors. Placing the anterior portal superior in the rotator interval permits higher visualization. Placing the anchors perpendicular to the glenoid margin and shuttling the posterior suture is paramount in preventing suture entanglement. Portal placement Anchor placement Repair the repair ought to be tailor-made to the precise pathology of the affected person as determined by the historical past, physical examination, and imaging studies. We choose suture anchors no matter which type of repair is critical (capsule plication, capsulolabral plication, or labral repair). Knot tying the surgeon should really feel comfy with each sliding and nonsliding knots earlier than attempting arthroscopic repair methods. We allow 90 levels of forward elevation and external rotation to zero degrees by four weeks after surgical procedure. The sling is discontinued 6 weeks after surgery and activeassisted range-of-motion workout routines and gentle passive rangeof-motion workout routines are progressed. At 2 to 3 months after surgery, vary of movement is progressed to achieve full passive and active vary of motion. Stretching exercises could be instituted for any deficiency in motion at this point. After 4 months, the shoulder is commonly pain-free and eccentric rotator cuff strengthening is begun.
Discount 60caps cystone otcA 19-year-old lady complains of progressive right decrease quadrant ache over the last 5 days. The stomach is delicate, with tenderness to deep palpation of the proper lower quadrant. A 57-year-old man with hypertension and diabetes reports 4 days of right upper quadrant and epigastric ache. The patient has constitutional symptoms suggestive of malignancy and progressive obstructive signs with no prior screening colonoscopy. Gallstone ileus typically presents as a small bowel obstruction, and never with proper higher quadrant ache. For each of the next eponyms, choose the proper website of the metastatic deposit. Each choice could additionally be used once, more than once or not at all: 1 Ovaries 2 Supraclavicular lymph node three Rectovesical pouch four Periumbilical lymph node a Blumer b Virchow c Sister Mary Joseph d Krukenberg Answers a 3 Rectovesical pouch. It should be remembered that nodal or peritoneal metastases from gastrointestinal malignancies may be palpable on physical examination. Each choice may be used once, greater than as soon as or by no means: 1 Right heart failure 2 Ovarian cancer three Liver failure four Colon cancer a Ascites, gynaecomastia, caput medusae b Ascites, a agency palpable left decrease quadrant mass, bloody stools c Ascites, a pulsatile liver d Ascites, and a firm adnexal mass Answers a 3 Liver failure. Patients with liver failure as a outcome of cirrhosis may show ascites, gynaecomastia and caput medusae. Patients with advanced colon most cancers might have ascites, a palpable mass in the decrease left quadrant and bloody stools on rectal examination. The major questions that the clinician must reply when evaluating a patient with belly ache are `Does the patient have an acute abdomen or not A detailed medical and surgical history and an intensive physical examination help to slender the differential prognosis. During the interview, specific traits of the pain need to be evaluated (Table 36. Characteristics of the Abdominal Pain the embryology and innervation of the stomach organs determine the type and location of the ache: � Visceral pain is described as boring, cramping and poorly localized. It is felt in a exact location comparable to the somatic innervation of the overlying muscle group and corresponds to the organs that underlie the world anatomically. For instance, ipsilateral subscapular or shoulder ache could also be felt with diaphragmatic irritation, or ache in the groin or genitalia with the passage of a ureteral stone. The gastrointestinal contents leak into the peritoneal cavity, inflicting first chemical, then inflammatory and eventually infectious peritoneal irritation. The perforation normally develops acutely and presents with a sudden onset of pain that quickly builds up to maximal depth. Inflammation may result from infectious (purulent, faeculent) or chemical (bilious) irritation of the peritoneal cavity. Depending on the illness, the peritonitis could additionally be diffuse (from a perforated viscus) or focal (with cholecystitis or an intraabdominal abscess). Torsion is an acute twist of the organ (such as the bowel or ovary) around its axis, usually the vascular pedicle. Initially, the abdomen is gentle and the tenderness is localized to the affected organ. Torsion of a segment of the gastrointestinal tract (volvulus) typically leads to bowel obstruction. Whereas a rotation of lower than 180� around the axis might end in partial obstruction, a rotation of over 360� ends in complete visceral obstruction and interruption of the blood supply (one of the causes of ischaemia). Bowel obstruction is related to nausea, vomiting, constipation and distension as material fails to cross usually via the gastrointestinal tract. The abdominal ache is of a visceral kind and is as a result of of intestinal distension and peristalsis. With overdistension of the bowel, pain and abdominal tenderness may become severe and constant. With ongoing distension (as in complete bowel obstruction), bowel wall ischaemia could develop.
Discount cystone 60 caps free shippingA unicortical drill hole, no more than 1 to 2 cm deep, initiates entry throughout the crest. The second pin and the third if relevant are inserted one fingerbreadth posterior to the earlier pin. In an effort to retain intrapelvic tamponade, pins may be introduced via an identical approach without elevation of periosseous muscular attachments. Small Kirschner wires or spinal needles are directed along the iliac fossa to orient correct pin placement. The "rule of thirds" (cross-sectional junction of internal third and outer two thirds of the crest) aids in establishing the preferential pin entry level. Alternatively, pins could additionally be placed via percutaneous wounds subjacent to the open surgical incision. Pins should converge on the supra-acetabular region whereas remaining within the anterior pillar. Fluoroscopic steering facilitates correct pin placement throughout the inner and outer tables. This orientation diminishes undesirable gentle tissue tension across the pin on pelvic discount and significantly permits pin tract launch in the event of impending pin tract infection. After completing the pores and skin incision, dissection continues by spreading a surgical clamp, clearing away subcutaneous fats. Through these small wounds, Kirschner wires or spinal needles may be launched alongside either side of the iliac wing. This supplies a focusing on methodology to accurately place the pins within the two tables of the ilium. Guided by the spinal needles, a delicate tissue trocar assembly is launched and located medial of the midline to account for lateral overhang ("rule of thirds"). This requires that the drill be held extra cephalad (directed caudad) than expected to allow proper position inside the desired supra-acetabular bone (superior and cephalad to the acetabulum), somewhat than the skinny bone of the ilium. The fixation pin is inserted, allowing the cortical partitions of the ilium to establish path. Stab wounds (1 to 2 cm long) are established perpendicular to the iliac crest in the direction of the umbilicus. Safe introduction and correct positioning of the pin require the assist of fluoroscopic steering. The open strategy for pin placement begins with a vertically oriented 5- to 10-cm incision, relying on affected person physique habitus and prereduction pelvic deformity. A smaller transverse incision has been described in addition to completely percutaneous strategies of pin insertion. This vertical strategy begins along the lateral border of the anterior superior iliac backbone, extending distally and lateral to the anterior inferior iliac spine. Tissue planes are developed with blunt dissection and the anterior inferior spine is palpated. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is mostly recognized medial to the anterior iliac backbone. Anatomic research have demonstrated the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve to have a variable course, typically within 10 mm of inserted pins. Supra-acetabular pins must be inserted no much less than 2 cm proximal to the joint to avoid intra-articular pene- tration. An obturator indirect view with slight cephalad angulation (obturator outlet view) is first obtained. The trocar meeting is positioned under fluoroscopic management superior to the hip joint. The drill, followed by the pin, is directed inside the pelvis, avoiding intra-articular penetration of the hip joint. Pin angulation is often 20 degrees medial from the vertical axis and barely cephalad. The drill is directed toward and superior to the sciatic notch (30 to 45 degrees within the sagittal plane). The interval between the sartorius and the tensor fascia lata is established (lateral femoral cutaneous nerve protected (*).
60 caps cystone with mastercardAnterior scalene block with local anaesthetic has been proven to relieve the symptoms by stress-free the anterior scalene muscle and alleviating tension on the brachial plexus. Surgical therapy corresponding to resection of the first rib and anterior scalenectomy is reserved for patients who fail to enhance or who develop progressive neurological weak point or disabling ache. Angioplasty and stenting are reserved for persistent stenosis following surgical decompression. In addition, a work-up for hypercoagulability must be undertaken at the aspect of this to determine on long-term anticoagulation and follow-up. The diagnosis can be confirmed with duplex ultrasonography, which reveals acute thrombosis of the axillary subclavian vein. Severe ischaemia often requires surgical embolectomy with or without thrombolysis. If the subclavian artery has a brief affected section, resection and primary anastomosis may be carried out. Distal vascular occlusions due to persistent embolization could require a distal bypass. Haemangiomas normally turn into evident within the early neonatal period; roughly 80 per cent are single tumours and 20 per cent happen at multiple websites. The tumour proliferates in the superficial dermis, and the skin turns into raised, bosselated and a vivid crimson color. If the haemangioma lies within the deeper dermis or the subcutaneous tissue, the overlying skin is barely elevated with a bluish hue. The old terms cavernous haemangioma to describe a deep lesion and capillary haemangioma for a superficial one are confusing and greatest prevented. Palpation makes it simpler to differentiate a haemangioma from a venous malformation. By contrast, a venous malformation is delicate and simply evacuated by compression; it enlarges with dependency and disappears with elevation of the involved limb. A typical haemangioma grows rapidly over the primary 6�8 months of life and reaches a plateau by 1 12 months. After this, indicators of involution seem � the color fades from vivid crimson to a dullish purple hue, the skin progressively will get paler, the tumour is less tense on palpation and its dimension slowly diminishes. Infants with limb haemangiomas have a excessive threat of visceral lesions, primarily intrahepatic haemangiomas. Platelet trapping � Kasabach�Merritt syndrome � is another complication of cutaneous haemangiomas. The concerned skin becomes deep reddish-purple, tense and shiny, and petechiae and ecchymoses are sometimes seen overlying and adjoining to the haemangioma. Severe thrombocytopenia carries a threat of haemorrhage, both gastrointestinal, peritoneal, pleuropneumonic Table 32. For example, a small haemangioma in the eyelid can distort the growing cornea, producing astigmatism and amblyopia, and a subglottic haemangioma may be doubtlessly life-threatening, presenting insidiously as biphasic stridor at 6�8 weeks of life. Vascular Malformations Congenital vascular malformations are medical syndromes that current with quite so much of characteristics such as naevi (see p.
[newline]They are the results of an interaction between genetic and environmental elements, and these factors are incorporated into the Hamburg classification (Table 32. This abandons much less descriptive terms similar to Klippel�Trenaunay and Parkes�Weber syndromes. Although cutaneous vascular malformations are current at birth, not all are necessarily apparent: � A capillary malformation, or port wine stain, is visible in a neonate. These lesions develop in parallel with the child but generally abruptly increase, as seen, for example, with a lymphatic lesion difficult by a viral or bacterial an infection. This additionally happens when a venous lesion thromboses, or when venous and arteriovenous lesions are affected by hormonal adjustments. In basic, the lesions are macular and sharply demarcated, ranging from pale pink to deep red in colour. The overlying skin is normal in texture, and varicosities, ectasias or localized spongy masses could additionally be evident.
Order 60 caps cystone with visaThe treatment of distal femur fractures could be sophisticated by the various muscle attachments, which may impede or hamper correct fracture reduction. The quadriceps and hamstrings result in fracture shortening; thus, wonderful muscle paralysis have to be obtained for proper reduction. The medial and lateral gastrocnemius results in posterior angulation and displacement of the distal segment. The neurovascular structures in regards to the knee are in danger when an harm of the distal femur happens. View of the distal femur displaying the wider posterior aspect and trapezoidal shape. Lateral view of the distal femur; the shaft is in line with the anterior half of the distal femoral condyles. The axial loading is accompanied by both varus or valgus with or with out rotation. The fracture pattern can vary from the most simple extra-articular type to probably the most complex intra-articular damage. Owing to the gastrocnemius complicated, an apex posterior deformity of the condyles happens because the fragments are flexed due to the muscle attachment. The affected person presents with a swollen and tender knee after either a fall or some high-energy trauma (motor vehicle or bike accident). Any makes an attempt at vary of movement result in extreme ache, and important crepitus is often noted with palpation. The bodily examination is directed primarily at ascertaining the neurovascular standing of the lower limb and determining whether any related accidents exist, especially the hip (see Exam Table for Pelvis and Lower Extremity Trauma, pages 1 and 2). If there are any small wounds or tenting of the skin anteriorly, the fracture ought to be thought-about as being open. High-energy injuries usually are from motor vehicle accidents and occur within the young patient. These patients usually have associated accidents corresponding to a hip fracture or dislocation or vascular or nerve damage. These high-energy accidents usually result in comminuted fractures, mostly of the metaphyseal region. Dedicated knee films ought to always be obtained within the assessment of distal femur fractures. In instances of extreme comminution, radiographs of the contralateral knee can assist in preoperative planning as nicely. Patient with a distal femur fracture with intercondylar extension displaying the refined rotational deformities of the individual condyles. The muscle forces are shown on the distal femur, as is the femoral artery and vein entering the canal of Hunter (arrow). The adductor magnus inserts on the adductor tubercle, leading to a varus deformity of the distal segment. A lateral image of the identical patient with the popliteal artery and tibial nerve drawn in to show the relative proximity to the fracture ends. Patient with a spiral distalthird femur fracture that appears to be extra-articular. Patient with a closed femur fracture that was initially thought to be extra-articular. Spinal wire damage (paraplegia or quadriplegia) Some particular conditions may warrant nonoperative care on case-by-case foundation. Nondisplaced or minimally displaced fracture Select gunshot wounds with incomplete fractures Extra-articular and stable Unreconstructable Lack of experience by the obtainable surgeon or lack of apparatus or applicable facility to adequately treat the harm. Transfer is indicated in these situations; otherwise, nonoperative therapy could be the only possibility. Skeletal traction Cast bracing Knee immobilizer Long-leg forged There are acceptable limits for nonoperative management: 7 levels of varus or valgus 10 degrees of anterior or posterior angulation. Once surgical procedure is deemed applicable for the affected person and the actual injury, the surgical technique choices out there are determined by the actual fracture sample. Treatment also should be determined based mostly on elements aside from the classification alone. Simple intra-articular splits may be treated with closed reduction and percutaneous fixation.
|