|
Mebendazole dosages: 100 mg
Mebendazole packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Order cheap mebendazole on-lineThe latter is associated with a threat of lacerating the heart or coronary arteries and of pneumothorax. Traumatic postoperative (following thoracotomy) cardiac tamponade is kind of at all times treated surgically, whereas tamponade from different causes might extra usually be amenable to pericardiocentesis. Surgical treatment can also be often undertaken for large recurrent pericardial effusions (infectious, malignant, autoimmune, uremic, or radiation induced) to forestall tamponade. Simple drainage of pericardial fluid could also be achieved via a subxiphoid approach, whereas drainage combined with pericardial biopsy or pericardiectomy could also be performed via a left anterior thoracotomy or median sternotomy. For awake conscious sufferers who will endure left thoracotomy or median sternotomy, basic anesthesia and endotracheal intubation are necessary. Local anesthesia could also be used for sufferers present process simple drainage through a subxiphoid approach or pericardiocentesis. Removal of even a small quantity of fluid could also be enough to tremendously enhance cardiac output and permit protected induction of general anesthesia. Small doses (10 mg intravenously at a time) of ketamine additionally present glorious supplemental analgesia. We find it useful to have an epinephrine infusion out there and we sometimes provoke it before induction. Cardiac depression, vasodilation, and slowing of the heart charges should be avoided. Similarly, will increase in imply airway pressures can seriously jeopardize venous return. Awake intubation with maintenance of spontaneous air flow is theoretically desirable, but coughing, straining, hypoxemia, and respiratory acidosis are equally detrimental and must be averted. Ketamine is the agent of choice for induction and upkeep till the tamponade is relieved. Small doses of epinephrine (5�10 mcg) could also be useful as a brief inotrope and chronotrope. Generous intravenous fluid administration is helpful in sustaining cardiac output. Anesthetic Considerations Pericardiectomy is usually reserved for patients with moderate to severe illness. It is complicated by the need for in depth manipulations of the heart that intrude with cardiac filling and ejection, induce frequent arrhythmias, and threat cardiac perforation. Selection of specific anesthetic agents is less essential than avoiding extreme cardiac depression, vasodilation, and bradycardia. Adequate large-bore intravenous access and direct arterial and central venous pressure monitoring are usually employed. Although cardiac perform often improves instantly following pericardiectomy, some patients show a persistently low cardiac output and require temporary postoperative inotropic help. Constrictive Pericarditis Preoperative Considerations Constrictive pericarditis may develop as a sequela of acute or recurrent pericarditis. The parietal pericardium is usually adherent to the visceral pericardium on the center, often obliterating the pericardial area. The stiffened parietal pericardium limits diastolic filling of the heart to a set and decreased volume. In distinction to acute cardiac tamponade, filling throughout early diastole is often accentuated and manifested by a outstanding y descent on the central venous pressure waveform. Patients with constrictive pericarditis show jugular venous distention, hepatomegaly, and sometimes ascites. Regardless of which part of the vessel is involved, the procedure is sophisticated by the want to cross-clamp the aorta and by the potential for large intraoperative blood losses. Severe hypertension, myocardial ischemia, left ventricular failure, or aortic valve regurgitation could additionally be precipitated. Interruption of blood move to the spinal cord, kidneys, and intestines can produce paraplegia, kidney failure, or intestinal infarction, respectively. Lesions of the ascending aorta lie between the aortic valve and the innominate artery, whereas lesions of the aortic arch lie between the innominate and left subclavian arteries. Disease distal to the left subclavian artery but above the diaphragm involves the descending thoracic aorta; lesions under the diaphragm contain the abdominal aorta. This often consists of intravenous vasodilators (nicardipine or nitroprusside) and -adrenergic blockade (esmolol or an extended acting agent).
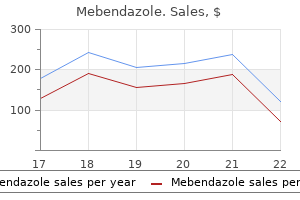
Buy mebendazole 100mg cheapInflow pressures should remain below 300 mm Hg; higher pressures may indicate a clogged arterial filter, obstruction of the arterial tubing or cannula, or aortic dissection. Marked increases in serum potassium concentrations (secondary to cardioplegia) are normally handled with a furosemide-induced diuresis. Hypothermia & Cardioplegia Moderate (26�32�C) or deep (20�25�C) hypothermia is used routinely for many procedures. The lower the temperature, the longer the time required for cooling and rewarming. Cardioplegia ought to be established immediately, as fibrillation consumes high-energy phosphates at a larger price than slower rhythms. Cardioplegia is achieved by cross-clamping the ascending aorta proximal to the aortic inflow cannula and (as beforehand described) infusing cardioplegia resolution through a small catheter proximal to the cross-clamp or directly into the coronary ostia if the aorta is opened (eg, for aortic valve replacement). Many surgeons routinely make use of retrograde cardioplegia by way of a catheter in the coronary sinus (see above). During aortocoronary bypass grafting, cardioplegia answer can also be given by way of the graft when the surgeon elects to carry out the distal anastomosis first. Ventilation Ventilation of the lungs is discontinued when sufficient pump flows are reached and the heart stops ejecting blood. The significance of this mechanism is decided by the relative ratio of remaining pulmonary blood move to pump circulate. At some facilities, once air flow is stopped, oxygen move is continued within the anesthesia circuit with a small quantity of steady positive airway pressure (5 cm H2O) within the hope of preventing postoperative pulmonary dysfunction. Most facilities both stop all gasoline flow or continue a low circulate of oxygen (1�2 L/min) within the anesthesia circuit. Increased cerebral blood move is beneficial to enhance uniformity of brain cooling prior to deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (more often utilized in children than adults). On the other hand, elevated cerebral blood move also can direct a higher fraction of atheromatous arterial emboli to the brain- a larger concern than uniformity of brain cooling during cardiac surgery in adults. At physiological pH, these costs are primarily located on the imidazole rings of histidine residues (referred to as residues). Moreover, as temperature decreases, Kw-the dissociation constant for water-also decreases (pKw increases). In contrast to pH-stat administration, -stat administration appears to protect cerebral autoregulation of blood circulate. Despite the theoretical and observed differences, in most studies comparisons between the 2 methods fail to reveal considerable variations in affected person outcomes besides in children present process circulatory arrest. Neurobehavioral deficits detectable eight weeks or extra (20�25%) after operation or strokes (2�6%) are much less common. Factors which were related to neurological sequelae embrace increased numbers of cerebral emboli, mixed intracardiac (valvular) and coronary procedures, advanced age, and preexisting cerebrovascular illness. During open-heart procedures, deairing of cardiac chambers, assumption of a head-down place, and venting before and through preliminary cardiac ejection are essential in stopping gasoline emboli. During coronary bypass procedures, minimizing the quantity of aortic manipulation, the variety of aortic clampings, and the number of graft websites on the surface of the aorta, and using sutureless proximal anastomotic units may help scale back atheromatous emboli. Although embolic phenomena seem answerable for most neurological deficits, the contribution of cerebral hypoperfusion stays unclear. The information are controversial and sparse that prophylactic drug infusions (eg, barbiturates or propofol to suppress electroencephalographic activity) instantly earlier than and through intracardiac (open ventricle) procedures will decrease the incidence and severity of neurological deficits. With gentle anesthesia hypertension may be seen and, if muscle paralysis is also allowed to wear off, the patient might transfer. Some clinicians routinely administer a benzodiazepine (eg, midazolam) or scopolamine (0. Surface cooling delays rewarming and can also facilitate adequacy of mind cooling. Administration of lidocaine, 100�200 mg, and magnesium sulfate, 1�2 g, previous to removing of aortic cross-clamping is a typical protocol and may lower the chance of fibrillation. Many clinicians advocate a head-down position whereas intracardiac air is being evacuated to decrease the probability of cerebral emboli. Lung inflation facilitates expulsion of (left-sided) intracardiac air by compressing pulmonary vessels and returning blood into the left heart. Initial reinflation of the lungs requires larger than regular airway pressure and will generally be carried out beneath direct visualization of the surgical field as a result of excessive lung growth can interfere with inside mammary artery grafts.
Diseases - Van der Woude syndrome 2
- Branchio-oculo-facial syndrome Hing type
- Hyperglycemia
- HEC syndrome
- Hibernian fever, familial
- Contractural arachnodactyly
- Acromesomelic dysplasia Hunter Thompson type
- Acrospiroma
- Eronen Somer Gustafsson syndrome
- Foix Alajouanine syndrome
Buy mebendazole 100mg overnight deliveryFacioscapulohumeral Dystrophy Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy, an autosomal dominant dysfunction with an incidence of approximately 1�3:100,000, impacts each sexes, though extra females than males are asymptomatic. Muscles in the decrease extremities are less commonly affected, and respiratory muscle tissue are often spared. Limb-Girdle Dystrophy Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy is a heterogeneous group of genetic neuromuscular illnesses. Most sufferers current in childhood to the second or third decade of life with slowly progressive muscle weak point that will contain the shoulder girdle, the hip girdle, or both. Cardiac involvement is comparatively uncommon however could current as frequent arrhythmias or congestive coronary heart failure. Respiratory complications, similar to hypoventilation and recurrent respiratory infections, might occur. Patients with very important capacities less than 30% of predicted appear to be at biggest threat and infrequently require temporary postoperative mechanical ventilation. Preoperative premedication with sedatives or opioids must be prevented due to increased aspiration risk due to respiratory muscle weak point, gastric hypomotility, or both. Intraoperative positioning may be complicated by kyphoscoliosis or by flexion contractures of the eight extremities or neck. Marked respiratory and circulatory depression may be seen with unstable anesthetics in sufferers with superior disease, and regional or native anesthesia may be preferable in these sufferers. Myotonic Dystrophy Patients with myotonic dystrophy are at elevated danger for perioperative respiratory and cardiac issues. Most perioperative issues arise in sufferers with severe weak point and in those cases by which surgeons and anesthesiologists are unaware of the diagnosis. The diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy has been made in some sufferers in the center of investigating extended apnea following general anesthesia. Patients with myotonic dystrophy have altered responses to a number of anesthetic medicines. They are sometimes very sensitive to even small doses of opioids, sedatives, and inhalation and intravenous anesthetic agents, all of which can trigger sudden and prolonged apnea. Succinylcholine is relatively contraindicated because it may precipitate intense myotonic contractions, complicating orotracheal intubation. Myotonic contraction of respiratory, chest wall, or laryngeal muscular tissues could make air flow difficult or inconceivable. Other medication that act on the motor finish plate, similar to decamethonium, neostigmine, and physostigmine, can worsen myotonia. Postoperative shivering commonly associated with volatile agents, significantly when associated with decreased body temperature, can induce myotonic contractions within the recovery room. Small doses of meperidine can typically forestall such shivering and should preempt myotonic contractions. An association between myotonic dystrophy and malignant hyperthermia has been advised but not established. Close postoperative monitoring must be accompanied by aggressive pulmonary hygiene with bodily remedy and incentive spirometry. Patients undergoing higher stomach surgical procedure or those with extreme proximal weak spot usually tend to experience pulmonary issues. Perioperative cardiac conduction abnormalities are much less likely to occur however still warrant shut cardiovascular monitoring. Other Forms of Muscular Dystrophy Patients with facioscapulohumeral and limb-girdle muscular dystrophy generally have regular responses to anesthetic agents. The stiffness worsens with exercise, in distinction to true myotonia, thus the term paramyotonia. Serum potassium focus could rise following an assault just like hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (see below). Medications that have been used to block the chilly response embody mexiletine and tocainide. Anesthetic administration of sufferers with myotonia congenita and paramyotonia is complicated by an irregular response to succinylcholine, intraoperative myotonic contractions, and the need to avoid hypothermia. Among sufferers with these kind of myotonia, none have been reported with positive in vitro checks for malignant hyperthermia. Excised muscle in these sufferers does, nonetheless, display a chronic myotonic contraction when exposed to succinylcholine.
Order cheapest mebendazole and mebendazoleMuscle strength and serum potassium concentrations are usually regular between attacks. The episodes of weak point are because of a loss of muscle fiber excitability secondary to partial depolarization of the resting potential. This partial depolarization prevents the technology of action potentials and thereby precipitates weak spot. The genetic types are because of dominantly inherited mutations within the voltage-gated sodium, calcium, or potassium ion channels. Different defects in the same channel may cause totally different medical pictures, whereas mutations in numerous channels might have comparable scientific footage. However, the scientific classifications stay useful as guides to prognosis and remedy. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis is usually associated with low serum potassium levels, and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis with elevated serum potassium ranges, throughout episodes of weak spot. In these defects, muscle membranes are inexcitable to each direct and oblique stimulation because of either decreased potassium conductance or elevated sodium conductance, respectively. Thyrotoxicosis is related to a secondary type of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. It resembles the first type however is rather more frequent in men than girls, significantly in individuals of Asian descent and in younger adults. The metabolic sequelae and fluid and electrolyte shifts seen within the primary kind are additionally seen in secondary hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Treatment includes administration of the hyperthyroidism, avoidance of high carbohydrate and low potassium meals, and administration of potassium chloride for acute assaults. Secondary hypokalemic paralysis also can develop if there are marked losses of potassium through the kidneys or the gastrointestinal tract. The related weak point is, at times, episodic and potassium levels are a lot lower than in different variants of hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Management of the first disease with potassium alternative, and remedy of acidosis or alkalosis, is essential in stopping assaults. Patients who consume large quantities of barium salts, which block potassium channels, can also develop hypokalemic periodic paralysis. This condition is handled by stopping the barium salts and administering oral potassium. Potassium ranges that exceed 7 mEq/L between episodes of weak point counsel a secondary type of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Treatment is targeted towards the primary disease and involves restriction of potassium. The analysis of myopathy can be difficult to make and the differential analysis may include any considered one of a number of hereditary, inflammatory, endocrine, metabolic, or poisonous problems. Respiratory muscle involvement should at all times be suspected in sufferers with muscle weak point. Pulmonary reserve may be assessed clinically by asking about dyspnea and activity degree. Pulmonary operate tests are indicated if important dyspnea on exertion is current. An increased danger of pulmonary aspiration is recommended by a historical past of dysphagia, regurgitation, recurrent pulmonary infections, or belly distention. Cardiac abnormalities could additionally be manifested as arrhythmias, mitral valve prolapse, or cardiomyopathy. A 12-lead electrocardiogram can also be helpful in excluding conduction abnormalities. A chest radiograph can evaluate inspiratory effort, the pulmonary parenchyma, and cardiac size; gastric distention secondary to smooth muscle or autonomic dysfunction may also be evident. Preoperative laboratory analysis should have excluded a metabolic trigger with measurement of serum sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and phosphate concentrations. The choice of anesthesia must be primarily based on each affected person and surgical requirements.
Order mebendazole 100mg amexMultiple popliteal pterygia, ankyloblepharon, cleft lip/palate, filiform bands between the jaws, syndactyly and digital hypoplasia. Basal cell nevus syndrome (Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, Gorlin syndrome). Multiple jaw keratocysts, basal cell carcinomas, distinctive facial look (macrocephaly, coarse features, facial milia), falx calcification, skeletal anomalies (bifid ribs, wedge vertebrae), cardiac and ovarian fibrosarcomas, medulloblastoma. Craniosynostosis, ear anomalies, natal enamel, cutis gyrata, furrowed palms and soles, acanthosis nigricans, anogenital anomalies (bifid scrotum, distinguished labial raphe, rugated labia majora, anteriorly placed anus), pores and skin tags, outstanding umbilical stump, accent nipples, pyloric stenosis, mental incapacity. Upper limb melanosis, with progressive enlargement, thickening, and hypertrichosis. Becker nevus and ipsilateral breast hypoplasia or different cutaneous or musculoskeletal anomalies. Omphalocele, renal anomalies, adrenocortical cytomegaly, visceromegaly, ear creases/pits, macrosomia, macroglossia, hemihypertrophy, embryonal tumors, neonatal hypoglycemia. Iris coloboma, weight problems, hypogenitalism, postaxial polydactyly, intellectual disability; could represent a ciliopathy. Anterior midline defect of infraumbilical stomach wall, involving pelvis, urinary tract, external genitalia, variable further anomalies. Distinctive facial appearance (lack of expression, hypoplastic superior orbital ridges, small palpebral fissures, ptosis, hypertelorism, epicanthus inversus, hypoplastic, or fibrotic extraocular muscles). Intrauterine development restriction, distinctive craniofacial appearance (including trigonocephaly, outstanding metopic suture, exophthalmos, facial nevus flammeus, upslanting palpebral fissures), hirsutism, elbow and wrist flexion with wrist and metacarpophalangeal joint deviation, severe mental incapacity. Lethal skeletal dysplasia with femoral bowing; can embrace extraskeletal manifestations (encephalocele, omphalocele). Short stature, microcephaly, distinctive facial look (angular face with distinguished cheekbones, deeply set eyes, massive thick ears, small triangular nose), narrow shoulders, tapered fingers, quick toes, small genitalia, hypotonia, obesity, seizures, intellectual incapacity. Brachial amelia, cleft lip, forebrain anomalies together with holoprosencephaly, variable extra anomalies. Branchial cleft sinus defects, ophthalmologic anomalies (microphthalmia, lacrimal duct obstruction), cleft or pseudocleft lip/palate, frequent conductive hearing loss. Preauricular pits, dysplastic ears, microtia, dysplastic auricles, branchial cysts or fistulas, listening to loss (no renal anomalies). Preauricular pits, dysplastic ears, microtia, dysplastic auricles, branchial cysts or fistulas, listening to loss, renal anomalies. Palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and warty thickening of the flexural areas appears later. Trigonocephaly, redundant pores and skin, distinctive facial features (upslanting palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, depressed nasal bridge, low-set, posteriorly angulated ears), variable cardiac anomalies, mental incapacity. Omphalocele, anterior diaphragmatic hernia, cleft sternum, ectopia cordis, congenital coronary heart defect (ventricular septal defect or left ventricular diverticulum). Skeletal dysplasia with cortical diaphyseal lengthy bone hyperostosis, which can extend to the metaphyses with disease progression, sclerotic changes of the cranium base. Neonatal macrosomia, hypertrichosis, osteochondrodysplasia (osteopenia, thickened calvaria, enlarged medullary canals, metaphyseal widening, slender thorax with widened ribs and flattened or ovoid vertebral our bodies, coxa valga), cardiomegaly, distinctive facial look (macrocephaly, coarse features, broad nasal bridge, epicanthal folds, broad mouth, full lips), variable intellectual incapacity. Carbohydrate poor glycoprotein syndrome, kind Ia (see Congenital dysfunction of glycosylation, sort Ia). Short stature, curly hair, coarse facial options, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, cardiovascular anomalies (septal defects, pulmonary valve stenosis, cardiomyopathy) pectus deformation, mental incapacity, seizures. Variable head measurement, Moebius facies, micrognathia, cleft palate, myopathy, variable intellectual incapacity. Nevi, pigmented lesions of the skin and mucosa, atrial myxoma, neurofibromas, endocrine and nonendocrine tumors. Acrocephaly, craniosynostosis, distinctive facial appearance, brachydactyly, polydactyly syndactyly, heart defects, umbilical hernia, development retardation, hypogenitalism, weight problems, mental incapacity. Pierre Robin sequence, bilateral second finger radial deviation/hyperphalangy, with accent bone between second metacarpal and proximal phalanx.
Purchase discount mebendazole lineLung expansion increases both alveolar and arterial oxygen tensions and reduces pulmonary vascular resistance. The enhance in oxygen rigidity is a potent stimulus for pulmonary arterial vasodilation. The resultant improve in pulmonary blood move and augmented circulate to the left coronary heart elevates left atrial stress and functionally closes the foramen ovale. Other chemical mediators that may play a task in ductal closure embody acetylcholine, bradykinin, and prostaglandins. Hypoxia or acidosis during the first few days of life can stop or reverse these physiological modifications, leading to persistence of (or return to) the fetal circulation, or persistent pulmonary hypertension of the new child. Right-to-left shunting may occur across the foramen ovale, the ductus arteriosus, or each. Controversy exists over when the elevated risk for pulmonary aspiration diminishes following pregnancy. Certainly, many factors contributing to delayed gastric emptying are alleviated shortly after delivery: mechanical distortion of the abdomen is relieved, labor pains stop, and the circulating progesterone level rapidly declines. Some studies recommend that the risk of pulmonary aspiration as judged by gastric volume and gastric fluid pH (see the part on Renal and Gastrointestinal Effects) normalizes inside 24 h. Therefore, most clinicians still contemplate the postpartum patient to be at elevated risk for pulmonary aspiration and take acceptable precautions (see Chapters 17 and 41). Although some physiological changes related to being pregnant may require as a lot as 6 weeks for resolution, the elevated danger of pulmonary aspiration probably returns to "normal" well before that time. Other than aspiration threat, what components decide the "optimum" time for postpartum sterilization The choice about when to perform postpartum tubal ligation (or laparoscopic fulguration) is advanced and varies based on affected person and obstetrician preferences as well as native practices. Factors influencing the choice include whether the patient had a vaginal or cesarean supply and whether or not an anesthetic was administered for labor (epidural anesthesia) or delivery (epidural or general anesthesia). Postpartum tubal ligation or fulguration may be (1) carried out immediately following delivery of the child and repair of the uterus throughout a cesarean section, (2) delayed 8�48 h following delivery to enable an elective fasting period, or (3) deferred till after the postpartum interval (generally 6 weeks). Many obstetricians are reluctant to carry out sterilizations instantly postpartum as a end result of the patient may change her thoughts later, significantly if something untoward happens to the baby. Furthermore, they need to be certain that the affected person is steady, notably after a complicated delivery. On the other hand, sterilization is technically much simpler to perform within the immediate postpartum interval due to the enlargement of the uterus and tubes. Postpartum sterilizations following pure vaginal supply are usually performed within 48 h of delivery, as a result of bacterial colonization of the reproductive tract thereafter is believed to enhance the danger of postoperative infection. What components determine choice of an anesthetic approach for postpartum sterilization When continuous epidural anesthesia is administered for labor and vaginal supply, the epidural catheter may be left in place as a lot as forty eight h for subsequent tubal ligation. A T4�5 sensory stage with regional anesthesia is normally necessary to ensure a painfree anesthetic expertise. Lower sensory ranges (as low as T10) could additionally be adequate however typically fail to forestall ache during surgical traction on viscera. When the patient has not had anesthesia for supply, postpartum sterilization may be performed under both regional or common anesthesia. Because of the elevated threat of pulmonary aspiration, regional anesthesia usually is most popular for bilateral tubal ligation through a minilaparotomy. Many clinicians prefer spinal over epidural anesthesia on this setting due to the danger of unintentional intravascular or intrathecal injections with the latter (see Chapter 45). Moreover, the danger of a precipitous lower in blood strain following spinal anesthesia could also be significantly diminished following supply (particularly when preceded by an intravenous fluid bolus). Dosage requirements for regional anesthesia generally return to regular inside 24�36 h after delivery. In contrast, when laparoscopic tubal fulguration is planned, common endotracheal anesthesia is usually most well-liked. Insufflation of fuel throughout laparoscopy impairs pulmonary gasoline trade and predisposes the affected person to nausea, vomiting, and presumably pulmonary aspiration. Endotracheal intubation usually ensures sufficient air flow and protects the airway. What concerns are important for postpartum patients undergoing general anesthesia Preoperative concerns include a decreased blood hemoglobin focus and the persistent elevated threat of pulmonary aspiration.
Vegetable Sponge (Luffa). Mebendazole. - How does Luffa work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Luffa?
- Treating and preventing colds, nasal swelling, sinus problems, removing dead skin, stimulating the skin, shingles infection in the face and eye area, pain, menstrual problems, promoting breast-milk production, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Luffa.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96230
Buy 100 mg mebendazole otcWhen compared with open retropubic prostatectomy, laparoscopic robot-assisted prostatectomy is related to an extended procedure time but might have a lower fee of complications. It can additionally be related to much less blood loss and fewer blood transfusions, decrease postoperative ache scores and decrease opioid requirements, less postoperative nausea and vomiting, and shorter hospital length of keep. The steep Trendelenburg position can lead to head and neck tissue edema and to elevated intraocular strain. Complications reported to be associated with such positioning embrace upper airway edema and postextubation respiratory misery, postoperative visual loss involving ischemic optic neuropathy or retinal detachment, and brachial plexus damage. The surgeon ought to be routinely advised as to the size of time during which steep Trendelenburg positioning is maintained, and a few facilities have abandoned the routine use of this positioning totally. Most clinicians use a single large-bore intravenous catheter, and an arterial catheter may be used if clinically indicated. The danger of hypothermia must be minimized by using a forced-air warming blanket and an intravenous fluid warmer. Adequate postoperative analgesia is supplied initially by intravenous opioids with ketorolac and/ or intravenous acetaminophen, and subsequently by oral analgesic preparations. Bilateral Orchiectomy Bilateral orchiectomy is usually performed for hormonal control of metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The procedure is comparatively short (20�45 min) and is performed via a single midline scrotal incision. Although bilateral orchiectomy could be performed under local anesthesia, most patients and plenty of clinicians prefer general anesthesia (usually administered by way of a laryngeal mask airway) or spinal anesthesia. Bladder Cancer Preoperative Considerations Bladder cancer occurs at a median affected person age of sixty five years with a three:1 male to female ratio. Transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder is second to prostate adenocarcinoma as the commonest malignancy of the male genitourinary tract. The association of cigarette smoking with bladder carcinoma ends in coexistent coronary artery and persistent obstructive pulmonary disease in lots of of those sufferers. Underlying renal impairment, when present, could additionally be age related or secondary to urinary tract obstruction. Some patients could obtain preoperative radiation to shrink the tumor earlier than radical cystectomy. Unfortunately, laterally located tumors might lie in proximity to the obturator nerve. In such instances, if spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia with out paralysis is run, every use of the cautery resectoscope ends in stimulation of the obturator nerve and adduction of the legs. It is often performed by way of a midline incision but is increasingly performed as a robot-assisted laparoscopic procedure. All anterior pelvic organs together with the bladder, prostate, and seminal vesicles are removed in males; the bladder, uterus, cervix, ovaries, and a part of the anterior vaginal vault could also be eliminated in females. These procedures typically require 4�6 h and frequently are related to blood transfusion. General endotracheal anesthesia with a muscle relaxant offers optimal working situations. Controlled hypotensive anesthesia may scale back intraoperative blood loss and transfusion requirements. Many surgeons additionally consider managed hypotension improves surgical visualization. Supplementation of common anesthesia with spinal or steady epidural anesthesia can facilitate the induced hypotension, lower general anesthetic requirements, and provide extremely effective postoperative analgesia. Close monitoring of blood strain, intravascular quantity, and blood loss is always acceptable. Direct intraarterial pressure monitoring is indicated in most patients, and central venous catheters are sometimes placed. Urinary output must be monitored and correlated with the progress of the operation, because the urinary path is interrupted at an early point during most of these procedures.
Buy mebendazole onlineHowever, as noted by Beecher and Todd in 1954: "[m]uscle relaxants given inappropriately may present the surgeon with optimum [operating] conditions in. This chapter reviews the principles of neuromuscular transmission and presents the mechanisms of motion, bodily buildings, routes of elimination, beneficial dosages, and unwanted effects of several muscle relaxants. Each neuromuscular junction contains roughly 5 million of these receptors, but activation of only about 500,000 receptors is required for regular muscle contraction. It can be typically referred to as extrajunctional because, unlike the mature isoform, it may be located wherever within the muscle membrane, inside or outside the neuromuscular junction when expressed in adults. Perijunctional areas of muscle membrane have the next density of these sodium channels than different elements of the membrane. A Upper gate Membrane Distinctions Between Depolarizing & Nondepolarizing Blockade Neuromuscular blocking brokers are divided into two lessons: depolarizing and nondepolarizing (Table 11�1). This division reflects distinct variations within the mechanism of motion, response to peripheral nerve stimulation, and reversal of block. The sodium channel is a transmembrane protein that may be conceptualized as having two gates. When the muscle membrane reaches threshold voltage depolarization, the higher gate opens and sodium can cross (B). When the membrane repolarizes to its resting voltage, the upper gate closes and the lower gate opens (A). Depolarizing Short-acting Succinylcholine Nondepolarizing Short-acting Gantacurium1 Intermediate-acting Atracurium Cisatracurium Vecuronium Rocuronium Long-acting Pancuronium 1 Not yet commercially available in the United States. This primary difference in mechanism of motion explains their varying results in sure disease states. This up-regulation causes an exaggerated response to depolarizing muscle relaxants (with extra receptors being depolarized), however a resistance to nondepolarizing relaxants (more receptors that must be blocked). Drugs that will cause channel block in the laboratory embody neostigmine, some antibiotics, cocaine, and quinidine. Fortunately, this is a pretty fast process, as a end result of no specific agent to reverse a depolarizing blockade is on the market. Reversal of their blockade is decided by unbinding the receptor, redistribution, metabolism, and excretion of the relaxant by the physique, or administration of particular reversal brokers (eg, cholinesterase inhibitors) that inhibit acetylcholinesterase enzyme exercise. Sugammadex, a cyclodextrin, is the primary selective relaxant-binding agent; it exerts its reversal effect by forming tight complexes in a 1:1 ratio with steroidal nondepolarizing brokers (vecuronium, rocuronium,). The newer neuromuscular blocking brokers, such as gantacurium, which are nonetheless underneath investigation, show promise as ultrashort-acting nondepolarizing brokers; they bear chemical degradation by speedy adduction with L-cysteine. Four patterns of electrical stimulation with supramaximal square-wave pulses are considered: Tetany: A sustained stimulus of 50�100 Hz, normally lasting 5 sec. Because fade is extra apparent throughout sustained tetanic stimulation or double-burst stimulation than following a train-of-four pattern or repeated twitches, the first two patterns are the preferred methods for figuring out adequacy of restoration from a nondepolarizing block. The ability of tetanic stimulation during a partial nondepolarizing block to enhance the evoked response to a subsequent twitch is termed posttetanic potentiation. Newer quantitative strategies of assessment of neuromuscular blockade, corresponding to acceleromyography, allow dedication of tangible train-of-four ratios, versus subjective interpretations. Succinylcholine, like all neuromuscular blockers, has a small volume of distribution as a end result of its very low lipid solubility, and this also underlies a rapid onset of motion. This course of is so environment friendly that only a small fraction of the injected dose ever reaches the neuromuscular junction. As drug levels fall in blood, succinylcholine molecules diffuse away from the neuromuscular junction, limiting the duration of motion. However, this period of motion may be prolonged by high doses, infusion of succinylcholine, or irregular metabolism. The latter might outcome from hypothermia, decreased pseudocholinesterase levels, or a genetically aberrant enzyme. Reduced ranges of pseudocholinesterase (measured as items per liter) accompany pregnancy, liver illness, renal failure, and sure drug therapies (Table 11�3). One in 25-30 patients of European extraction is a heterozygote with one normal and one abnormal (atypical) pseudocholinesterase gene, leading to a barely prolonged block (20�30 min).
Purchase mebendazole on lineRheological factors make a comparatively low hematocrit (eg, 27% to 30%) desirable when microvascular free flaps are performed. Excessive diuresis should be prevented during microvascular-free flap surgical procedure to be able to allow enough graft perfusion within the postoperative interval. Infiltration of the carotid sheath with local anesthetic will usually moderate these issues. Bilateral neck dissection could result in postoperative hypertension and lack of hypoxic drive as a outcome of denervation of the carotid sinuses and carotid bodies. Intraoperative Management Maxillofacial reconstructive and orthognathic surgical procedures may be prolonged and related to substantial blood loss. An oropharyngeal ("throat") pack is often positioned to reduce the amount of blood and other debris reaching the larynx and trachea. Strategies to reduce bleeding include a slight head-up position, managed hypotension, and local infiltration with epinephrine solutions. In addition, the anesthesia provider should be alert to the increased risk of venous air embolism in the setting of headup tilt. This increases the probability of great intraoperative airway issues, such as endotracheal tube kinking, disconnection, or perforation by a surgical instrument. If the operative procedure is near the airway, the use of electocautery or laser increases the chance of fire. At the top of surgery, the oropharyngeal pack must be eliminated and the pharynx suctioned. Bloody particles is typically found throughout preliminary suctioning, but should 9 diminish with repeat efforts. In addition, the working staff ought to be ready for emergent tracheotomy or cricothyrotomy. Patients with intermaxillary fixation (eg, maxillomandibular wiring) must have suction and acceptable wire slicing instruments continuously at the bedside in case of vomiting or different airway emergencies. Extubating a patient whose jaws are wired shut and whose oropharyngeal pack has not been removed can lead to life threatening airway obstruction. Obviously, the precise amount of time required to wash out the nitrous oxide is dependent upon many factors, together with alveolar ventilation and contemporary gas flows (see Chapter 8), but 15�30 min is usually recommended. Myringotomy with insertion of tympanostomy tubes is the most common pediatric surgical procedure and is mentioned in Chapter forty two. Hemostasis As with any form of microsurgery, even small quantities of blood can obscure the operating area. Techniques to decrease blood loss during ear surgical procedure include mild (15�) head elevation, infiltration or topical utility of epinephrine (1:50,000� 1:200,000), and reasonable controlled hypotension. Because coughing on the endotracheal tube during emergence (particularly during head bandaging) will improve venous stress and may trigger bleeding (as nicely as elevated middle ear pressure), deep extubation is often utilized. Facial Nerve Identification Preservation of the facial nerve is a crucial consideration during some types of ear surgery (eg, resection of a glomus tumor or acoustic neuroma). Patients present process ear surgery must be fastidiously assessed for vertigo postoperatively so as to decrease the danger of falling throughout ambulation secondary to an unsteady gait. Because nitrous oxide is more soluble than nitrogen in blood, it diffuses into air-containing cavities more quickly than nitrogen (the main component of air) could be absorbed by the bloodstream (see Chapter 8). Normally, modifications in center ear pressures caused by nitrous oxide are properly tolerated on account of passive venting by way of the eustachian tube. However, sufferers with a historical past of persistent ear problems (eg, otitis media, sinusitis) usually undergo from obstructed eustachian tubes and may, on rare occasion, experience listening to loss or tympanic membrane rupture from administration of nitrous oxide anesthesia. Once the surgeon has placed a tympanic membrane graft, the center ear turns into a closed house. If nitrous oxide is allowed to diffuse into this house, center ear strain will rise, and the graft could additionally be displaced. Conversely, discontinuing nitrous oxide after graft placement will create a unfavorable center ear pressure that would additionally cause graft dislodgment. If intravenous sedation is employed, or if the procedure is advanced, a professional anesthesia supplier ought to be current. For mild to moderate ranges of sedation, the oropharyngeal pack prevents irrigating fluids and dental fragments from getting into the airway.
Cheap mebendazole 100mgMaximal drug effect might happen at very low receptor occupancy, or (for partial agonists) at higher than one hundred pc receptor occupancy. Prolonged binding and activation of a receptor by an agonist might result in hyporeactivity ("desensitization") and tolerance. If the binding of an endogenous ligand is chronically blocked, then receptors might proliferate resulting in hyperreactivity and increased sensitivity. Keifer J, Glass P: Context-sensitive half-time and anesthesia: How does principle match actuality Prolonged publicity to anesthetic concentrations of nitrous oxide can lead to bone marrow depression (megaloblastic anemia) and even neurological deficiencies (peripheral neuropathies). Desflurane and isoflurane bear a lot less metabolism than halothane, leading to fewer of the metabolite protein adducts that result in immunologically mediated hepatic damage. Dilation of normal coronary arteries may theoretically divert blood away from mounted stenotic lesions. Three components affect anesthetic uptake: solubility in the blood, alveolar blood move, and the difference in partial strain between alveolar fuel and venous blood. Many of the factors that velocity induction additionally speed recovery: elimination of rebreathing, excessive contemporary gas flows, low anesthetic-circuit volume, low absorption by the anesthetic circuit, decreased solubility, high cerebral blood flow, and elevated ventilation. The unitary speculation proposes that each one inhalation agents share a typical mechanism of action on the molecular degree. This is supported by the remark that the anesthetic efficiency of inhalation agents correlates immediately with their lipid solubility (Meyer�Overton rule). Anesthetic interactions at specific protein ion channels, as nicely as extra nonspecific membrane results, could mix to produce the anesthetized state. Nitrous oxide, chloroform, and ether have been the primary universally accepted common anesthetics. Methoxyflurane and enflurane, two potent halogenated agents, were used for a couple of years in North American anesthesia practice. Methoxyflurane was essentially the most potent inhalation agent, however its excessive solubility and low vapor strain yielded longer inductions and emergences. Prolonged anesthesia with methoxyflurane was associated with a vasopressin-resistant, high-output, renal failure that was mostly seen when F- ranges increased to higher than 50 �mol/L. During deep anesthesia with hypocarbia electroencephalographic adjustments can progress to a spike-and-wave pattern producing tonic�clonic seizures. Five inhalation agents continue to be utilized in clinical anesthesiology: nitrous oxide, halothane, isoflurane, desflurane, and sevoflurane. The course of a basic anesthetic can be divided into three phases: (1) induction, (2) maintenance, and (3) emergence. Inhalation anesthetics, corresponding to halothane and sevoflurane, are particularly helpful within the induction of pediatric sufferers in whom it could be troublesome to start an intravenous line. Although adults are usually induced with intravenous agents, the nonpungency and fast onset of sevoflurane make inhalation induction sensible for them as nicely. Emergence relies upon primarily upon redistribution from the mind and pulmonary elimination of these brokers. Because of their unique route of administration, inhalation anesthetics have useful pharmacological properties not shared by different anesthetic agents. For occasion, administration through the pulmonary circulation permits a more fast look of the drug in arterial blood than intravenous administration. The precise composition of the inspired fuel mixture relies upon primarily on the fresh gas flow fee, the amount of the respiratory system, and any absorption by the machine or respiration circuit. The greater the fresh gas circulate fee, the smaller the respiratory system quantity, and the decrease the circuit absorption, the closer the inspired fuel focus might be to the contemporary fuel focus. Because anesthetic brokers are taken up by the pulmonary circulation throughout induction, alveolar concentrations lag behind impressed concentrations (Fa/Fi <1. The larger the uptake, the slower the speed of rise of the alveolar concentration and the lower the Fa:Fi ratio. Because the focus of a gasoline is instantly proportional to its partial strain, the alveolar partial pressure may also be sluggish to rise. The alveolar partial stress is important as a result of it determines the partial strain of anesthetic in the blood and, finally, within the mind. Similarly, the partial stress of the anesthetic within the mind is directly proportional to its brain tissue concentration, which determines scientific impact.
|