|
Oxcarbazepine dosages: 600 mg, 300 mg, 150 mg
Oxcarbazepine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Buy oxcarbazepine 600 mg without prescriptionThis could additionally be seen in a serum specimen in cases of thrombocytosis91 or leukocytosis,ninety two when the clot causes cell lysis in vitro. These days, many clinical laboratories measure electrolytes in plasma (unclotted) specimens. Even under these circumstances, extreme leukocytosis may cause pseudohyperkalemia if the specimen is chilled for an extended time 908 Pa rt 5 Renal Disease and Metabolic Disorders within the Critically Ill Specific 2-adrenoceptor agonists. Soluble barium salts are utilized in pesticides and a few depilatories, which can be ingested accidentally or deliberately. Hypokalemia has been reported through the cooling section of this therapy106 and may be a predictor of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in these sufferers. The familial variety-resulting from a skeletal muscle calcium channelopathy88-is inherited in an autosomal dominant sample, with onset of medical manifestations sometimes within the second decade of life. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis was first described in Asians however is now acknowledged to be nearly ubiquitous. Severe leukocytosis could trigger spuriously low plasma potassium concentrations if blood cells are left in contact with the plasma for a protracted time at room temperature or greater. This phenomenon outcomes from ongoing cell metabolism in vitro with glucose and potassium uptake. Pseudohypokalemia Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis Therapeutic Hypothermia Pharmacologic Agents potassium adaptation in chronic kidney illness. Hyperkalemia within the setting of unexplained hypotension ought to instantly raise suspicion for adrenal insufficiency. A widespread setting for isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency is the syndrome of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism. These medicine are reported to be implicated in 10% to 38% of hyperkalemia in hospitalized sufferers. High- and low-dose heparin therapy decreases circulating aldosterone levels by selectively inhibiting aldosterone biosynthesis. Two antibiotics, pentamidine128 and trimethoprim,129,one hundred thirty cause hyperkalemia, occasionally extreme, by blocking sodium reabsorption in the distal nephron. Chronic Hyperkalemia Renal Failure Chronic Hypokalemia Chronic hypokalemia is just about always the outcomes of altered exterior balance: inadequate potassium consumption, excessive potassium losses, or a mix of the two. Thus only huge gastric fluid losses would, alone, considerably deplete complete physique potassium shops. The gastric fluid losses, nevertheless, stimulate renal potassium secretion in a quantity of ways. First, by generating a metabolic alkalosis and growing bicarbonate delivery to the distal nephron, potassium secretion is stimulated. The metabolic alkalosis additionally leads to cellular proton loss and potassium uptake, which in renal epithelial cells, enhances potassium secretion. Thus on this situation, urinary potassium focus is often excessive while urinary chloride concentration is low owing to quantity contraction. Those drugs that act proximal to the potassium secretory website within the nephron promote a kaliuresis by rising supply of fluid distally and causing secondary aldosteronism. Thus hypokalemia incessantly accompanies the usage of the two most typical courses of diuretics: thiazides and loop diuretics. Mineralocorticoid excess may be primary137 (Conn syndrome) or secondary to diminished actual or "effective" circulating quantity. All glucocorticoid medicine except dexamethasone possess some mineralocorticoid exercise. Magnesium deficiency is associated with renal potassium losing and may lead to severe potassium depletion (see later text). Because magnesium, like calcium, acts to stabilize excitable membranes, the deleterious results of hypokalemia on the myocardium are magnified by concurrent hypomagnesemia. Hypercalcemia causes a salt and water diuresis and is due to this fact generally related to renal hypokalemia (see "Calcium").
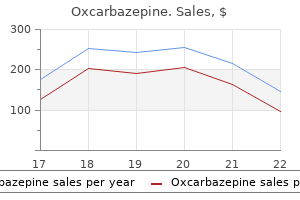
Purchase generic oxcarbazepineFamilies ought to be informed in regards to the unlikely occasion of significant recovery and in these circumstances, if the patient is a candidate for organ donation, donation after circulatory Rappaport et al. If neither of those features is present, the supplier ought to wait no much less than another 24 hours before a second reassessment. A recent research confirmed that prognostication after cardiac arrest occurs on the idea of inadequate medical knowledge, which may lead to early withdrawals on the basis of self-fulfilling prophecies of doom. The establishment of a identified cause and presence of coma, the absence of brainstem reflexes, and apnea help the prognosis of brain death. Most jurisdictions require that the willpower of mind death be made by a licensed physician, which generally ought to be an attending doctor who has experience in the assessment of comatose sufferers and the authorized requirements relevant to the jurisdiction of follow. When in doubt, a further interval of statement or a confirmatory test should be carried out to support the determination of brain dying. Key Points � the scientific examination of mind useless sufferers is the most unequivocal in neurology. Prognostication in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: An advisory statement from the European Resuscitation Council and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Evidence-based guideline update: determining mind demise in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Evidence-based guideline update: determining brain dying in adults: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Ad Hoc Committee of the Harvard Medical School to Examine the Definition of Brain Death. Statement issued by the honorary secretary of the Conference of Medical Royal Colleges and their Faculties in the United Kingdom on eleven October 1976. Practice parameter: Prediction of consequence in comatose survivors after cardiopulmonary resuscitation (an evidence-based review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Brain dying worldwide: accepted truth however no global consensus in diagnostic standards. Efficacy of a T-piece system and a steady constructive airway strain system for apnea testing in the prognosis of mind death. Apnea testing during mind dying assessment: a evaluation of medical apply and revealed literature. Diagnostique electro-sous-cortico-graphique de la mort du systeme nerveux central au cours de sure comas. Usefulness of venous oxygen saturation within the jugular bulb for the prognosis of mind death: report of 118 patients. Brief evaluation: the position of ancillary checks in the neurological determination of death. Estimated provide of organ donors after circulatory willpower of death: a population-based cohort study. Hypothermia for neuroprotection after cardiac arrest: systematic evaluation and individual patient information meta-analysis. Outcome following postanoxic status epilepticus in sufferers with targeted temperature administration after cardiac arrest. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation to help cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults. The challenges with mind dying willpower in grownup patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Apnea check for brain dying willpower in a affected person on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Performance of an apnea check for mind demise dedication in a patient receiving venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. To-and-fro movement and external escape of carotid arterial blood in mind dying instances. Brainstem auditory and short-latency somatosensory evoked responses in mind dying. The role of transcranial Doppler in confirming mind death: sensitivity, specificity, and suggestions for performance and interpretation.
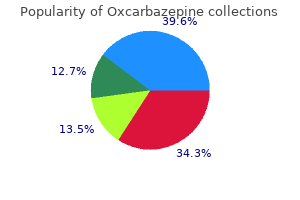
Cheap 300 mg oxcarbazepine amexThe terrorism assaults on September 11, 2001, on the World Trade Center in New York were associated with a excessive incidence of inhalation injuries. Among the 790 injured survivors, 49% incurred inhalation harm caused by poisonous compounds within the smoke and dust. Pathogenesis of Inhalation Injury Toxic Smoke Compounds Smoke is a heterogeneous compound. Each hearth produces completely different toxic options referring to the fabric combusted and the setting in which the fire occurs, specifically oxygen content material. Hence, every patient with smoke inhalation may represent a new situation with a chance of many different inhalants. At that web site, these chemically laden particles enhance airway resistance and cause cell lysis and irritation while diminishing pulmonary surfactant production and efficacy. Water-soluble gases such as ammonia and hydrogen chloride react with water contained in mucous membranes and produce robust alkalis and acids, which elicit profound inflammatory reactions, which rapidly induce systemic changes through the dense alveolar-capillary interphase. Thermal decomposition of nitrogen-containing polymers in oxygen-poor environments produces smoke containing hydrogen cyanide, inhibiting electron transport and mobile respiration. Carbonaceous particles (soot) impregnated with a multitude of toxins reach the alveolar stage suspended in air. Less water-soluble compounds (such as phosgene) penetrate the airway mucosa deeply and will cause severe delayed damage via late interplay with distal airway tissues, up to 48 hours after exposure. This is a crucial consideration when treating patients who initially current with apparently gentle scientific results after smoke inhalation. This may find yourself in upper airway obstruction, which may be fatal earlier than the sequelae of pulmonary burn turn out to be obvious. Furthermore, neutrophils are sequestered from the systemic circulation to the intrapulmonary compartment and are activated, and fibrinogen release by inflammatory mediators causes airway forged formation and widespread plugging. These casts impede numerous the smaller airways, and subsequent efforts to mechanically ventilate this inhomogeneous lung can induce ventilator-induced barotrauma as normal lung is overdistended, whereas other regions collapse and atelectasis happens. The additional tissue injury is heightened with biotrauma of air flow, and the manufacturing of chemokines leads to a potent accumulation of harm. Attempts to manipulate and alter the chain of results experimentally have bolstered these theories and advised exciting remedy targets. Nevertheless, experimental therapies have yet to deliver particular therapeutic modalities that enhance the course of smoke inhalation injury. Diagnostics and Treatment Initial Prehospital Rescue the primary priority on the harm scene is rescue of the sufferer from the supply of fire to minimize the publicity time. Standard early management of extreme trauma protocols should be observed, together with stabilization of the neck. In addition, it could be very important decide whether or not the sufferer has been exposed to an explosion and to assess the possibility of blast damage to the lung. Standard cardiopulmonary monitoring (electrocardiogram, pulse oximetry, and noninvasive blood pressure) and intravenous access ought to be established. The threat of quickly developing airway edema has to be taken under consideration even if no dyspnea is current, but it have to be balanced by the real risks confronted by endotracheal intubation itself in an unstable, probably hypoxic affected person with attainable neck injuries. Nevertheless, the airway with early edema is more likely to worsen, particularly if vital fluid resuscitation is required for burn harm, and hence repeated and thorough evaluation of the airway is necessary. Patients with proof of stridor or warmth and smoke inhalation damage mixed with in depth face or neck burns could mandate early intubation. In the case of oral burn with out inhalation harm, an airway secured early represents the most secure strategy. However, victims with smoke inhalation damage but no facial or neck burns may be carefully observed and may be intubated later, if necessary. Finally, 2-agonists are associated with improved airspace fluid clearance and stimulation of mucosal restore. Airway Management Clinical suspicion of inhalation harm of the upper airway is aroused by the presence of sure danger factors such as historical past of publicity to fire and smoke in an enclosed house or a period of unconsciousness at the accident scene, burns including the face and neck, singed facial or nasal hair, altered voice, dysphagia, oral or nasal soot deposits, or carbonaceous sputum. Early intubation is recommended when this complication threatens and the affected person was not intubated on scene. When intubation occurs within the field, the optimal approach to secure a tough airway is a contentious problem.
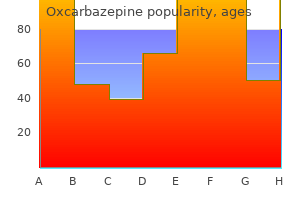
Oxcarbazepine 150mg otcValganciclovir as pre-emptive remedy for cytomegalovirus an infection in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Antibiotic synergism and response in gram-negative bacteremia in granulocytopenic cancer sufferers. Additional anti-Gram-positive antibiotic therapy for febrile neutropenic cancer sufferers. Empirical antibiotics towards Gram-positive infections for febrile neutropenia: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Beta-lactam versus beta-lactam-aminoglycoside mixture therapy in cancer patients with neutropaenia. Beta lactam monotherapy versus beta lactam-aminoglycoside combination therapy for fever with neutropenia: systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. Efficacy and safety of micafungin in febrile neutropenic sufferers treated for hematological malignancies. Staphylococcus epidermidis: an growing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. LiposomalamphotericinBfor empirical remedy in sufferers with persistent fever and neutropenia. Voriconazole in contrast with liposomal amphotericin B for empirical antifungal therapy in patients with neutropenia and protracted fever. Caspofungin versus liposomal amphotericin B for empirical antifungal remedy in 60. Micafungin, a novel antifungal agent, as empirical remedy in acute leukemia patients with febrile neutropenia. Granulocyte transfusions for kids with infection and neutropenia or granulocyte dysfunction. Safety and efficacy of therapeutic early onset granulocyte transfusions in pediatric patients with neutropenia and severe infections. Granulocyte transfusions for treating infections in sufferers with neutropenia or neutrophil dysfunction. Transmissionofinfection with human allografts: essential issues in donor screening. Delayed seroconversion and rapid onset of lymphoproliferative illness after transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus kind 1 from a multiorgan donor. Current points in critical care of the human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient. Management of individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus requiring admission to the intensive care unit. Prophylaxis against opportunistic infections in patients with human immunodeficiency virus an infection. Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical findings, analysis and treatment, and evaluate of the literature. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: improved detection in sputum with use of monoclonal antibodies. A managed trial of early adjunctive therapy with corticosteroids for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Corticosteroidsasadjunctive remedy for severe Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Decreasing incidence of cryptococcal meningitis in West Africa in the era of extremely lively antiretroviral therapy. The effect of therapeutic lumbar punctures on acute mortality from cryptococcal meningitis. Use of cerebrospinal fluid shunts in patients having acquired immunodeficiency syndrome with cryptococcal meningitis and uncontrollable intracranial hypertension. Management of elevated intracranial pressure in patients with cryptococcal meningitis. Usefulness and limitations of polymerase chain response in the etiologic analysis of neurotoxoplasmosis in immunocompromised sufferers. A randomized trial evaluating pyrimethamine plus clindamycin to pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a evaluation of the neuroimaging options and differential prognosis.
Cheap 300 mg oxcarbazepine visaElectrolyte disturbance (magnesium/potassium) occurs via tubular membrane losing. The use of amphotericin B is related to frequent renal tubular harm that ends in low magnesium and potassium ranges through renal tubular leaking of electrolytes. Thus close monitoring of serum electrolytes is necessary, and some consultants suggest to preemptive supplementation of the patient with magnesium and potassium to avoid such a complication. Patients are termed immunocompromised or immunosuppressed if their defect, whether acquired congenitally or postpartum, particularly includes immune response. The innate immune system is the first-line barrier that rapidly responds to microbial invasion. The innate immune system is an inherited system, inherited from father or mother to child, and directed towards microbial molecules which may be distinctive to microorganisms. Knowledge is rapidly expanding about specific defects within the parts of innate immunity, such as defects in Toll-like receptors, mannose binding lectin, and complement. The crucial effector part of the innate immune system consists of "skilled" phagocytes (neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages). This article emphasizes the essential methods by which immunosuppressed sufferers differ from immunologically regular individuals when it comes to infectious problems. Defects in every arm of the immune system are related to attribute infections. Knowledge of the defect produced by the underlying disease, or by medical interventions together with chemotherapy, permits the clinician to develop logical preventive and empiric therapeutic administration plans. These blended immunodeficiencies make predictions of causative organisms and suggestions for optimum management extra advanced given the various variables involved in underlying disease, immunosuppressive regimen, and patient comorbidities. The danger of lifethreatening infection related to neutropenia increases as the period of neutropenia will increase. More just lately, nearly all of such infections are due to gram-positive cocci, largely because of the frequent use of prophylactic regimens that embrace a quinolone (to forestall gram-negative bacillary infections) and trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole (for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and toxoplasmosis, however which also inhibit many gram-negative bacilli as properly as many non�group D streptococci). Life-threatening issues typically present with subtle signs and indicators that may simply be ignored. Because immunocompromised patients might lack inflammatory and immunologic mediators. It must be clear to clinicians, nevertheless, that modifications corresponding to tachycardia, tachypnea, altered mental status, belly ache, and delicate tissue tenderness might characterize life-threatening, quickly progressive infections even in the absence of an elevated temperature. Intensivists should also be cognizant of the potential unreliability in the methods that some health care amenities use to measure temperature, an important problem because a distinction of a tenth of a degree can decide whether a fever workup is initiated and whether empiric remedy is began. Temperatures are measured with a huge selection of temporal artery, brow, oral, rectal, or axillary approaches, not all of which have good interdevice concordance. Thus fever is just one of many parameters that ought to result in a radical analysis for infection. Immunosuppressed sufferers are predisposed to speedy progression of infectious complications. As indicated earlier, sufferers with life-threatening infection may current with delicate symptoms and indicators that progress rapidly to turn out to be life-threatening. These early manifestations merit aggressive attempts to define the anatomy of the lesion and the causative microbial pathogen(s). Because the spectrum of potential pathogens in such patients often consists of a huge selection of viruses, fungi, protozoa, and micro organism, clinicians have to be sure that appropriate specimens are obtained and the appropriate microbiologic and histologic exams are ordered to determine causative organism. Patients often have enhanced threat elements for issues of invasive procedures, such as thrombocytopenia, coagulation issue deficiencies, hypoxemia, or renal failure. Part of the art of drugs is figuring out when to be aggressive with diagnostic procedures and when to depend on empiric therapeutic approaches. However, the good thing about definitive diagnosis usually outweighs these dangers when the procedures are performed by experienced operators. Prior colonization and exposures are essential clues to the probably causative organisms. For any affected person in any health care setting, a history of exposure to influenza, tuberculosis, or methicillin-resistant S. Monitoring sufferers to decide the exercise of viral, fungal and parasitic infections requires particular experience. They monitor fungal pathogens with periodic serum galactomannan and -D-glucan assays. Such info will help focus empiric remedy while the definitive cause is identified, although considerable expertise is needed to perceive the sensitivity and specificity of those assays.
Cheap 600mg oxcarbazepine with amexVarious findings on urinalysis could recommend particular categories of renal illness and in sure circumstances be pathognomonic, however these findings have to be interpreted within the appropriate context of the history, bodily examination, and other laboratory information. Gross hematuria might be secondary to bleeding anyplace in the urinary system, together with the urethra, bladder, ureters, or the kidneys. Dipstick albuminuria is suggestive of a potential glomerular injury, though non-albumin proteins similar to immunoglobulin light chains seen in multiple myeloma are sometimes not constructive on urine dipstick. Overall, albuminuria has been related to worse cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Glyosuria is usually seen in the setting of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, however it may be a manifestation of a proximal renal tubular damage seen with Fanconi syndrome. Distinguishing between glomerular and non-glomerular bleeding is the key preliminary step in identifying the supply of hematuria. However, eosinophiluria can be seen in many problems, together with atheroembolic renal illness, cystitis, pyelonephritis, transplant rejection, and in sufferers with ileal conduits. As such, its diagnostic accuracy and clinical use must be revisited and interpreted with warning. Urine casts are cylindrical buildings which would possibly be fashioned within the tubular lumen and are composed primarily of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein. The presence of fatty casts, oval fat our bodies, or free fats on urine microscopy suggests nephrotic syndrome. In prerenal azotemia, the physiologic response of the proximal renal tubule remains intact and urine sodium reabsorption is usually increased. Urine potassium excretion can also be helpful in identifying sure causes of hypertension which will present with hypertensive urgency or emergency and even renal insufficiency. Patients with hypokalemia not attributable to urinary losses are anticipated to have an appropriate lower in urinary potassium excretion to less than 30 mEq/day,228 a spot urine potassium of lower than 15 mEq/L,229 and a spot urine potassium-to-creatinine ratio of less than 13 mEq/g. In sufferers with each hypokalemia and hypertension with inappropriately elevated urinary potassium excretion, secondary causes of hypertension corresponding to major aldosteronism and renovascular illness should be thought of. However, most often a final diagnosis is achieved by utilizing and reviewing many related laboratory findings that will help slender the differential and lead to a diagnosis; at times, a renal biopsy is required for definitive diagnosis. Hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia, and severe hyperkalemia raise the potential of a tumor lysis syndrome. Considerations of performing a renal biopsy within the critically ill affected person is often confounded by comorbid circumstances (such as infections, coagulopathy, respiratory failure requiring ventilator support) and sure medicines (such as antiplatelet brokers and different anticoagulants). Absolute contraindications to renal biopsy initially included uncontrolled extreme hypertension, uncooperative sufferers, a bleeding diathesis, and a solitary kidney. Most clinically vital bleeding happens throughout the first 24 hours and thus most patients are noticed for in the future after a renal biopsy. These modifiable risk elements embody appropriate dosing of medications, avoidance of doubtless nephrotoxic agents, optimizing quantity standing to keep renal perfusion, and avoiding hypotension. Proposed mechanisms of renal damage in patients with sepsis have included renal ischemia owing to hypoperfusion and hypoxemia,266 but newer evidence suggests different multiple contributing factors, together with renal macrocirculatory and microcirculatory disturbances, surge of inflammatory markers and oxidative stress, coagulation cascade activation, and bioenergetic adaptive response with controlled tubule cell-cycle arrest. Septic shock with resulting hypotension is secondary to a mixture of factors, including diffuse vasodilatation, a redistribution of intravascular fluid, and myocardial despair. Excess amounts of fluid given to patients with sepsis have been proven to delay ventilator dependency. For hypovolemic shock not caused by bleeding, crystalloid solutions, particularly saline resolution, are most popular to colloidcontaining solutions because no mortality benefit has been attributed to colloids over crystalloid solutions275�277; additionally, colloids are much more costly. The kidney is a frequent site of drug toxicity as a end result of medicines can harm cells inside all compartments of the kidney, including the renal tubules, the interstitium, or most commonly, a combined tubulointerstitial damage. The prevention of nephrotoxicity from certain medicines requires a number of approaches, including early recognition of their potential nephrotoxicity, because stopping the offending agent usually leads to renal recovery. Additional issues in preventing medicationinduced nephrotoxicity embody avoiding mixed nephrotoxic brokers that will have additive nephrotoxicity, figuring out high-risk cohorts, utilizing nephrotoxic agents for the shortest interval potential, using alternative nonnephrotoxic medicines when available, monitoring renal perform carefully, and following measurable blood ranges when applicable. Aminoglycosides have been commonly used within the treatment of a number of infections in the hospitalized affected person and charges as high as 24% in vascular surgical procedure sufferers have been described.
Purchase oxcarbazepine overnightRandomized comparison in distal safety versus typical remedy in major percutaneous coronary intervention. Role of adjunctive thrombectomy and embolic protection units in acute myocardial infarction: a complete meta-analysis of randomized trials. Is aspiration thrombectomy useful in patients present process major percutaneous coronary intervention Impact of multivessel illness on reperfusion success and medical outcomes in patients undergoing major percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction. A comparability of thrombolytic remedy with major coronary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Primary coronary angioplasty vs thrombolysis for the management of acute myocardial infarction in aged sufferers. Primary angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: a quantitative evaluate of 23 randomised trials. Primary coronary angioplasty compared with intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction: six-month follow up and evaluation of individual affected person knowledge from randomized trials. The volume of major angioplasty procedures and survival after acute myocardial infarction. Influence of therapy delay on infarct size and scientific end result in patients with acute myocardial infarction handled with major angioplasty. Relationship of symptom-onset-to-balloon time and door-to-balloon time with mortality in patients present process angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Time delay to treatment and mortality in primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: every minute of delay counts. Door-to-balloon time with primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction impacts late cardiac mortality in high-risk sufferers and sufferers presenting early after the onset of signs. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus fibrinolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction: is timing (almost) every thing Thrombolytic therapy vs main percutaneous coronary intervention for myocardial infarction in sufferers presenting to hospitals with out on-site cardiac surgical procedure: a randomized managed trial. Angiographically documented late reocclusion after successful coronary angioplasty of an infarct-related lesion is a powerful predictor of long-term mortality. Comparison of angioplasty with stenting, with or without abciximab, in acute myocardial infarction. Delayed arterial therapeutic and increased late stent thrombosis at wrongdoer sites after drug-eluting stent placement for acute myocardial infarction patients. Strut protection and late malapposition with paclitaxel-eluting stents in contrast with bare metal stents in acute myocardial infarction. Rescue angioplasty after failed thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction. A meta-analysis of randomized trials of rescue percutaneous coronary intervention after failed fibrinolysis. Early intravenous then oral metoprolol in 45,852 patients with acute myocardial infarction: randomised placebo-controlled trial. Reduction of infarct dimension with the early use of timolol in acute myocardial infarction. Beneficial results of timolol on infarct size and late ventricular tachycardia in sufferers with acute myocardial infarction. Immediate versus deferred beta blockade following thrombolytic therapy in sufferers with acute myocardial infarction. Beta blockade after myocardial, infarction: systematic review and meta regression evaluation. Timolol-induced reduction in mortality and reinfarction in sufferers surviving acute myocardial infarction. Six-year follow-up of the Norwegian Multicenter Study on Timolol after Acute Myocardial Infarction.
Order line oxcarbazepinePatients commonest begin a combination of vancomycin, extended-spectrum penicillins, metronidazole, and higher-generation cephalosporins with escalation or de-escalation based mostly on tradition results. Prolonged surgical time and enormous amounts of contemporary frozen plasma transfusion lead to an elevated danger of infectious complications in transplant patients. Perioperative antibiotic regimens ought to embrace broad-spectrum antibiotics to cover methicillin-resistant S. Intraabdominal infections are mostly because of leak from the biliary anastomosis. During the primary 6 months of immunosuppression transplant patients are at high risk of opportunistic infections. A routine of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and ganciclovir is used to stop the opportunistic infections with Pneumocystis carinii and cytomegalovirus. A tertiary trauma survey includes a full physical examination to search for missed accidents, a review of laboratory values and radiographic knowledge, and a detailed medical historical past of the patient. These sufferers ought to have blood product resuscitation with a high ratio of red blood cells to plasma to platelet transfusion ratio. The use of tranexamic acid in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock may present some mortality profit, especially if delivered quickly after bleeding. Trauma hospitals using protocols for blood product resuscitation (massive transfusion protocol) will enhance the mortality price, lower the quantity of blood merchandise used, and decrease the amount of crystalloid used. Negative-pressure dressings may enable the visualization of continued hemorrhage or enteric content leak. Endotracheal intubation and appropriate oxygenation with mechanical air flow is required in patients with Glasgow Coma Scale scores lower than eight. Temporary hyperventilation may be used to scale back carbon dioxide levels to scale back intracranial pressures till surgical decompression of intracranial mass lesions. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: worldwide guidelines for administration of extreme sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Perioperative management of antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, ninth ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Efficacy and safety of a paired sedation and ventilator weaning protocol for mechanically ventilated patients in intensive care (Awakening and Breathing Controlled Trial): a randomized control trial. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 scientific follow tips by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. The impact of a checklist on the standard of affected person handover from the working room to the intensive care unit: a randomized controlled trial. Early bodily remedy and occupational remedy in mechanically ventilated, critically unwell sufferers: a randomised control trial. Hemodynamic monitoring of the injured affected person: from central venous pressure to targeted echocardiography. Identification and characterization of the high-risk surgical inhabitants within the United Kingdom. Analysis of indications for intensive care unit admission-clinical efficacy project-American College of Chest Physicians. Intensivists enhance outcomes and compliance with process measures in critically ill patients. Surviving sepsis marketing campaign: international tips for management of extreme sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Pharmacist participation on doctor and antagonistic drug events within the intensive care unit. Implementation of dietician suggestions for enteral diet outcomes improved outcomes. Early physical remedy and occupational remedy in mechanically ventilated, critically unwell patients: a randomized control trial. Nurse practitioners and physician assistants in the intensive care unit: an evidence-based evaluate. Handoff checklists enhance the reliability of patient handoffs within the operating room and post-anesthesia care unit. A prospective, randomized, noninferiority trial of steroid dosing after major colorectal surgery. Association of perioperative blockade with mortality and cardiovascular morbidity following major noncardiac surgery.
|