|
Bisoprolol Fumarate dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Bisoprolol Fumarate packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Best bisoprolol 5mgCausative agent of Calabar swelling is: (a) Dracunculus medinensis (b) Wuchereria bancrofti (c) Brugia malayi (d) Loa loa 2. Microfilaria of Brugia malayidiffers from that of Wuchereria bancroftiby all except: (a) Coarse, overlapping and darkly stainednuclei (b) Tail-tipfreefromnuclei (c) Possessessecondarykinks (d) Cephalicspacelonger 5. Following diagnostic techniques are used for diagnosis of parasitic infections: z Morphological identification methods both macroscopically or microscopically z Culture methods z Immunodiagnostic methods z Molecular strategies z Intradermal skin tests z Xenodiagnostic strategies z Animal inoculation methods z Imaging methods. Microscopically they can be visualized immediately by moist mount (saline/iodine) for stool specimen or either by different staining methods. Various morphological forms of completely different parasites could be seen in numerous specimens (Table 15. When to study: Liquid stool specimens should be examined within 15�30 minutes, 294 Section 4 Miscellaneous Table 15. Fasciola hepatica Fasciolopsis buski Clonorchis sinensis Opisthorchis felineus Heterophyes heterophyes Metagonimus yokogawai D. Trichostrongylus Adult worm Adult worm segments Egg Peripheral blood smear Ring form, schizont and gametocyte Amastigote Trypomastigote Microfilaria � Plasmodium spp. Bone marrow, liver, lymph node Tachyzoite and spleen aspirate Amastigote Liver aspirate Lymph node aspirate Lymph node biopsy Trophozoite Trypomastigote Adult worm � Toxoplasma gondii � Leishmania donovani � Entamoeba histolytica � Trypanosoma spp. On prolonged storage, trophozoites could disintegrate, turn into non motile and will seem as artifacts Several preservatives. It can be h used for eggs of Schistosoma mansoni and Taenia species Duodenal contents: It is very helpful for the detection of small gut parasites like, Giardia intestinalis and larva of Strongyloides stercoralis. Duodenal fluid may be collected by intubation or by entero take a look at (discussed in Chapter 4). Cover slip is placed on the mount and examined underneath low energy goal (10X); followed by high energy goal (40X). Iodine mount Advantages Nuclear particulars of cysts, helminthic eggs and larvae are higher visualized; helps in species identification. Permanent stained smear Permanent stained smears are required for correct analysis of intestinal parasites. Commonly used methods are: z Iron-hematoxylin stain z Trichrome stain z Modified acid-fast stain All these permanent stained smears assist in the correct analysis of cysts and trophozoites by staining their inner constructions. Then the slide is immersed in 2% aqueous ferric ammonium sulphate resolution for 5�15 minutes adopted by washing in faucet water for five minutes. Finally the smear is immersed in aqueous resolution of picric acid for 10�15 minutes and dehydrated by immersing in 50%, 70%, 80% and 95% alcohol for 5 minutes each. Stained smear is placed in xylene (2�5 minutes); then mounted in Canada balsam and coated with coverslip. Trichrome stain: Fecal smear is prepared, fastened and treated with alcohol containing iodine as in case of iron-hematoxylin staining. It is rinsed in absolute alcohol a number of occasions and dehydrated in absolute alcohol for 2�5 minutes. Stained smear is positioned in xylene (2�5 minutes); mounted in Canada balsam and lined with coverslip. Modified acid-fast stain: Modified acid-fast stain is used for detection and identification of Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora and Isospora belli. The acid-fast oocyst stains purple with carbol fuchsin and the non-acid-fast background stains blue. It is then decolorized with 1% sulfuric acid for 2 minutes, washed with faucet water and counter stained with alkaline methylene blue for 1 minute. Concentration Techniques If the parasite output is low in feces (egg, cysts, trophozoites and larvae) and direct examination may not be capable of detect the parasites, then the stool specimens need to be concentrated. These methods are additionally useful in epidemiological analysis and for assessing the response to therapy. Eggs, cysts and larvae are recovered after concentration procedures; nonetheless, the trophozoites get destroyed. Sedimentation Techniques Principle: It includes concentration of stool specimen by centrifugation. Formol-ether sedimentation method Procedure (nine steps) Step 1: About half teaspoonful (~ 4g) of feces is transferred to a tube containing 10 mL of 5�10% formalin, blended completely and allowed to stand for 30 minutes Step 2: Then the combination is filtered right into a 15 mL conical centrifuge tube coated with two layers of gauze. About 8 mL of the filtrate is collected (3�4 mL for formalin persevered stool) Step three: 0.
Order bisoprolol 10mg onlineSevere hypoxia in labor when related to metabolic acidosis can cause organ damage or fetal dying. Severe hypoxia when related to metabolic acidosis can cause organ harm or fetal demise. In between contractions the intraluminal strain throughout the spiral artery (85 mm of Hg) is higher than the intramyometrial stress (10 mm of Hg) to preserve the utero placental blood move. During peak uterine contractions myometrial pressure (120 mm of Hg) exceeds the arterial stress (90 mm of Hg) causing short-term halting of O2 supply to the fetus through the placenta. Depending upon the intensity and length of contraction fetal hypoxia might develop. Even in a normal labor, the child is subjected to stress due to: (1) Uterine contractions quickly curtailing the utero-placental circulation. But in a compromised fetus and/ or in a pathological state of labor, the fetal misery might seem abruptly. The term "Fetal misery" has been deserted in favor of more applicable time period "Non-reassuring fetal status". The auscultation should be made for 60 sec significantly earlier than and instantly following an uterine contraction. Hypoxia vagal response peristaltic exercise and leisure of the anal sphincter passage of meconium. The vicious circle is: Placental insufficiency oligohydramnios cord compression hypoxia thick meconium gasping breath meconium aspiration. Meconium staining of the liquor as observed following rupture of the membranes offers a crude concept of intrauterine fetal jeopardy. Intermittent auscultation is really helpful to monitor the fetus for a girl in labor with none issues. The transducers are positioned on the maternal abdomen, one over the fundus and the other at a web site the place the fetal coronary heart sound is best audible. Frequency of uterine contractions and uterine strain are recorded simultaneously by tocodynamometer. Intrauterine stress might be concurrently measured by passing a catheter inside the uterine cavity. Can detect hypoxia early and may clarify the mechanism of hypoxia and its particular therapy. Drawbacks: (i) Interpretation is affected by intra and interobserver error (ii) Due to error of interpretation cesarean part fee may be high (iii) Instruments are expensive and trained personnel are required to interpret a trace (iv) Mother has to be confined in mattress. Decelerations are variable in all respect of measurement, shape, depth, period and timing to the uterine contractions. It is assumed to point out cord compression and may disappear with the change in place of the patient. Fetal scalp stimulation by pinching with an Allis forceps or by mild digital stroke is finished before scalp blood pH take a look at. An illuminated plastic cone is inserted through the dilated cervix in opposition to the fetal head. Oxygen saturation (SaO) for a standard fetus in labor ranges between 40 and 70 p.c. Procedure: the sensor is placed in opposition to the fetal cheek transcervically when the membranes are ruptured. Umbilical arterial wire (or neonatal) blood samples with pH < 7 and base deficit of > 2 mmol/L signifies profound metabolic acidemia. Intrapartum umbilical artery Doppler study was poor to predict umbilical artery acidosis. It have to be emphasised that hypoxia and acidosis is the last word results of the numerous causes of intrauterine fetal compromise. Because of this uncertainty concerning the analysis of fetal distress terminologies used are "Reassuring" and "Non-reassuring" patterns as a substitute of fetal misery. During hypoxia when O2 saturation falls below 40%, anaerobic glycolysis happens, resulting within the accumulation of lactic acid and pyruvic acid leading to metabolic acidosis. H-ions first stimulate after which depress the sinoauricular node resulting in tachycardia and bradycardia respectively. It additionally causes parasympathetic stimulation resulting in hyperperistalsis and relaxation of the anal sphincter with passage of meconium. Decreased fetal oxygenation in labor hypoxia metabolic acidosis asphyxia tissue damage/fetal demise.
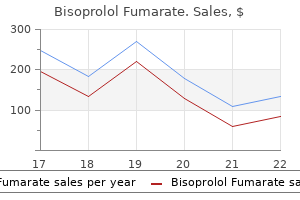
Bisoprolol 10 mgThe traditional cause is speedy descent during air flight, underwater diving or compression in stress chamber. It is the presence of latter kind of epithelium within the middle ear or mastoid that constitutes a cholesteatoma. It arises from the embryonic epidermal cell rests in the middle ear cleft or temporal bone. Congenital cholesteatoma occurs at three essential websites: center ear, petrous apex and the cerebellopontine angle, and produces symptomatology depending on its location. A middle ear congenital cholesteatoma presents as a white mass behind an intact tympanic membrane and causes conductive hearing loss. It may typically be discovered on routine examination of kids or on the time of myringotomy. It can also spontaneously rupture through the tympanic membrane and current with a discharging ear indistinguishable from a case of persistent suppurative otitis media. Persistent negative stress in the attic causes a retraction pocket which accumulates keratin particles. Thus, attic perforation is actually the proximal end of an increasing invaginated sac. There is proliferation of the basal layer of pars flaccida induced by subclinical childhood infections. Expanding cholesteatoma then breaks via pars flaccida forming an attic perforation. Normal pavement epithelium of attic undergoes metaplasia, keratinizing squamous epithelium because of subclinical infections. This is often related to posterosuperior marginal perforation or typically massive central perforation. Any concept of its genesis must clarify how squamous epithelium appeared within the middle ear cleft. The outer surface of tympanic membrane is lined by stratified squamous epithelium which after invagination varieties the matrix of cholesteatoma and lays down keratin in the pocket. The basal cells of germinal layer of pores and skin proliferate under the affect of an infection and lay down keratinizing squamous epithelium. The epithelium from the meatus or outer drum floor grows into the middle ear through a pre-existing perforation especially of the marginal type where a part of annulus tympanicus has already been destroyed. Middle ear mucosa, like respiratory mucosa elsewhere, undergoes metaplasia because of repeated infections and transforms into squamous epithelium. Basal cell hyperplasia An attic cholesteatoma could extend backwards into the aditus, antrum and mastoid; downwards into the mesotympanum; medially, it may encompass the incus and/or head of malleus. It might cause destruction of ear ossicles, erosion of bony labyrinth, canal of facial nerve, sinus plate or tegmen tympani and thus trigger a quantity of issues. Bone destruction by cholesteatoma has been attributed to numerous enzymes corresponding to collagenase, acid phosphatase and proteolytic enzymes, liberated by osteoclasts and mononuclear inflammatory cells, seen in association with cholesteatoma. Perforations, involving tympanic annulus as in acute necrotizing otitis media, are more likely to allow in-growth of squamous epithelium. Middle ear mucosa undergoes metaplasia because of repeated infections of middle ear via the pre-existing perforation. In India, the general prevalence rate is 46 and sixteen individuals per thousand in rural and concrete inhabitants, respectively. It can be the single most necessary reason for listening to impairment in rural population. Also known as the secure or benign type; it entails anteroinferior a part of middle ear cleft, i. Also called unsafe or dangerous sort; it involves posterosuperior part of the cleft. The illness is usually associated with a boneeroding course of such as cholesteatoma, granulations or osteitis.
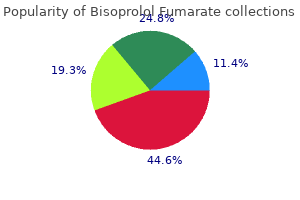
Bisoprolol 10 mg onlineMany organisms are developing resistance to antibiotics and acute infections are either not controlled or progress to subacute or persistent otitis media. Insufficient dose, much less effective drug or inadequate interval of administration of antibiotic may cause problems. Haemophilus influenzae is creating resistance to -lactam antibiotics and chloramphenicol. Other resistant strains are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infection can easily travel past the middle ear cleft if preformed pathways exist. Osteitis or granulation tissue in continual otitis media destroys the bone and helps an infection to penetrate deeper. In acute and continual center ear infection, illness process is restricted solely to the mucoperiosteal lining of the cleft but if it spreads into the bony partitions of the cleft or past it, varied issues can come up. Extradural abscess Subdural abscess Meningitis Brain abscess Lateral sinus thrombophlebitis Otitic hydrocephalus. Perforation of tympanic membrane Ossicular erosion Atelectasis and adhesive otitis media Tympanosclerosis Cholesteatoma formation Conductive hearing loss due to ossicular erosion or fixation Sensorineural hearing loss Speech impairment Learning disabilities organism although different organisms answerable for acute otitis media can also be seen. Very often, anaerobic organisms are additionally related to mastoiditis and want antibacterial therapy against them. Extension of inflammatory course of to mucoperiosteal lining of air cell system will increase the amount of pus produced because of large surface space concerned. Swollen mucosa of the antrum and attic also impede the drainage system resulting in accumulation of pus under rigidity. Hyperaemia and engorgement of mucosa causes dissolution of calcium from the bony partitions of the mastoid air cells (hyperaemic decalcification). Both these processes mix to trigger destruction and coalescence of mastoid air cells, converting them right into a single irregular cavity crammed with pus (empyema of mastoid). Pain is seen in acute otitis media however it subsides with institution of perforation or treatment with antibiotics. It is the persistence of pain, increase in its depth or recurrence of ache, once it had subsided. The final two are secondary to lack of hearing in the developmental phase of the infant or baby. The time period "mastoiditis" is used when an infection spreads from the mucosa, lining the mastoid air cells, to involve bony walls of the mastoid air cell system. It is the persistence or recurrence of fever in a case of acute otitis media, in spite of adequate antibiotic remedy that points to the event of mastoiditis. In some circumstances, discharge may cease as a outcome of obstruction to its drainage however other signs would worsen. Any persistence of discharge past three weeks, in a case of acute otitis media, factors to mastoiditis. Tenderness is elicited by pressure over the middle of mastoid course of, at its tip, posterior border or the basis of zygoma. Mucopurulent or purulent discharge, usually pulsatile (light-house effect), may be seen coming through a central perforation of pars tensa. It is due to periostitis of bony party wall between the antrum and deeper posterosuperior a half of bony canal. Usually, a small perforation is seen in pars tensa with congestion of the rest of tympanic membrane. Sometimes, tympanic membrane is undamaged however uninteresting and opaque especially in those that have acquired inadequate antibiotics. Later retroauricular sulcus turns into obliterated and pinna is pushed forwards and downwards. Bony partitions between air cells become vague, however the sinus plate is seen as a distinct define. It is differentiated from acute mastoiditis by: (a) Absence of previous acute otitis media. Mucoid component in discharge can only come from the middle ear and not from the exterior ear which is devoid of mucus-secreting glands.
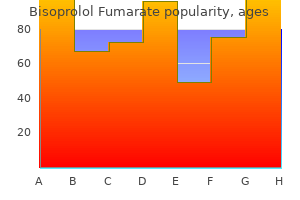
Generic bisoprolol 5mg free shippingCharacterization of patients with low baseline impedance on multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH reflux testing. Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring to choose patients with persistent gastro-oesophageal reflux for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Acid and non-acid reflux in patients with persistent signs regardless of acid suppressive remedy: a multicentre study utilizing mixed ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Yield of combined impedance-pH monitoring for refractory reflux symptoms in medical apply. Simultaneous intraesophageal impedance and pH measurement of acid and nonacid gastroesophageal reflux: effect of omeprazole. Comparison of reflux frequency during extended multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring on and off acid suppression therapy. Efficacy of esophageal impedance/ pH monitoring in sufferers with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease, on and off remedy. Systematic evaluate: signs of rebound acid hypersecretion following proton pump inhibitor remedy. Development of the 24-hour intraesophageal pH monitoring composite scoring system. Optimal thresholds, sensitivity, and specificity of long-term pH-metry for the detection of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ambulatory 24-h oesophageal impedance-pH recordings: reliability of automated evaluation for gastrooesophageal reflux assessment. Bravo catheter-free pH monitoring: normal values, concordance, optimum diagnostic thresholds, and accuracy. Wireless oesophageal pH monitoring: feasibility, security and normal values in healthy subjects. Twenty-four hour ambulatory simultaneous impedance and pH monitoring: a multicenter report of normal values from 60 healthy volunteers. Normal values and day-to-day variability of 24-h ambulatory oesophageal impedance-pH monitoring in a BelgianFrench cohort of healthy subjects. Normal values of pharyngeal and esophageal 24-hour pH impedance in people on and off remedy and interobserver reproducibility. Differential usefulness in suspected acid-related complaints of heartburn and chest pain. The symptom sensitivity index: a priceless extra parameter in 24-hour esophageal pH recording. The symptom-association likelihood: an improved methodology for symptom evaluation of 24-hour esophageal pH knowledge. Acoustic cough-reflux associations in continual cough: potential triggers and mechanisms. Double blind cross-over placebo managed research of omeprazole within the treatment of patients with reflux signs and physiological levels of acid reflux�the "sensitive oesophagus". Symptom association probability and symptom sensitivity index: preferable but nonetheless suboptimal predictors of response to high dose omeprazole. Otolaryngologists and gastroenterologists commonly disagree with the underlying cause for the complaints in patients with one of the suspected extraesophageal reflux syndromes. The accuracy of diagnostic checks (laryngoscopy, endoscopy, and pH- or pH-impedance monitoring) for patients with suspected extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease is suboptimal. An empiric trial of proton pump inhibitors in patients with out alarm features might help some patients, but the response to therapy can be quite variable. Esophageal reflux testing with pH- or pH-impedance monitoring must be reserved for sufferers with an inadequate response to empiric therapy. The esophageal syndromes had been categorised as symptomatic syndromes (typical reflux syndrome and reflux-chest ache syndrome) or syndromes with esophageal damage (reflux esophagitis, reflux stricture, Barrett esophagus, and esophageal adenocarcinoma). Four key ideas regarding the extraesophageal syndromes with established associations have been emphasised in this consensus classification3: 1. These syndromes not often occur in isolation without concomitant manifestations of the everyday esophageal syndrome. Data supporting a significant benefit of antireflux remedy for these syndromes are weak.
Purchase cheapest bisoprololSome clinicians choose to bisect the specimen themselves, perpendicular to the dermatoglyphs. Mitoses, confluent development or an expansile progress sample (nodule) should by no means be present. They are composed of fusiform melanocytes with vesicular nuclei and outstanding nucleoli. A closely related lesion referred to as an epithelioid blue nevus is associated with the Carney complicated. Deep penetrating nevi are composed of melanocytes with small hyperchromatic nuclei, a smudged chromatin pattern, and inconspicuous nucleoli. They include lesions with blended features of various kinds of blue nevi, as nicely as lesions with components of blue and ordinary nevus. Dendritic "equine-type" melanomas are quite uncommon; they are often differentiated from blue nevi by the presence of nuclear atypia and the lack of sclerotic stroma. Grading dysplastic nevi � Low-grade: atypia restricted to shoulder area � Moderate: atypia in both shoulder region and central portion, some irregularity and confluence of nests � High-grade: high-grade cytologic atypia in areas, not completely properly nested at junction, irregular nests, could also be marginal in distinction from malignant melanoma in situ a Some have questioned the importance of grading of dysplastic nevi. Most of the atypical cells are found within the shoulder area on the lateral edges of the specimen. The shoulder extends up to 2 mm beyond the clinically apparent edge of the specimen. The threat of melanoma arising in a lesion with low-grade or reasonable atypia is low. A larger risk is that a recurrent nevus within the scar might be misdiagnosed as melanoma. For a low-grade dysplastic nevus that entails a margin, I will usually include a remark: the patient could be reassured that the lesion seems benign histologically. When they recur, lesions similar to these generally seem atypical clinically and histologically. Prompt removing of any recurrent lesion will minimize the potential for future diagnostic confusion. Clinically, they current as deep blue patches on the face (Ota) or shoulder (Ito). As the atypical melanocytes are just one cell thick at the dermal�epidermal junction, the lateral borders are poorly defined clinically. Nodal nevi occur, but are typically positioned throughout the capsule and are composed of bland nuclei. The tumor is also outlined by a attribute chromosome translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12). Clinico-pathological impression of fibroplasia in melanocytic nevi: a critical revision of 209 instances. Histologic similarities between lentigo maligna and dysplastic nevus: importance of clinicopathologic distinction. Spitz nevi and atypical Spitz nevi/tumors: a histologic and immunohistochemical analysis. Lentiginous melanoma: a histologic pattern of melanoma to be distinguished from lentiginous nevus. Congenital melanocytic nevi: clinical and histopathologic features, threat of melanoma, and clinical administration. Vacuolesmaybepresent in the lowest cells of stratum spinosum, however the basal layer is gone. The presence of eosinophils strongly favors a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption. The earliest stage of evolution may show vacuolar interface dermatitis with a lymphocyte in everyvacuole. It has been likened to a vacuum cleaner sucking the b lymphocytes towards the surface. Acral and intertriginous lesions of psoriasis commonly demonstrate a background of spongiosis, however spongiosis is distinctly absent from the encompassing epidermis in most other locations. Although pallor and ballooning of the upper dermis are attribute, many biopsies show solely non-specific dermatitis with diffuse parakeratosis. Papillary dermal fibrosis is often accompanied by capillary proliferation (angiofibroplasia).
Diseases - Alveolar soft part sarcoma
- Pulmonar arterioveinous aneurysm
- Thyroid hormone plasma membrane transport defect
- Blamronesis
- Parathyroid cancer
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum, recessive form
- Gombo syndrome
- Juberg Hayward syndrome
- Livedoid dermatitis
- Mucopolysaccharidosis type II Hunter syndrome- mild form
Safe 5mg bisoprololOpioid drugs, such as heroin, are readily self-administered intravenously by mice, rats, monkeys, and people. If provided restricted entry, rats will preserve stable levels of every day drug consumption with none major indicators of bodily dependence, similar to "chipping" in people. This heroin self-administration sample sometimes entails rapid responding at the beginning of a test session, adopted by extra common interinjection intervals. Decreases within the dose of heroin out there to the animal change the sample of self-administration. The animals will lower their interinjection interval and increase the variety of injections. The animals will also attempt to compensate for opioid antagonism (for instance, when they also obtain an injection of naloxone) by increasing the amount of drug injected. Direct intracerebral administration of opioid antagonists into the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area block the locomotor-activating results and intravenous self-administration of opioids in rats. Such research point out that opioid receptors in each the ventral tegmental space and nucleus accumbens are essential for the acute reinforcing actions of opioids. Strong evidence of the position of the ventral tegmental space within the acute reinforcing results of opioids in nondependent rats has additionally been present in place conditioning studies. Intracranial self-administration studies, by which opioids are immediately self-administered into the brain, showed a major overlap with the sites identified with opioid receptor antagonists. The lateral hypothalamus, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, periaqueductal gray, and ventral tegmental area all help morphine self-administration. Animals will perform an operant task, similar to lever urgent, to have morphine delivered immediately into these mind regions. Further research of the neurocircuitry involved in opioid reward revealed a dopamine-independent function for the nucleus accumbens and a dopamine-dependent function. Researchers discovered that dopamine receptor blockade with dopamine antagonists and dopamine denervation in the nucleus accumbens eradicated cocaine and amphetamine self-administration but spared heroin and morphine self-administration. The initiation of heroin self-administration was unaltered by administration of huge doses of the dopamine antagonist haloperidol into the midbrain dopamine system, together with the nucleus accumbens, prefrontal cortex, caudate putamen, 158 5. This is particularly true for the 1 receptor binding sites, which represent only 10% of the total opioid receptor binding sites in the rat mind. Differences in distributions indicative of receptor transport are observed within the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal twine, exterior plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb, and the superficial layer of the superior colliculus. Responses to medication are proven on the left with medicine indicated; behaviors within the absence of medication are shown on the best. A focus for the involvement of the nucleus accumbens in opioid reward was the statement that selective destruction of the neurons themselves in the nucleus accumbens blocked cocaine, heroin, and morphine selfadministration. Similarly, lesions of the ventral pallidum blocked both heroin and cocaine selfadministration. Lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus additionally blocked intravenous heroin self-administration. These research counsel that neurons within the nucleus accumbens mediate the acute reinforcing properties of opioids and involve the processing of a circuit that features not solely the nucleus accumbens but in addition the ventral pallidum and pedunculopontine nucleus. Opioids activate opioid receptors within the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala through direct actions or interneurons. Opioids facilitate the release of dopamine (red) within the nucleus accumbens by way of an action both within the ventral tegmental space or the nucleus accumbens, but additionally are hypothesized to activate parts impartial of the dopamine system. Endogenous cannabinoids could interact with postsynaptic elements in the nucleus accumbens involving dopamine and/or opioid peptide techniques. The blue arrows symbolize the interactions inside the extended amygdala system hypothesized to have a key role in opioid reinforcement. The analgesic results of opioids are attributable to direct inhibition of nociceptive activity that ascends from the dorsal horn of the spinal wire to the mind circuitry related to pain and in addition by activation of pain management circuits that descend from the midbrain by way of the rostral ventromedial medulla to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Tolerance At the receptor degree, two mechanisms have been implicated within the within-system adjustments 162 5.
Cheap bisoprolol 5 mg without a prescriptionMost of the proof helps the viral aetiology as a end result of herpes simplex, herpes zoster or the Epstein� Barr virus. Other cranial nerves may be involved in Bell palsy which is thus thought-about a part of the whole image of polyneuropathy. Secondary ischaemia is the outcome of primary ischaemia which causes elevated capillary permeability leading to exudation of fluid, oedema and compression of microcirculation of the nerve. The fallopian canal is narrow because of hereditary predisposition and this makes the nerve vulnerable to early compression with the slightest oedema. Physiotherapy or massage of the facial muscles gives psychological help to the affected person. If affected person reports within 1 week, the adult dose of prednisolone is 1 mg/kg/day divided into morning and night doses for 5 days. If paralysis is incomplete or is recovering, dose is tapered through the next 5 days. If paralysis stays complete, the same dose is continued for an additional 10 days and thereafter tapered in subsequent 5 days (total of 20 days). Contraindications to use of steroids embody pregnancy, diabetes, hypertension, peptic ulcer, pulmonary tuberculosis and glaucoma. Steroids have been discovered useful to prevent incidence of synkinesis, crocodile tears and to shorten the restoration time of facial paralysis. Nerve decompression relieves strain on the nerve fibres and thus improves the microcirculation of the nerve. Some employees have advised total decompression including labyrinthine section by postaural and center fossa method. Some complain of noise intolerance (stapedial paralysis) or lack of taste (involvement of chorda tympani). This requires careful history, complete otological and head and neck examination, X-ray research, blood exams similar to whole depend, peripheral smear, sedimentation rate, blood sugar and serology. Nerve excitability exams are done every day or on alternate days and compared with the conventional facet to monitor nerve degeneration. Localizing the site of lesion (topodiagnosis) helps in establishing the aetiology and also the site of surgical decompression of nerve, if that turns into necessary. Ten to fifteen per cent recover incompletely and may be left with some stigmata of degeneration. Prognosis is nice in incomplete Bell palsy (95% full recovery) and in those the place medical restoration starts within three weeks of onset (75% full recovery). Recurrent facial palsy is seen in Bell palsy (3�10% cases), Melkersson syndrome, diabetes, sarcoidosis and tumours. Simultaneous bilateral facial paralysis could additionally be seen in Guillain-Barr� syndrome, sarcoidosis, sickle cell illness, acute leukaemia, bulbar palsy, leprosy and another systemic disorders. Roof of external and middle ear and antrum Parietal or temporal blow causes longitudinal fracture A B. Paralysis is due to intraneural haematoma, compression by a bony spicule or transection of nerve. In these cases, you will need to know whether or not paralysis was of immediate or delayed onset. Delayed onset paralysis is handled conservatively like Bell palsy whereas immediate onset paralysis might require surgical procedure in the form of decompression, re-anastomosis of reduce ends or cable nerve graft (Table 14. Paralysis could additionally be immediate or delayed and therapy is the same as in temporal bone trauma. Typically, it begins at squamous part of temporal bone, runs through roof of exterior ear canal and center ear in path of the petrous apex, and to foramen lacerum. Typically, it begins at foramen magnum, passes by way of occipital bone, jugular fossa, petrous pyramid ending in middle cranial fossa. Sometimes, nerve is paralyzed due to stress of packing on the exposed nerve and this ought to be relieved first. Operative accidents to facial nerve could be prevented if consideration is paid to the next: (a) Anatomical information of the course of facial nerve, attainable variations and anomalies and its surgical landmarks. Starts at squamous part of temporal bone to end at foramen lacerum Common, as a result of harm to tegmen and tympanic membrane Present, typically combined with blood Tegmen, ossicles and tympanic membrane Conductive Less typically; due to concussion Less (20%), delayed onset. Nerve is injured in tympanic segment, distal to geniculate ganglion Transverse Less widespread (20%) Occipital blow Runs throughout the petrous.
Order 5mg bisoprolol with amexThe maternal floor is dark red in colour and oozes blood due to torn maternalbloodvessels. The villous chorion develops most prolifically on the website of the decidua basalis. The villous chorion is in distinction to an space of no villus improvement generally identified as the graceful chorion (which is said to the decidua capsularis). Thefetalsurfacehasasmooth, shiny, light-blue or blue-pink look (because the amnion covers the fetal surface), and 5�8 large chorionic (fetal) blood vesselsshouldbeapparent. Placenta previa happens when the placenta attaches within the lower part of the uterus, covering the interior os. Uterine (maternal) blood vessels rupture in the course of the later a part of pregnancy because the uterus begins to gradually dilate. The mom might bleed to dying, and the fetus may also be placed in jeopardy due to the compromised blood supply. Because the placenta blocks the cervical opening, delivery is normally achieved by cesarean section (C- ection). This situation is clinically related to repeated s episodes of bright-red vaginal bleeding. Placenta accreta/increta/percreta occurs when a placenta implants on the myometrium,deepintothemyometrium,orthroughthewalloftheuterus, respectively. The small arrows (outer set) point out that because the fetus grows within the uterine wall the decidua capsularis expands and fuses with the decidua parietalis, thereby obliterating the uterine cavity. The small arrows (inner set) point out that because the fetus grows, the amnion expands toward the sleek chorion, thereby obliterating the chorionic cavity. This diagram of the placenta is oriented in the identical course as (A) for comparability. Note the connection of the villous chorion (fetal component) to the decidua basalis (maternal component). Maternal blood enters the intervillous area (curved arrow) via the spiral arteries and bathes the villi in maternal blood. The villi include fetal capillaries, and thus maternal and fetal blood exchange occurs. In early being pregnant, the placental membrane consists of the syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast(Langerhans cells),connective tissue,andendothelium of the fetal capillaries. Hofbauer cells are discovered in the connective tissue and are most likely macrophages. IfthemotherisRh-negativeandthefetusis h-positive, R the mom will produce Rh antibodies. Polyhydramnios could also be related to the lack of the fetus to swallow because of anencephaly, tracheoesophageal fistula, or esophageal atresia. Premature rupture of the amniochorionic membrane is the most typical reason for premature labor and oligohydramnios. During this process, angioblasts throughout the middle of angiogenic cell clusters give rise to primitivebloodcells. Fetal circulation includes three shunts: theductus venosus,ductusarteriosus,andforamenovale. She says that she did nothing to cause the bleeding and "was involved for the safety of her baby. The affected person is in advancing maternal age and reveals bright-red bleeding in the course of the third trimester with the implantation positioned at or close to the internal os. Placental abruption would have proven a separation of the placenta and showed dark-red bleeding accompanied by stomach ache. Placenta accreta would have shown the placenta implanted a lot deeper within the myometrium. Differentials � Preeclampsia,renaldisease,molarpregnancy Relevant Physical Exam Findings � Hypertension � Handandfacialedema Relevant Lab Findings � Proteinuria � Ultrasoundwasunremarkable Diagnosis � Preeclampsia:Hersymptomsofhypertension,proteinuria,andedemaarealltelltalesigns of preeclampsia.
Generic 5mg bisoprolol free shippingEach vessel has several layers of easy muscle that merge with the intervascular clean muscle fascicles. Secondary bone formation occurs by way of metaplasia within a pre-existing lesion such as a pilomatricoma, chondroid syringoma, intradermal nevus (nevus of Nanta), acne scar, scleroderma, or dermatomyositis. The osteoblasts that type bone in cutaneous ossification originate in pre-existing fibrous connective tissue and lead to intramembranous quite than enchondral bone formation. An essential exception could be chondroid syringoma by which endochondral bone formation may happen. Parachordomas are similar histologically however develop on the extremities adjoining to tendons, synovium, or bone. Intradermal and subcutaneous leiomyosarcoma: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical research of 41 instances. Two distinctive subungual pathologies: subungual exostosis and subungual osteochondroma. Smooth muscle tumours of the external genitalia: clinicopathological analysis of a series. Cutaneous pilar leiomyoma: clinicopathologic evaluation of fifty three lesions in forty five patients. Cutaneous mixed tumor with intensive chondroid metaplasia: a possible mimic of cutaneous chondroma. The linear raised or depressed erythematous macules reveal a diminished dermis with fatty alternative. Other findings include verrucous and papillomatous lesions, skeletal defects together with "lobster claw" hand, syndactyly, polydactyly, osteopathia striata, colobomata, deafness, and aplasia cutis. Neuraltumors 22 Chapter 357 Neuromas Neuromas are nerve sheath tumors with a roughly 1: 1 ratio of axons to Schwann cells. In addition to the multiple mucosal neuromas, the syndrome is characterised by a marfanoid habitus, medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, pheochromocytoma, and hyperparathyroidism. Also in the differential analysis of small blue cell tumors is lymphoma, which can be distinguished by positivity for hematopoietic markers. Neuroblastoma typically demonstrates elongated, angulated "carrot-shaped" blue cells and should kind rosettes. Bland cytology is often a poor predictor of biologic behavior, and enormous tumors should be thought to be potentially malignant. Neurothekeoma Neurothekeomas are benign neoplasms which are divided into myxoid, combined, and mobile varieties. S100A6 also stains histiocytic tumors, including atypical fibroxanthoma, as nicely as Spitz nevi. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor with focal rhabdomyosarcoma is named malignant Triton tumor. Ganglioneuroma has mature ganglion cells scattered in a Schwann cell background, in contrast to ganglion cell choristoma, which accommodates solely a proliferation of ganglion cells without supporting neuromatous elements. The sclerosing variant, seen most on the hand of younger adults, is characterised by prominent hyalinized stroma. It is congenital and is also referred to as ectopic meningothelial hamartoma and rudimentary or sequestered meningocele. Connection with the frontal lobe have to be excluded with neuroimaging research preoperatively. Cutaneous neural heterotopias and related tumors related for the dermatopathologist. Epithelioid blue nevus and psammomatous melanotic schwannoma: the unusual pigmented pores and skin tumors of the Carney complex. The ectatic vessels start as minute puncta in clusters, but merge to type a serpiginous array. Glomangiomas have been described as vascular malformations with a few glomus cells, whereas glomus tumors have been described as tumors of glomus cells surrounding inconspicuous vessels. Two types of endothelial cell have been famous: cells with large vesicular nuclei, an open chromatin sample, and large amount of cytoplasm, and a second inhabitants with small basal nuclei, a dense chromatin pattern, and scant cytoplasm.
|